Name: Study Guide Cells/Organelles/Microscopes Part A. Cells and
advertisement

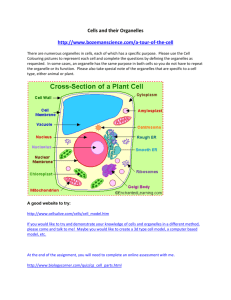
Name: ____________________ Study Guide Cells/Organelles/Microscopes Part A. Cells and Cell Theory 1. What is the cell theory? State the three sections of the cell theory below. a. All cells come from pre-existing cells b. The cell is the basic unit of structure or function of all living organisms c. All living organisms are made up of one or more cells 2. What did the following men do that increased our understanding of cells? a. Anton Von Leeuwenhoek discovered “animalcules” in the pond water b. Robert Hooke given credit for discovering cells c. Schleiden discovered that all plants are made up of cells d. Schwann discovered that all animals are made up of cells e. Virchow developed the theory that all cells come from other cells 3. What do all cells have in common? a. cell membrane b. cytoplasm c. ribosomes d. DNA 4. What are the two major classes of cells? a. Prokaryotes b. Eukaryotes 5. What is the major difference between the two classes of cells you identified in question 4? Prokaryotes do not have organelles or a defined nucleus. Eukaryotes have organelles and nucleus. 6. List some of the differences between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell? You can make a table if you want to. Prokaryotes: Older ~3.5 billion Smaller 1-10 um No organelles or nucleus Eukaryotes: Younger ~1.5 billion 2-1000 um organelles and nucleus 7. What do the following organelles do for the cell? What is the definition for organelles? Structure Nucleus Function Control center, directs all the cells activities Nucleolus Organelle in the nucleus that produces ribosomes Cell membrane Regulates what enters and leaves the cell, acts as a boundary Cell wall Extra protection Lysosomes Organelle that breaks down bacteria, old worn out cell parts, sugars etc Golgi apparatus Modifies, packages and ships out proteins Ribosomes Produces proteins, not a true organelle Flagella Structure used for movement Central vacuole Large organelle in plants that holds water, enzymes and waste products Smooth er Membranes that produces lipids, hormones, detoxifies alcohol and drugs Rough er Membranes that make proteins and move the proteins around the cell Cytoplasm Where all the chemical reactions take place in the cell. Cytoplasm is made up of cytosol and organelles Chloroplast Organelle that uses the energy of the sun, chlorophyll and enzymes to produce carbohydrates. Cytoskeleton Made up of microtubules and microfilaments this aids with structure and support Mitochondria Organelle that provides the cell with energy. Powerhouse 8. What are some of the major differences between an animal cell and a plant cell? Plant cell has a cell wall, central vacuole and chloroplasts. Animal cells have lysosomes, centrioles and some have flagella 9. Where do you find ribosomes? Ribosomes are round free floating in the cytoplasm and attached to the membranes of the rough ER 10. Why are ribosomes NOT considered to be true organelles? Ribosomes are not true organelles because they are NOT membrane bound structures. The large subunit and the small subunit will dissemble once the protein has been produced. 11. What type of cell would you expect to find hundreds/thousands of mitochondria in? Why? Cells that require a large amount of energy all the time would have many mitochondria in them. Cell examples would be sperm cells (swim to the egg) and muscle cells. 12. What type of cell would you expect to find a lot of smooth endoplasmic reticulum in? Why? Cells that detoxify poisons and break down alcohol would have a lot of smooth er (liver cells for example) Also cells that excrete (ship) lipids would have a lot of smooth er. (hormones ) 13. What is unique about the mitochondria and chloroplast? Both of these organelles contain their own DNA, which might indicate that they were organisms that once were able to live on their own. 14. Why did it take so long for us to discover the golgi apparatus? Golgi was not discovered until technology improved, better microscopes. The golgi was considered to be part of the endoplasmic reticulum.