cjce22068-sup-0001-SuppData-S1
advertisement

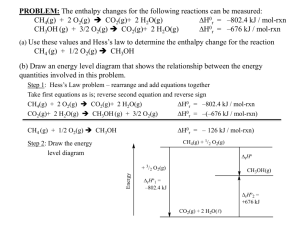
Supporting Information Methanol Production by Bi-Reforming Bruno A.V. Santos, José M. Loureiro, A.M. Ribeiro, Ana E. Rodrigues, Adelino F. Cunha* Laboratory of Separation and Reaction Engineering, Department of Chemical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, University of Porto, Rua Dr. Roberto Frias s/n, 4200-465 Porto, Portugal Corresponding Author *E-mail: afcunha@fe.up.pt. Telephone: +351-22-5081671. Fax: +351-22-5081674. 1 This supporting informations contain three tables and five figures, with physical data, equations, and additional informations used for our calculations and to support the discussion. Table S1: Main physical properties (for ideal gas assumption) of the compounds involved in BMR. C Properties CH4 CO2 H2O CO H2 f H o / kJ·mol-1 -74.85 -393.51 -285.83 -110.54 0 0 -200.94 f S o / J·K-1·mol-1 186.27 213.68 69.91 197.9 130.59 5.74 239.88 A 14.71 24.91 30.89 27.29 28.96 -0.4493 31.262 B 0.0724 0.0474 0.0079 0.0055 -0.0006 0.0355 0.00418 10 C -1.375 -1.759 0.249 0.021 0.190 -1.308 - (graphite) CH3OH Cp o / J·K-1·mol-1 5 * Cpº A B T C T 2 (Fitted) Table S2: Main reactions involved in BMR process. Number Reaction Equilibrium CH4 + CO2 ⇌ 2CO + 2H2 K1 2 y CO y H2 2 P 2 y CH 4 y CO2 P o 2 CH4 + H2O ⇌ CO + 3H2 K2 y CO y H3 2 P 2 y CH 4 y H 2O P o 3 CO+ H2O ⇌ CO2 + H2 1 K3 y CO2 y H 2 y CO y H 2O 4 CH4 ⇌ C + 2H2 a C y H2 2 P K4 y CH 4 P o 5 2CO ⇌ C + CO2 K5 a C y CO2 P o 2 y CO P 6 C + H2O ⇌ CO + H2 K6 y CO y H 2 P a C y H 2O P o 7 CO + 2H2 ⇌ CH3OH K7 yCH 3OH P o yCO y H2 2 P 2 Table S3: Enthalpy, Entropy and Gibbs free energy of the reactions involved in methanol synthesis. Reactions r H o / kJ·mol-1 r S o / J·K-1·mol-1 o -1 r G 550 K / kJ·mol CO + 2H2 ⇌ CH3OH -91 -333 92 CO2 + 3H2 ⇌ CH3OH + H2O -47 -380 162 CO + H2O ⇌ H2 + CO2 -41 77 -83 CO + 3H2 ⇌ CH4 + H2O -206 -335 -22 2CO + 4H2 ⇌ (Me)2O + H2O -248 -583 73 2CO + 4H2 ⇌ EtOH + H2O -342 -567 -30 Figure S1: Primary energy and raw material resources. 3 Figure S2: Atmospheric CO2 concentration along the time [8]. Figure S3: Methanol Economy. 4 Figure S4: Free Gibbs energy changes of reaction (direct methanol synthesis from BMR) versus temperature. Figure S5: CO2 conversion for direct synthesis of methanol (at different water ratios) as function of pressure (at 1300K). 5