GENERAL PSYCHOLOGY 11103
advertisement

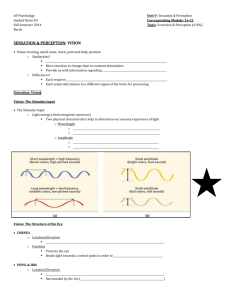
GENERAL PSYCHOLOGY 11103-01 NOTES September 8, 2010 Professor Fish advised that any student having difficulty with the writing assignment to come see him during office hours. He acknowledges that your personal bias is a component with which you will choose your selection, but you must remain objective when writing your paper. There is no way to eliminate bias, but it can be reduced. Chapter 3 Sensation and Perception Sensation - The experience of sensory stimulation Perception - The process of creating meaningful patterns from raw sensory information. The Basic Process 1. Receptor Cells - A specialized cell that responds to a particular type of energy. 2. Doctrine of specific nerve energies - one to one relationship between stimulation of a specific nerve and the resulting sensory experience. 3. Sensory Thresholds: a. Absolute Threshold - the minimum amount of energy that can be detected 50% of the time that it is presented. i. Taste - 1 g (0.0356 oz.) of table salt in 500 L (529 qt.) of water. ii. Smell - 1 drop of perfume diffused throughout a 3-room apartment. iii. Touch - The wing of a bee falling on the cheek from a height of 1 cm (0.39 in.). iv. Hearing - The tick of a watch from 6 m (20 ft.) in very quiet conditions. v. Vision - A candle flame seen from 50 km (30 mi.) on a clear, dark night. b. Difference Threshold - the smallest change in stimulation that can be detected 50% of the time. Also called Just Noticeable Difference (JND). c. Sensory Adaptation - an adjustment of the senses to the level of stimulation they are receiving. d. Weber’s Law - states the difference threshold or JND is a constant proportion of a specific stimulus. Senses vary in their sensitivity to changes in stimulation. 4. Subliminal Perception a. The notion that we may respond to stimuli that are below our level of awareness. b. Research shows that the effect only occurs in controlled lab studies. GENERAL PSYCHOLOGY 11103-01 NOTES September 8, 2010 c. Research outside the lab shows no significant effects of subliminal information. Subliminal message have been outlawed. 5. Extrasensory Perception (ESP) a. Refers to extrasensory perceptions such as: i. Clairvoyance - awareness of an unknown object or event. ii. Telepathy - knowledge of someone else’s thoughts or feelings. iii. Pre-Cognition - foreknowledge of future events. b. Research has been unable to conclusively demonstrate the existence of ESP. VISION Parts of the Eye Pg 90 1. 2. 3. 4. Cornea - The transparent protective coating over the front part of the eye. Pupil - A small opening in the iris through which light enters the eye. Iris - The colored part of the eye that regulates the size of the pupil. Lens - The transparent part of the eye behind the pupil that focuses light onto the retina. 5. Retina - The lining of the eye containing receptor cells that are sensitive to light. 6. Fovea - The area of the retina that is the center of the visual field. The receptor cells in the retina that are sensitive to light. Visual receptors are rods and cones. RODS CONES About 120 Million rods. About 8 Million cones. Respond to light and dark. (very sensitive to light). Respond to color as well as light and dark. Work best in bright light. Bipolar Cells 1. Receive input from receptor cells. 2. Ganglion Cells. a. Receive input from bipolar cells. 3. Blind Spot a. Area where the axons of ganglion cells leave the eye.

![Intro Sen_Perception[1]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/010002256_1-28ffd325610c7021bf76412ea038525b-300x300.png)