File
advertisement

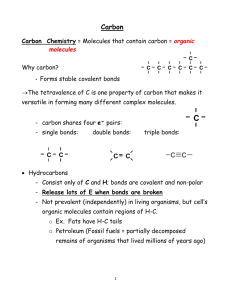
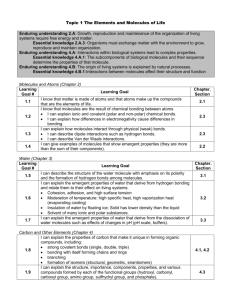
Nature of Science and Water (chemistry & properties) test review You are expected to know the following terms: Biology Proton Covalent bonds Electron Hydrogen bonds Control Hydrophilic Independent variable Hydrophobic Dependent variable Quantitative Acid Qualitative Base Solution pH scale Mixture Hypothesis Neutron Theory Water properties Cohesion Adhesion Surface tension Capillary action Scientific method Solute Solvent Germination Nature of Science 1. What are the steps of the scientific method (in order)? 1) _____________________________________________ 2) _____________________________________________ 3) _____________________________________________ 4) _____________________________________________ 5) _____________________________________________ 2. What is the difference between a hypothesis and a theory? 3. What makes a valid hypothesis? 4. What is the difference between the dependent and independent variable? Identify the dependent and independent variables in the following cases. 5. People with an income greater than $50,000 spend more money on eating out than people who make less than $30,000. a. Independent variable: b. Dependent variable: 6. An investigator hypothesizes that the adult weight of a dog is higher when it has fewer littermates. a. Independent variable: b. Dependent variable: Identify what the control and experimental groups would be in the following cases. 7. Athletes who do not get enough sleep the night before will not run as fast the next day. a. Control group: b. Experimental group: 8. The 3N Chemical Company has developed a new termite prevention treatment for wood. The researchers want to find out if it is more effective than the leading brand on the market. a. Control group b. Experimental group 9. Explain each type of observation a. Quantitative b. Qualitative Read the following passage and answer the questions 6 & 7 below Two different types of data can be collected during scientific investigations: qualitative data and quantitative data. The following data were collected by scientists studying the feeding habits of the purple-throated carib hummingbird, Eulampis jugularis. This hummingbird is found on several Caribbean islands including Dominica and St. Lucia. It feeds on both nectar and insects. In this study, scientists observed the birds in two different locations on the island of Dominica. One area was a landscaped garden with red ginger and several species of Heliconia. The other was a forested area dominated by Heliconia (spp.). A summary of the data collected is listed below. • The males of the species are larger than the females. • The males’ bills are shorter and less curved than those of the female. • The hummingbirds in the landscaped garden spent 21% of the time feeding. Of that time, 20% was spent feeding on insects and 80% was spent feeding on nectar. • The males get nectar from a species of Heliconia in which the flowers have shorter and less curved petals. • The females get nectar from a species of Heliconia in which the flowers have longer and more curved petals. • The hummingbirds in the forested area spent 23% of the time feeding. Of that time, 92% was spent feeding on insects and 8% was spent feeding on nectar. 10. Identify Which are the quantitative data in the example above? Explain. 11. Identify Which are the qualitative data in the example above? Explain. 12. Draw an atom with its three parts. Label each part including its charge. 13. On your drawing above, label what the space around the atom is called. How many levels can there be? 14. What tends to happens when the outer shell of an element/ atom is not complete? 15. What type of electrons are available to form bonds? Water Chemistry 16. What is the chemical formula of water? 17. Describe & illustrate the following chemical bonds a. Covalent bonds: i. Polar covalent: ii. Non-polar covalent: b. Hydrogen bonds: 18.Explain why each bond is important to life (creating molecules, compounds that make up living organisms) 19. Rank the two types of bonds in order of strength and explain your reasoning 20. Sketch a diagram of two water molecules. Label and describe the bonds that exist between the water molecules and within the water molecules. 21. Draw 3 water molecules. Show & label the following 1.The bonds between the water molecules 2. The slight negative and positive charges on each water molecule that account for the hydrogen bonds. Water Properties 22. Fill out the following table: Property of water Explanation of property Density (ICE) Evaporative cooling 23. What is the formula for density? 24. What are the measurement units for density? Example of how it benefits life 25. For the following examples explain what property or properties of water are acting to allow the situation/example to occur; a. Some insects can walk on water b. In order for the photosynthesis reaction to occur a plant needs water. Plants absorb water through their roots. That water travels upwards through small tube like structures present in roots and trunks until it reaches the leaves. (water traveling up a plant through small tube like structures) c. Water forming a small bubble on a penny d. Ice in a cup of soda e. Soda traveling up a straw f. Boiling temperature of water g. Water drops sticking to a plant’s leaves or your car window after it rains h. After working out in the Texas heat you tend to sweat i. Water bonding to other water molecules 26. Compare and contrast the properties of cohesion and adhesion and how they apply to water. Acid/bases/ solutions 27. What is a solution? Include the two parts that make up a solution. 28. Identify and explain the three types of solutions. 29. When mixing sugar and water together, the sugar dissolves. Label the following: Sugar - _________________ Water-_______________________ Sugar Water - _________________________ 30. What is a mixture? 31. Mixtures can be classified into two different categories. Identify, describe and provide an example for each category 32. What are the characteristics of an acid? 33. What are the characteristics of a base? 34. DRAW & LABEL THE pH SCALE: