16.2a B-L concept
advertisement

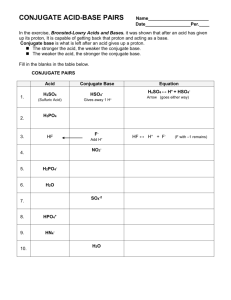
Chapter 16: Equilibrium in AcidBase Systems 16.2a: Bronsted-Lowry Acid-Base Concept Definition of Acid and Base Bronsted-Lowry independently created by two scientists around the same time (1923) looked at how acid/base acted in reactions instead of their properties in aqueous solutions theoretical definitions based upon proton transfer during a reaction Proton transfer concept Acid: molecule or ion that is a proton (H+) donor HCl + H2O H3O+ + Cl Base: molecule or ion that is a proton (H+) acceptor NH3 + H2O NH4+ + OH Bronsted-Lowry concept B-L acid a proton donor; B-L base a proton acceptor B-L neutralization is a competition for protons from the SA to the SB B-L rxtn. eqtn. is an eqtn. that shows this transfer of protons from one entity to another Acids or Bases? C5H5N acid (weak) base (weak) HC2H3O2 base (strong) CH3NH2 acid (strong) KOH base (weak) H2CO3 acid (weak) NH3 H2SO4 base (strong) HF base (weak) Mg(OH)2 acid (weak) HI acid (strong) Acid – Base Reactions Identify the acids and bases of the following reactions C6H5NH2 + H2O C6H5NH3+ + OHB A HNO3 + H2O H3O+ + NO3A B HCH3COO + H2O H3O+ + CH3COOA B Acid-Base Reactions Amphoteric Substances proper term used in B-L reactions a substance that can react as either acid or base depending on what they are mixed with example: water, HSO4 Amphiprotic incorrect term to use with B-L rxtns. refers to an entity (ion or molecule) Amphoteric Water Water as a base (proton acceptor) Water as an acid (proton donor) Conjugate Acid-Base Pairs Conjugate acids and bases are always created by a B-L reaction (as products) Conjugate base an acid that has lost a H+ missing a hydrogen ex: H2PO4-, OH-, Cl- Conjugate acid a base that has gained a H+ has an extra hydrogen NH4+, C6H5NH3+, H3O+ A pair of substances with formulas that differ only by a proton is called a conjugate acid-base pair Identify the parts of these reactions C6H5NH2 + H2O C6H5NH3+ + OHbase acid CA CB HNO3 + H2O H3O+ + NO3acid base CA CB HCH3COO + H2O H3O+ + CH3COOacid base CA CB NH3 + H2O NH4+ + OHbase acid CA CB Homework Textbook p724 #1-6 Textbook p726 #7 LSM 16.2A summary 1