Acids & Bases KEY
advertisement

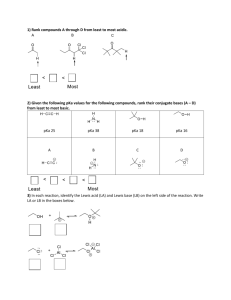
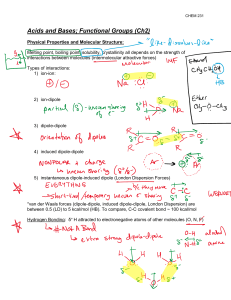
SI WS #4 1. A Bronsted-Lowry acid is a proton (donor). A Bronsted-Lowry base is a proton (acceptor). A Lewis acid is an electron-pair (acceptor). A Lewis base is an electron-pair (donor). 2. Why are the terms proton and H+ used interchangeably? The name proton is often used as a synonym for H+ because loss of the valence electron from a neutral hydrogen atom leaves only the hydrogen nucleus – a proton. 3. Define the terms conjugate acid and conjugate base. Conjugate acid – the species that results from accepting a proton Conjugate base – the species that remains after a proton has been donated from the acid 4. What does the constant Ka measure? Ka measures acid strength Ka = [A-][H+]/[HA] As Ka increases, acidity (acid strength) increases. As pKa increases, acidity (acid strength) decreases. What does this mean in terms of pH? Higher acidity = Lower pH 5. Formic acid has a pKa of 3.75 and picric acid has a pKa of 0.38. a. What is the Ka of each? Formic acid – (1.78*10^-4) Picric acid – (0.417) b. Which is the stronger acid, formic acid or picric acid? Picric acid is stronger – lower pKa – lower pH 6. In the following reactions, identify the acid/base and the conjugate acid/base. Then write a Ka expression for the reaction. a. H2SO4 + H2O <=> H3O+ + HSO4acid base c. acid c. base Ka = [H3O+][HSO4-]/[H2SO4] b. CH3COOH + H2O <=> H3O+ + CH2COOacid base c. acid c. base + Ka = [H3O ][CH2COO ]/[CH3COOH] SI WS #4 7. Acid HA dissociates in water to yield a concentration of H3O+ of 1.0x10-4 M. What is its pH? pH = 4 (-log[1x10^-4]) 8. The pKa of water is 15.74. Acetone, What is the pKa of acetone? 9.9 or , is a weaker acid than water. 19.3 9. Label the reactants in the following equation as a Lewis acid or Lewis base. Draw the product that would be formed in this reaction. The product formed in this reaction is called a(n) adduct. + acid <=> base AlCl3-N(CH3)3