quantum angular
advertisement
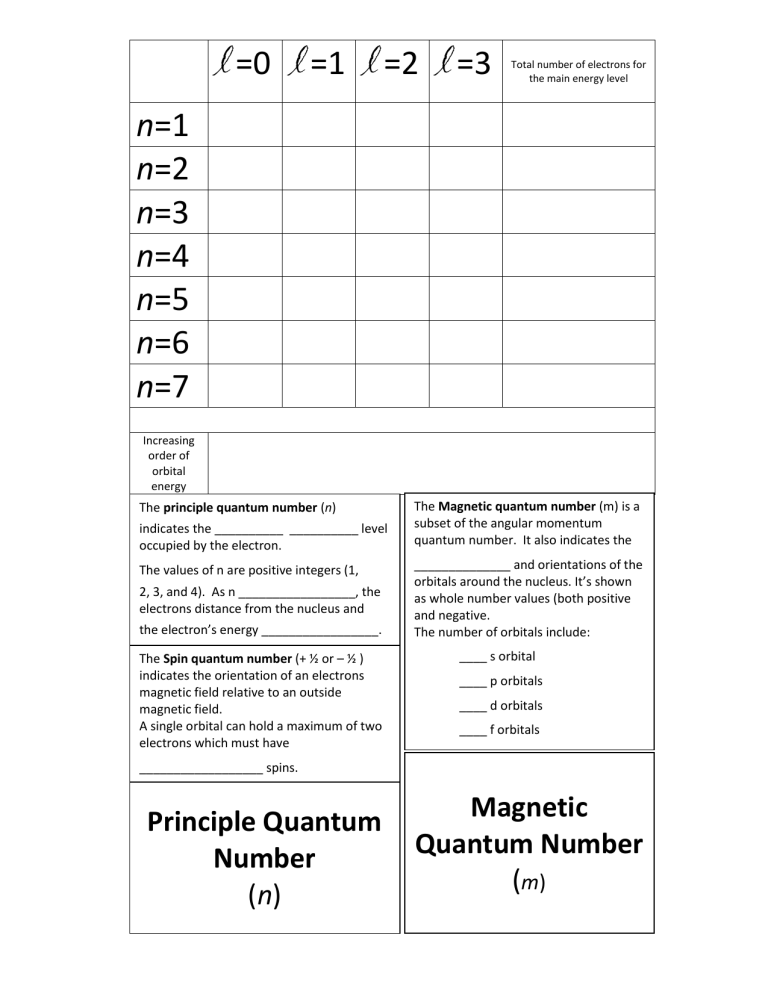
l =0 l =1 l =2 l =3 Total number of electrons for the main energy level n=1 n=2 n=3 n=4 n=5 n=6 n=7 Increasing order of orbital energy The principle quantum number (n) indicates the __________ __________ level occupied by the electron. The values of n are positive integers (1, 2, 3, and 4). As n _________________, the electrons distance from the nucleus and the electron’s energy _________________. The Spin quantum number (+ ½ or – ½ ) indicates the orientation of an electrons magnetic field relative to an outside magnetic field. A single orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons which must have The Magnetic quantum number (m) is a subset of the angular momentum quantum number. It also indicates the ______________ and orientations of the orbitals around the nucleus. It’s shown as whole number values (both positive and negative. The number of orbitals include: ____ s orbital ____ p orbitals ____ d orbitals ____ f orbitals __________________ spins. Principle Quantum Number (n) Magnetic Quantum Number (m) The Angular momentum quantum number (l) indicates the ___________ or type of orbital that corresponds to the particular energy sublevel of that electron. (s, p, d, or f) l = _____ is for an ___ orbital l = _____ is for a ____ orbital l = _____ is for a ____ orbital l = _____ is for an ____ orbital Ex: an electron occupying an orbital with n = 3 and l = 1 is called a ______ electron Angular Momentum Quantum Number (l) ____ orbitals are spherically symmetrical around a nucleus, like a hollow ball, made of chucky material with a nucleus at the centre. ____ orbitals are like two identical balloons tied together at the nucleus. These point in a particular direction (unlike s orbitals). ____orbitals & ____ orbitals have complicated shapes and orientations. Spin Quantum Number (+ ½ or – ½) Pauli Exclusion Principle – two particles of a certain class cannot be in the ________ energy state (cannot have the same _____ quantum numbers). They can have the same n, l, and m numbers but the spin must be ______________________. _________________ _______________________ - shows the arrangement of ________________ in an atom. Assume arrangements that have the lowest possible energies. Aufbau Principle – electrons fill orbitals that have the _________________ energy first. The structure of each successive element is obtained by adding one proton to the nucleus of the atom and one electron to the lowest energy orbital that is available. Electron Configuration Is a Shorthand Notation Based on the quantum model, the arrangement of the electrons around the nucleus can be shown by the nucleus’s electron configuration. Sulfur’s electron configuration. Atomic Number = 16 Atomic number tells us that sulfur has 16 protons and so 16 electrons. Practice 1. Write the electron configuration for an atom whose atomic number is 20. 2. Write the electron configuration for an atom that has 17 electrons. 3. What is the atomic number of an element whose atom has the following electron configuration 1s22s22p63s23p63d24s2 4. Write the electron configuration for an atom that has 13 electrons.