4.8 - Crystalline Solid Structures
advertisement

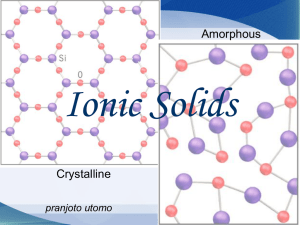
4.8 THE STRUCTURE AND PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS *Amorphous solids: solids whose constituent particles are ________________ arranged and have ___ ordered long-range structure *Crystalline solids: solids whose atoms, ions, or molecules have an _______________ arrangement extending over a long range Types of Crystalline Solids *In all types of bonding, we can consider a solid as a lattice of particles. The type of bonding depends on the type of particle and the forces that exist between them. 1) Ionic Crystalline Solids The attractive force between oppositely charged ions. The lattice is made of _______________ charged ______. Salts are ______________. SALTS ARE NOT ____________________! e.g. NaCl – A crystal of sodium chloride is composed of alternating _____ and ____ ions ordered into a regular threedimensional arrangement held together by _________ bonds. *Why do ionic compounds shatter…if they are hit with a hammer, for example? Conductivity: How do ionic substances conduct? In what state must they be in? 2) Covalent – Giant/Network Crystalline Solids Regular ________________ bonds, but they exist between _________ atoms in a giant three-dimensional array – that is, every atom is covalently bonded to all its nearest neighbours. In effect, a covalent network is one very large molecule. Some Examples of Covalent Networks (all with “diamond” structure): *SiO2 (silica/quartz) *Silicon Silicon Carbide (a.k.a. moissonite) 1 Allotropes of Carbon – Graphite, Diamond and Fullerene (giant covalent network solids) *Allotropes are different molecular or crystalline forms of the _____________element that differ in _______________ and ________________ properties. Diamond __________ – all electrons are used in localized bonds Graphite ________ – only ___ electrons from each carbon are used in bonding – the fourth electron is found in a ________________ pi cloud …formed by unhybridized ___ - orbitals Fullerene _____________ – surface of the “ball” is conductive, but imagine an ant running across the surface of a lot of basketballs Geometry 3-dimensional ____________ arrangement of carbons “2-dimensional”…layers of __________ of carbon “2-dimensional”, large (C60), ______________ molecules Hardness Very ________ – all atoms are held together in the lattice by strong ___________ bonds Very _______ – _________ 2 - dimensional sheets slide over each other because of weak ____ ____ _______’ forces between the sheets Conductivit 3) Covalent – Molecular Crystalline Solids CO2(s) Regular covalent bonds, but the atoms form little “packages” called _________________. Each “package” is held together by strong _____________ bonds; however, they are attracted to each other by weak __________________forces such as ________________, ________________or _________________. Examples include: Sucrose [C12H22O11(s)], ice[H2O(s)], carbon dioxide[CO2(s)], iodine[I2(s)] and sulfur[S8(s)]. Remember: A change of state is NOT a ______________ reaction. It is a physical change. Examples: H2O(s) ------------------- C2H5OH(s) ---------------- CO2(s) ------------------------ C12H22O11(s) ---------------- 4. Metallic Crystalline Solids Metallic crystals such as silver, lead, aluminum, or iron are like covalent network solids, but they consist of metal atoms. Kept together by ___________ bonds – (i.e. the electrostatic attraction between a lattice of positive _______________ _______and a “sea” of _____________ valence electrons that moves among them) In general, the strength of the metallic bond increases when the charge on the cation ____________ and the number of valence electrons, participating in metallic bonding, also _____________. Metals are: 1) malleable can be hammered into ___________; and, ductile can be molded into ___________ *Why are metals malleable and ductile while ionic crystals are brittle? (How does the ionic crystal differ from the metallic crystal?) 2) excellent _______________ of _______________ *Why? *Metals are excellent conductors due to the presence of ________________________ electrons. They are able to conduct in BOTH the _________________and ________________ state. 2 Summary: Solid Ionic Lattice Forces Boiling Point Metallic Giant Covalent Networks Molecular Covalent Practice Questions: 1. Identify the main type of bonding and the type of solid for each of the following: Solid SiO2 Type of Bonding Type of Solid/Crystal Na2S CH4 C Cr CaO SiC Fe PCl5 2. Match the solids, NaBr(s), V(s), P2O5(s), and SiO2(s), to the property listed below. a) high melting point, conducts electricity …………………………______________ b) low melting point, soft……………………………………………______________ c) high melting point, soluble in water………………………………______________ d) very high melting point, nonconductor…………………………...______________ 3