Powerpoint - Shana M. McDermott, PhD
advertisement

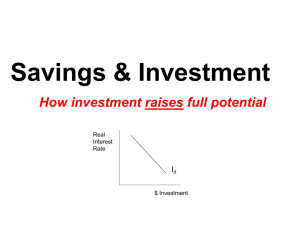
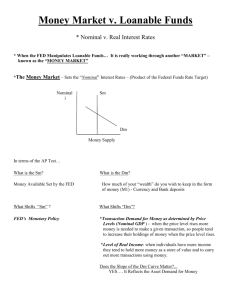
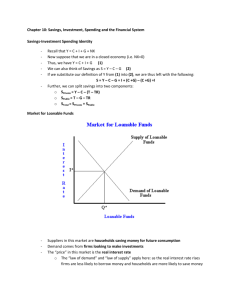
Economic Growth and the Financial system Economic Growth, the Financial System, and Business Cycles Business cycle: Alternating periods of economic expansion and economic recession. Long-Run Economic Growth Long-run economic growth: The process by which rising productivity increases the average standard of living. The Growth in Real GDP per Capita, 1900–2010 Measured in 2005 dollars, real GDP per capita in the United States grew from about $5,600 in 1900 to about $42,200 in 2010. The average American in the year 2010 could buy nearly eight times as many goods and services as the average American in the year 1900. The Connection between Economic Prosperity and Health Long-Run Economic Growth Calculating Growth Rates and the Rule of 70 Number of years to double 70 Growth rate What Determines the Rate of Long-Run Growth? Labor productivity: The quantity of goods and services that can be produced by one worker or by one hour of work. Long-Run Economic Growth What Determines the Rate of Long-Run Growth? Increases in Capital per Hour Worked Capital Manufactured goods that are used to produce other goods and services. Technological Change Economic growth depends more on technological change than on increases in capital per hour worked. Technological change is an increase in the quantity of output firms can produce using a given quantity of inputs. Saving, Investment, and the Financial System Financial system: The system of financial markets and financial intermediaries through which firms acquire funds from households. Saving, Investment, and the Financial System The Macroeconomics of Saving and Investment Y = C + I + G + NX Y=C+I+G I=Y−C−G Sprivate = Y + TR − C − T Spublic= T − G − TR Saving, Investment, and the Financial System The Macroeconomics of Saving and Investment S = Sprivate + Spublic or S = (Y + TR − C − T) + (T − G − TR) or S=Y−C−G So, we can conclude that total saving must equal total investment: S=I Market for loanable funds: The interaction of borrowers and lenders that determines the market interest rate and the quantity of loanable funds exchanged. The Market for Loanable Funds Demand and Supply in the Loanable Funds Market The Market for Loanable Funds Equilibrium in Loanable Funds The Market for Loanable Funds Explaining Movements in Saving, Investment, and Interest Rates An Increase in the Demand for Loanable Funds Crowding out: A decline in private expenditures as a result of an increase in government purchases. The Effect of a Budget Deficit on the Market for Loanable Funds - Who sets the interest rate? Central Banks? - Kind of. ANY good tradesman will tell you the importance of the bits of a house that you cannot see. Never mind the new kitchen: what about the rafters, the wiring and the pipes? So it is with financial markets. The stockmarkets are the most visible: as they soar or swoon, the headlinewriters get to work. The money markets, however, are the plumbing of the system. Normally, they function efficiently and unseen, allowing investment institutions, companies and banks to lend and borrow trillions of dollars for up to a year at a time. They are only noticed when they go wrong. And, like plumbing, when they do get blocked, they make an almighty stink. (Source: Blocked Pipes, The Economist, Oct 2nd 2008) Business cycle The Business Cycle Some Basic Business Cycle Definitions The Business Cycle What Happens during a Business Cycle? The Effect of the Business Cycle on Boeing The Effect of the Business Cycle on Boeing What Happens during a Business Cycle? The Effect of the Business Cycle on the Inflation Rate What Happens during a Business Cycle? The Effect of the Business Cycle on the Inflation Rate The Impact of Recessions on the Inflation Rate Don’t Let This Happen to YOU! Don’t Confuse the Price Level and the Inflation Rate What Happens during a Business Cycle? The Effect of the Business Cycle on the Unemployment Rate How the Recession of 2001 Affected the Unemployment Rate What Happens during a Business Cycle? The Effect of the Business Cycle on the Unemployment Rate How Recessions Affect the Unemployment Rate What Happens during a Business Cycle? The Effect of the Business Cycle on the Unemployment Rate The Impact of Recessions on the Unemployment Rate What Happens during a Business Cycle? Recessions Have Been Milder and the Economy Has Been More Stable Since 1950 Fluctuations in Real GDP, 1900–2008 Fluctuations in real GDP were greater before 1950 than they have been since 1950. Why Is the Economy More Stable? • The increasing importance of services and the declining importance of goods. • The establishment of unemployment insurance and other government transfer programs that provide funds to the unemployed. • Active federal government policies to stabilize the economy.