Need to Know List: Chapter 13 What is the financial system and
advertisement

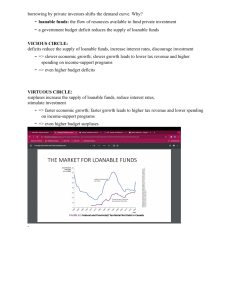
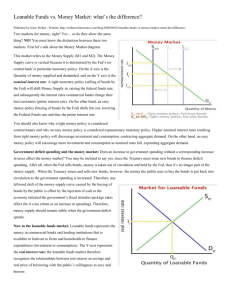
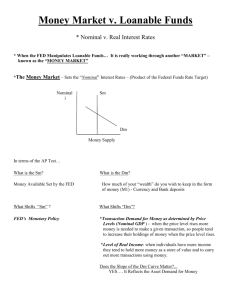
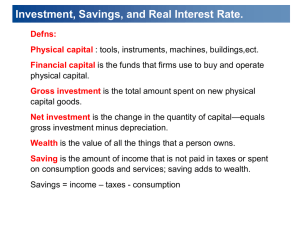
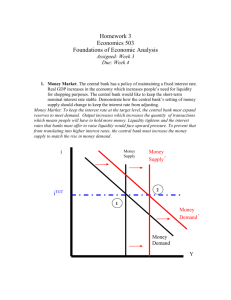
Need to Know List: Chapter 13 What is the financial system and what does it do? o What expectations do savers and borrowers have? What are financial markets o What is a bond meaning of date of maturity, principal characteristics of a bond meaning of term o what does the interest rate depend on & why? o why are long term bonds riskier than short term bonds? Which pays higher interest? Meaning of credit risk & default o Does a high credit risk cause low or high interest rates? Why? o What are junk bonds? What agencies judge credit risks? Meaning of tax treatment o Which bonds do owners have to pay taxes on? o What exactly are they paying taxes on? o How does this affect the interest rate? o Stock market Meaning of : stock, equity finance, debt finance Difference between stocks and bonds Who gets part of the profits of a corporation? Which is riskier? Which yields a potential higher reward? What does a stock exchange do? What determines the price of a stock? Purpose of a stock index Difference between stock index & stock exchange What are financial intermediaries? o Purpose of banks Why do small businesses use banks instead of bonds to finance investments? how do banks act as a medium of exchange? Difference from being a “store of value” o Mutual funds What are they composed of? Meaning of portfolio, index fund How to invest in mutual fund & risks associated Advantages of mutual fund Why are economists skeptical of professional money managers’ skills? National Income Accounts o Difference between close and open economy o In a closed economy, how is the formula for GDP different? What is national saving? Why is it equal to investment spending? o Meaning of “T” in the GDP equation Difference between private saving & public saving o Meaning of budget surplus? When does the government run budget surplus? o Meaning of budget deficit? When does the government run budget deficit? Difference between saving & investment Meaning of Market for loanable funds o What are loanable funds? o How many interest rates are there in market for loanable funds? Who does this interest rate apply to? What assumptions does this model make? o Who does the supply for loanable funds come from? What are ways that they supply money? o Who does the demand for loanable funds come from? What are ways that they “demand” loanable funds? o What is the price of a loan? What does it represent? How does the price of a loan relate to supply & demand As the price of a loan goes up, what happens to the demand for a loan? Supply? Why is the real interest rate a better measure of the price of the loan? Read P. 279 & understand the formula for computing final value/future value Taxes & Savings o How do taxes on interest paid from loans affect savings? o How would a decrease in taxes affect quantity saved? How would this affect the interest rate on loans and investment? Taxes & Investment o How do tax credits on companies/individuals taking out loans affect demand for loans? How does this affect the interest rate & investment? Government budget deficits & Surpluses o Difference between budget deficit & government debt o Why does a budget deficit decrease the supply of loanable funds? How does this affect the interest rate & investment? o Meaning of “crowding out” (how do government deficits decrease the economy’s growth rate?) o How do budget surpluses increase the economy’s growth rate?