Types of Bonds Notes
advertisement

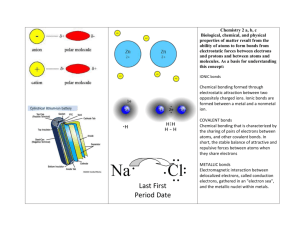
Types of Bonds Notes Ionic Bonds Ionic bonding is the gaining or losing of ve¯ . When atoms with different numbers of valence electrons combine, the atom with a higher electron affinity “takes” electrons from the other atom. This kind of electron transfer makes one cation and one anion. The opposite charges of ions create attractions (like a magnet) called ionic bonds. Ionic bonds tend to be fairly strong. Ionic bonds occur between metals and non-metal. Metallic Bonds Another type of chemical bond is the bond between two metal atoms. Metals lose electrons and cannot normally accept them. This means that, in a metallic bond, there are no atoms to accept the electrons. Instead, the electrons are given up to a "sea" of electrons that surrounds the metal atoms. This is how metals “move” electricity and heat (conduction) Covalent Bonds Covalent bonding is the sharing of ve¯. Atoms that hold their electrons more tightly may share them with other atoms. Only occurs in a Non-metal to Non-metal bond Molecules are formed in covalent bonds Electrons are always shared in pairs. Covalent bonds tend to be very weak. Electrons that are shared by the atoms have a high likelihood of being found in between the nuclei of the two atoms. These shared electrons form a “dense region of negative charge.” The region of negative charge attracts the nuclei, holding the two atoms together. This attraction is called the “electrostatic force.” The electrons that are shared are called “bonding pairs.” The electrons that are not shared are called “lone pairs” or “non-bonding pairs.”