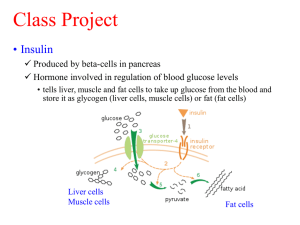
Insulin Therapy Actions of insulin Liver cells Fat cells Muscle cells
advertisement

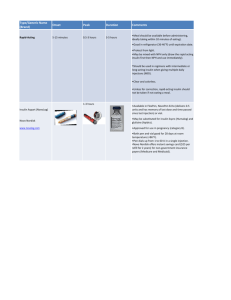
Insulin Therapy Actions of insulin Carbohydrate metabolism Fat metabolism Protein metabolism Liver cells ↑Glycolysis ↑Glycogenesis ↓Glycogenolysis ↓Gluconeogenesis ↓Lipolysis ↑Lipogenesis ↓Protein breakdown Fat cells ↑Glucose uptake Muscle cells ↑Glucose uptake ↑Glycolysis ↑Glycogenesis ↑Synthesis of TGs & FAs ↓Lipolysis ↑AA uptake ↑Protein synthesis Promotes tissue uptake & storage of glucose, AAs & fats Acutely lower blood glucose Inhibits hepatic glycogenolysis & gluconeogenesis Increases glycogen synthesis in muscle/liver Inhibits lipolysis Stimulates protein synthesis Longer term effects on growth & gene expression Uses of insulin Type I DM Improved metabolic control in type II DM Oral therapies for type II contraindicated or not tolerated Post-MI (DIGAMI) Severe intercurrent illness, surgery Gestational diabetes (not controlled by diet) Side effects Hypoglycaemia Weight gain Allergy Lipohypertrophy & lipoatrophy Transient deterioration of retinopathy Insulin neuritis Insulin preparations Short-acting Onset 30 minutes Peak 2-4 hours Duration 8 hours Intermediate 1-2 hours 4-12 hours 16-24 hours Long-acting 1-2 hours 4-12 hours 20-35 hours Analogue 0-15 minutes 1-2 hours 4-6 hours 24 hours Example Actrapid Humulin S Insulatard Humulin I Human Ultratard Humulin Zn Humalog (Lispro) Novorapid (Aspart) Apidra (Glulisine) Glargine, Levemir Rapid-acting e.g. novorapid, Humalog Onset 10 mins — Can give straight after meals rather than before, useful in children as can observe to see how much eat, then adjust dose accordingly (carb count) Peak 1-3 hours Duration 4-5 hours Rapid Short Short-acting e.g. actrapid (used in DKA) Onset 30 mins Peak 1-3 hours Duration up to 8 hours — Means need to snack before next meal to combat insulin Premixed insulin (2-dose regimen) Different combinations of rapid/short-acting & intermediate acting insulins — Short-acting e.g. 30/70 mixture = 30% fast-acting + 70% intermediate Onset 30 mins Peak 2-8 hours Duration up to 24 hours — Rapid-acting e.g. 25/75 or 30/70 Can’t use long-acting insulins (don’t combine well) Intermediate acting e.g. insulatard Onset 1.5 hours Peak 4-12 hours; unhelpful, predisposes to hypos Duration up to 24 hours (realistically don’t last this long) Long-acting analogues (background insulin) e.g. glargine, levemir Take at same time each day (usually at night before bed) Peak-less MOA Takes 2-3 days for dose to build up and action to kick in Not very responsive as a result e.g. difficult to cut down if doing out drinking Insulin regimes Twice daily mixture Once daily plus long-acting Four times rapid-acting plus daily basal bolus Continuous SC insulin infusion Basal bolus regime Twice daily mixture Long-acting analogue: glargine or levemir PLUS Rapid-/Short-acting analogue: novorapid, humalog, apidra (3-4x daily with meal Combination therapies Metformin Sulphonylureas Glitazones