Energy and Matter
advertisement

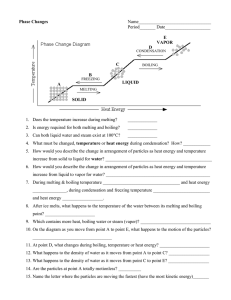
Energy & Matter Chemistry I 5.0 Name ____________________________ Properties & Changes 1. Completion energy kinetic potential destroyed created joule radiant a) _________________ is the capacity to do work or produce heat. b) Sunlight is an example of _________________ energy. c) The gasoline in your car is an example of chemical ___________________ energy. d) The SI unit for energy is the _____________. e) The Law of Conservation of Energy states that in any process, energy is neither ________________ nor ___________________. f) ____________________energy is the energy of motion. 2. Match the energy-requiring process with the correct energy transformation it involves. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. ______burning gas to drive a car ______friction ______photosynthesis ______electric mixer ______steam turbine making electricity ______flashlight a. electrical to mechanical b. light to chemical c. mechanical to heat d. chemical to electrical to light e. thermal to mechanical to electrical f. chemical to thermal to mechanical 3. Convert the following temperatures. Show all your work. Don’t forget significant digits! 47 °C = _______________ K 212 K = _______________ °C 1000. °C = _______________ K 32 K = ________________°C -20. °C = _______________ K 4120. K = _______________ °C -100. °C = _______________ K 301 K = ________________°C 4. Typical room temperature is 20.0 °C. What is room temperature on the Kelvin scale? 5. Pure gold melts at 1064 °C. What is the melting point of gold in kelvins? 6. Matter is anything that has _____________ and takes up __________________. a) Volume: Amount of _________________ an object takes up. b) Mass: Quantity of _________________ in a substance. ________________ everywhere. c) Weight: Force produced by _________________ acting on a mass. This is ____________ in different locations. d) ________________ possess the greatest amount of kinetic energy. e) Two factors that determine the state of matter of a substance: _______________________ and the ___________________________________. f) These two factors contribute to the ___________________ between the particles. g) Substances _____________ _______________ when they overcome these attractions. h) The overall _______________ ______________ (temperature) will remain constant until the entire substance has completely changed phase. 7. For each of the following, check the one box that applies. Physical Property a. A pond freezes over b. A puddle dries up c. Alcohol evaporating d. Blue color e. Boiling point f. Burning paper g. Butter melting h. Can neutralize a base i. Cracking an egg j. Cutting paper k. Density l. Digestion of food m. Dissolving sugar in water n. Flammability o. Glass breaking p. Hardness q. Iron rusting r. Is reactive with water s. Leaves changing colors on a tree t. Lighting a match u. Luster v. A change in atmospheric pressure w. Melting glass x. Melting point y. Mowing the lawn z. Odor Physical Change Chemical Property Chemical Change aa. Paint fading bb. Solubility cc. Exploding nitroglycerin dd. Stretching a rubber band ee. Supports combustion ff. Water boiling gg. Wood rotting hh. Will form H2 when mixed with acid Phase Changes E VAPOR D CONDENSATION C BOILING B FREEZING A LIQUID MELTING SOLID 8. Does the temperature increase during melting? _____________ 9. Is energy required for both melting and boiling? _____________ 10. Can both liquid water and steam exist at 100°C? _____________ 11. What must be changed, temperature or heat energy during condensation? How? ____________ 12. How would you describe the change in arrangement of particles as heat energy and temperature increase from solid to liquid for water? _______________________________________________ 13. How would you describe the change in arrangement of particles as heat energy and temperature increase from liquid to vapor for water? ______________________________________________ 14. During melting & boiling temperature __________________________________ and heat energy _______________, during condensation and freezing temperature _________________________ and heat energy __________________. 15. After ice melts, what happens to the temperature of the water between its freezing and boiling point? ______________________ 16. Which contains more heat, boiling water or steam (vapor)? _______________________________ 17. On the diagram as you move from point A to point E, what happens to the motion of the particles? ___________________________________ 18. At point D, what changes during boiling, temperature or heat energy? ______________________ 19. What happens to the density of water as it moves from point A to point C? __________________ 20. What happens to the density of water as it moves from point C to point E? __________________ 21. Are the particles at point A totally motionless? __________ 22. Name the letter where the particles are moving the fastest (have the most kinetic energy)_______ Two students performed the following experiment. They heated a beaker of ice and measured its temperature every one minute. After the ice melted, they continued measuring the temperature until it remained constant for a period of time. This is the graph of their results: °C 23. What is the starting temperature? ____________ 24. How long did this temperature remain constant? ____________ 25. What was the final temperature? ____________ 26. What is happening in the beaker at 0°C? ___________________ at 100°C? __________________ 27. At these temperatures, what was happening to the heat energy being added to the system? _______________________________________________________________________________ 28. How long did it take the students to reach 50°C ? ____________ 29. What was the temperature after 8 minutes? ____________ 30. How much did the temperature rise between 8 and 17 minutes? ____________ Classification and Separation 31. Classify each of the following statements with one or more of the following forms of matter. E – Element C – Compound HM – Heterogeneous Mixture S- Solution ____ soil ____ nitrogen gas ____ air ____ tin ____ pizza ____ hot chocolate ____ baking soda (NaHCO3) ____ mercury ____ 14-carat gold ring ____ distilled water ____ liquid dish detergent ____ steam ____ Italian salad dressing ____ various properties throughout ____ definite composition ____ dilute hydrochloric acid ____ uniform properties throughout ____ can be broken down into components by a chemical reaction ____ CH3OH ____ perfume ____ Jell-O ____ carbon dioxide ____ helium ____ salt ____ hot chocolate with marshmallows ____ tap water ____ diamond ____ sand (SiO2) ____ calcium ____ smog ____can be separated by evaporation ____ found on the periodic table ____ uniform distribution of particles throughout ____ made up of one kind of atom ____ spring water 32. Complete the following sentences using the correct separation technique term. filtration crystallization (evaporation) chromatography distillation a. Heterogeneous mixtures are often separated by ________________________________. b. Separating sand from water can be done by ___________________________________. c. The sugar in sugar water can be removed by __________________________________. d. The technique that takes advantage of different boiling points is __________________. e. Removing chlorophyll pigment from leaves might be done by ____________________. f. Crude oil is broken down by heat, vaporized, and allowed to condense into various liquids such as gasoline. This process is called ________________________________. 33. How could you separate a mixture of iron filings and aluminum filings? What property of these metals would allow such a separation? 34. How could you separate a mixture of alcohol, water, oil, and sand? Periodic Table 35. Write the correct symbol for each of the following elements. Name Symbol Name Hydrogen Mercury Helium Boron Lithium Aluminum Sodium Carbon Potassium Silicon Beryllium Tin Magnesium Lead Calcium Nitrogen Strontium Phosphorus Barium Arsenic Chromium Antimony Tungsten Oxygen Manganese Sulfur Iron Fluorine Nickel Chlorine Palladium Bromine Platinum Iodine Copper Neon Silver Argon Gold Krypton Zinc Xenon Cadmium Radon Symbol