Atoms-and-Bonding - Newark Catholic High School
advertisement

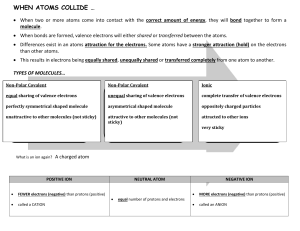
Atoms and Bonding CHEMICAL BONDS A chemical bond is the force of attraction holding atoms together due to the transfer or sharing of valence electrons between them. Atoms react in a way that will make them more stable. Atoms will either gain, lose or share electrons in order to chemically combine with other atoms and fill their valence shells. Ions -Ions are atoms with an electrical charge due to the loss or gain of electrons. -Anions have a negative charge due to the gain of electrons. -Cations have a positive charge due to the loss of electrons. Forming Ions During chemical changes aluminum loses its 3 valence electrons, resulting in Al+3. During chemical changes oxygen gains 2 electrons, resulting in O-2. How to determine the type of ion: Metals will lose their valence electrons to non-metal atoms. The charge of the ion corresponds to the # of electrons lost. The charge is always (+) They are called cations. Non-metals will gain valence electrons from metal atoms. The charge of the ion corresponds to the # of electrons gained. The charge is always (-) They are called anions. Types of Chemical Bonds: Ionic Covalent (molecular) * Coordinate Covalent Network covalent Metallic * Covalent bonds (molecular) can be divided into two categories; polar and non-polar. Ionic Bonds A metal atom bonds with a non-metal atom. The valence electrons are transferred. The metal atom loses them and the non-metal atom gains them. Ionic bonds form from electrical attraction between anions and cations Polyatomic ions are made of several atoms and have an overall positive or negative charge Ionic Compounds -consist of a combination of cations and anions in which the bonding balances out the negative and positive charges - ionic compounds are crystalline, have high melting points, conduct electricity when melted, and are water soluble. -in naming ionic compounds, the name of the cation is first followed by the name of the