Atomic Theory Webquest
advertisement

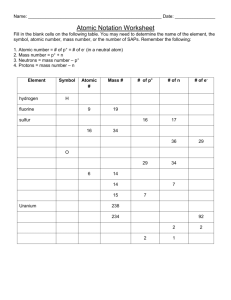
Atomic Theory Webquest Name________________________ Date ____________ Block_______ Overview: For thousands of years we have wondered about matter and what it is made of. The discovery of electricity and the use of magnets and batteries made learning about atoms possible. In this lesson, you will learn about the observations and discoveries made by scientists as they try seeing parts of atoms and complete practice problems based on these findings. Instructions: Download Atomic Structure Textbook.pdf. 1. Study page 134. a. What are three particles that make up atoms? b. Describe where the metals are in the periodic table shown on this page. Be specific. c. Describe where the nonmetals are in the periodic table shown on this page. d. Describe where the noble gases are in the periodic table shown on this page. 2. Watch the You Tube video The Cathode Ray Tube and Electron (1:09). Read page 135. What did J J Thomson prove about the electron? According to his observations, what is the charge on an electron? 3. Read p. 136 and watch the Youtube videos about Rutherford's experiment . An alpha particle is a helium atom. State what Rutherford observed when he fired these helium atoms at a sheet of gold foil. What do these observations tell us about how the atom is organized? 4. a. Use page 137 to fill in the following chart. Particle Mass in kg Charge Relative mass Relative Charge proton _______________ __________________ ___________ ____________ neutron _______________ __________________ ___________ ____________ electron _______________ __________________ ___________ ____________ 5. Watch the YouTube video Nucleus (2:03) Where in the atom do we find most of its mass? Explain how this agrees or disagrees with Rutherford’s results. 6. a. Read page 138. Define the term atomic number. Note: An atom’s position on the periodic table tells the number of protons in the atoms of that element. For example, Carbon is in position number 6 in the periodic table, therefore all carbon atoms contain 6 protons in their nuclei. The PROTON is the part of the atom that IDENTIFIES it as an atom of a certain element. b. Which part of the atom of one element distinguishes it from an atom of another element? 7. Define the term isotope. 8. a. Define the term mass number. Notice you can only obtain the mass number of an atom if you are given the exact number of neutrons. The mass number is NOT found in a standard periodic table. It can only be found if someone gives you the number of neutrons found in a certain atom. b. What is the mass number of an atom that contains 7 protons and 8 neutrons? _________ c. What is the element in item b? ___________ 9. a. Use page 139 to describe how average atomic mass is calculated: b. Examine any periodic table. Are average atomic masses given in your periodic table? c. Describe how you can tell the difference between a mass number and the atomic mass on a periodic table? Practice Questions: 1. All atoms of a certain element all contain the same number of ______ 2. How many protons does an atom of helium contain? __________ 3. How many protons does an atom of carbon contain? __________ 4. How many protons does an atom of nitrogen contain? __________ 5. How many protons does an atom of oxygen contain? __________ 6. How many protons does an atom of neon contain? __________ 7. The position number on the periodic table determines the number of protons in an atom of an element. Use a periodic table to find the number of protons contained in an atom of each of the following elements: a. aluminum (Al) ________ b. sulfur (S) _________ c. calcium (Ca) ________ d. strontium (Sr) ________ e. bromine (Br) _________ f. iodine (I) ________ g. silver (Ag) _______ h. gold (Au) ________ i. lead (Pb) _________ 8. The number of protons in an atom of a certain element is called its atomic ___________. 9. Protons have a positive charge, neutrons have no charge and electrons have a negative charge. All of these make up an atom. If an atom is neutral, it has no charge, so the number of __________________ and ____________ must be the same. 10. a. Label the diagram using the terms proton, neutron, and electron. Color & Make a legend. The charges are written inside each particle. b. Identify the atom shown in this diagram__________________ Describe how you obtained your answer ________________________________________________ c. The mass number is the number of protons plus the number of neutrons for a particular atom. What is this atom’s mass number? ___________ d. Defining “complete nuclear symbol”: The composition of any atom can be represented using a complete nuclear symbol which lists the atomic number (number of protons) to the lower left of the symbol and the mass number (protons plus neutrons) to the upper left of the symbol. This atom has an atomic number of 2 (making it helium,) and a mass number of 5. Its complete nuclear symbol would be: 5 He Another way to show the complete nuclear symbol is to have the name of the element followed by a dash then the mass number. This atom could also be written as helium-5. Since helium always contains 2 protons, it must have 3 neutrons if it has the mass number of 5 after it. Both of these styles of notation are shown on page 138 of your text. 11. Place the terms mass number and atomic number in the labels provided 12. Write the complete nuclear symbol for an atom containing 3 protons and 4 neutrons 13. Write the complete nuclear symbol for an atom containing 6 protons and 7 neutrons 14. Write the complete nuclear symbol for an atom containing 10 protons and 10 neutrons 15. Write the complete nuclear symbol for an atom containing 26 protons and 27 neutrons 15. Write the complete nuclear symbol for an atom containing 30 protons and 36 neutrons 16. Write the complete nuclear symbol for an atom containing 5 protons and 5 neutrons Fill in the blanks using the word bank provided. Chose the best term, some terms may not be used. group protons mass number atomic numbers isotopes neutrons period Average Atomic Mass 17. Isotopes are atoms of a same element because they have the same number of _______________, but have different numbers of _______________. Since the number of neutrons differ between these atoms, their ________________ _________________ are also different. 18. Consider a boron atom containing 4 neutrons, another containing 5 neutrons and a third one containing 6 neutrons. These three boron atoms are ___________________ of the element boron. 19. A horizontal row in the periodic table is called a ___________________, a vertical column is called a ___________________. 20. The ____________ ______________ of an element is the number of neutrons plus the number of protons. 21. The ____________________ ________________ _______________ is a weighted average of an element’s all known isotopes.