Lecture Chpt. 04 Carbon
advertisement

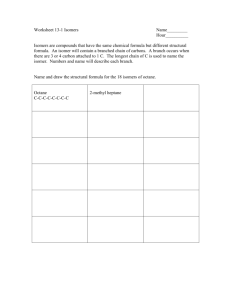
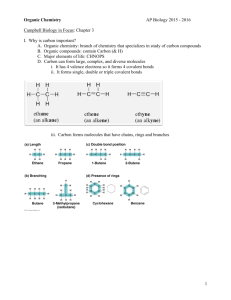
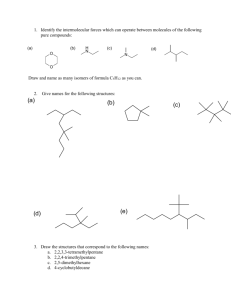
I had rather attempt something great and fail, than to attempt nothing at all and succeed! -Robert Schuller Chpt. 4 Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life Water is the Universal Medium for life… & CARBON is the universal element of life … C …how does carbon “get” into living organisms?? Can organic molecules form under conditions estimated to stimulate those on the early Earth? “lightening” atmosphere flask sea flask http://www.youtube.com /watch?v=9JaYWEsT7fU ORGANIC CHEMISTRY ORGANIC CHEMISTRY… Key to the chemical shape & affinity with other atoms, is in the configuration of the electrons Carbon: Proteins, DNA, Carbohydrates (molecules of life) all carbon based… Carbon: Proteins, DNA, Carbohydrates all carbon based, molecules of Life. Has tetra valence Carbon Backbone: BTW: this allows for large, complex molecules Importants of Carbon: Uses one or more of it valence electrons to form covalent bonds w/ other atoms (C,H,O,N,) This allows atoms to link to infinite variety of chains. aka… TONS OF SHAPES!! Importants of Carbon: …how does carbon “get” into living organisms?? Carbon Chains: … Form the “skeletons” of most organic compounds Variations in c-skeletons contribute to the diversity of organic molecules: Isomers same molecular formula, different structure (different function) C4H10 C4H10 Isomers also contribute to the diversity of organic molecules- Isomers StructuralCis-TransEnantiomers- Isomers Structural- Isomers Cis-TransCis-Trans Double bonds do not permit free rotation of atoms. Cis- both “X’s” on the same side Trans – “X’s” on the opposite side Isomers Enantiomers- Isomers Cis-Trans ISOMER QUICK QUIZ: CIS-TRANS ISOMER QUICK QUIZ: STRUCTURAL ISOMER QUICK QUIZ: ENANTIOMERS Functional Groups: they bond to the c-skeleton Can you find the “CARBON SKELETONS”? What is a characteristic that these hydrocarbons hold in common? HINT: polarity? IMPORTANCE OF FUNCTIONAL GROUPS Importance of Functional Groups KIM KARDASHIAN estradiol testosterone Functional Groups HydroxylCarbonylCarboxylAminoSulfydrylPhosphateMethyl- Functional Groups Hydroxyl- makes molecule polar (dissolves in H2O) - produces alcohol -OH Functional Groups Confers polarity Carbonyl- produces ketones (made when body breaks down fats for energy) & O C-C-C O -C aldehydes H Functional Groups Carboxyl- forms organic acids b/c H+ is commonly dissociated O -C OH Functional Groups Amino- base H + -N -H H usually acts as a buffer Functional Groups Sulfhydral- stabilizes protein structures, & commonly found in vitamins -SH Functional Groups Phosphate- energy storage / energy transfer Functional Groups Methyl- affects shape & function, also, affects / gene expression H -C -H H Summary • Be able to recognize isomers. • Know the six functional groups and what properties they give to molecules.