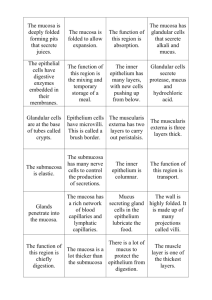
A&P II 2015 Exam 3A Name 1) The respiratory mucosa consists of A
advertisement

A&P II 2015 Exam 3A Name ___________________________________________ 1) The respiratory mucosa consists of A) epithelium and underlying layer of areolar tissue. B) dense irregular connective and adipose tissue. C) ciliated stratified squamous and columnar cells. D) fibrocartilage and mucous cells. E) dense regular connective and areolar tissue. 2) The nasal cavity, pharynx, and larynx constitute the ________ portion of the airway. A) conducting B) exchange C) respiratory D) sinus E) primary 3) The respiratory epithelium of the conducting airways consists of A) pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium. B) moist cuboidal epithelium. C) simple squamous epithelium. D) ciliated squamous epithelium. E) stratified squamous epithelium. 4) The larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles all make up the A) upper respiratory tract. B) lower respiratory tract. C) internal respiratory tract. D) alveoli of the respiratory tract. E) respiratory mucosa. 5) Which of the following statements about the trachea is false? A) It is lined by pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium. B) Tracheal cartilages prevent tracheal collapse. C) It contains many mucous glands. D) It alters its diameter in response to the autonomic nervous system. E) It is reinforced with D-shaped cartilages. 6) The airway that connects the larynx to the bronchial tree is the A) trachea. B) bronchiole. C) laryngopharynx. D) alveolar duct. E) bronchus. 7) The ________ branch from the trachea at the carina. A) terminal bronchioles B) secondary bronchi C) tertiary bronchi D) primary bronchi E) alveolar ducts 1 8) The C shape of the tracheal cartilages is important because A) large masses of food can move through the esophagus. B) large masses of air can pass through the trachea and thus the bronchi. C) it facilitates turning of the head. D) the bronchi are also C-shaped. E) it permits the trachea to pinch shut prior to sneezing. 9) The following is a list of some airways. What is the order in which air passes through them? 1. secondary bronchus 2. bronchioles 3. alveolar ducts 4. primary bronchus 5. respiratory bronchiole 6. alveoli 7. terminal bronchiole A) 4, 1, 2, 7, 5, 3, 6 B) 4, 1, 2, 5, 7, 3, 6 C) 1, 4, 2, 5, 7, 3, 6 D) 1, 4, 2, 7, 5, 3, 6 E) 2, 4, 1, 7, 5, 3, 6 10) The interlobular septa divide the lungs into A) lobes. B) pulmonary lobules. C) alveolar sacs. D) vital capacity and residual volume. E) visceral pleura and fibrous trabeculae. 11) The respiratory membrane of the gas exchange surfaces consists of A) pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium. B) moist cuboidal epithelium. C) simple squamous epithelium. D) ciliated squamous epithelium. E) surfactant cells. 12) The most superior portion of the lung is called the A) base. B) apex. C) cardiac notch. D) hilus. E) epipleurium. 13) Damage to the type II pneumocytes of the lungs would result in A) a loss of surfactant. B) an increased rate of gas exchange. C) decreased surface tension in the alveoli. D) expansion of alveoli. E) All of the answers are correct. 14) The resulting pain and inflammation when pleural fluid is unable to prevent friction between the opposing pleural surfaces is known as A) pleurisy. B) pulmonary hypertension. C) asthma. D) emphysema. E) COPD. 2 15) When there is no air movement, the relationship between the intrapulmonary and atmospheric pressure is that A) they are equal. B) intrapulmonary pressure is greater than atmospheric. C) atmospheric pressure is less than intrapulmonary. D) atmospheric pressure is more than intrapulmonary. E) intrapulmonary pressure is less than atmospheric. 16) External respiration involves the A) movement of air into and out of the lungs. B) diffusion of gases between the alveoli and the circulating blood. C) exchange of dissolved gases between the blood and the interstitial fluid. D) binding of oxygen by hemoglobin. E) utilization of oxygen by tissues to support metabolism. 17) In which direction does carbon dioxide move during internal respiration? A) from the blood into the tissue cells B) from the blood into the lungs C) from the lungs into the atmosphere D) from the tissue cells into the blood E) from the lungs into the blood 18) Boyle's law states that the pressure of a gas is A) inversely proportional to the volume of its container. B) always higher in the atmosphere than in the lungs. C) directly proportional to temperature. D) inversely proportional to temperature. E) directly proportional to the volume of its container. 19) Air moves out of the lungs when the pressure inside the lungs is A) greater than intraalveolar pressure. B) less than the pressure in the atmosphere. C) less than intrapulmonic pressure. D) equal to the pressure in the atmosphere. E) greater than the pressure in the atmosphere. 20) During quiet breathing, A) only the internal intercostal muscles contract. B) inspiration involves muscular contractions and expiration is passive. C) inspiration is passive and expiration involves muscular contractions. D) both inspiration and expiration are passive. E) both inspiration and expiration involve muscular contractions. 21) During exercise, which of the following contract for active exhalation? A) rectus abdominis and internal intercostal muscles B) diaphragm and internal intercostal muscles C) rectus abdominis and diaphragm muscles D) diaphragm and external intercostal muscles E) pectoralis major and serratus anterior muscles 3 22) The term ________ describes the result from an injury that permits air to leak into the intrapleural space. A) pleurisy B) pneumonia C) pneumothorax D) pulmonary edema E) emphysema 23) ________ is the amount of air that moves into the respiratory system during a single respiratory cycle. A) Residual volume B) Expiratory reserve volume C) Inspiratory reserve volume D) Tidal volume E) Inspiratory capacity 24) ________ is the amount of air that you can inhale above the resting tidal volume. A) Residual inhaled volume B) Expiratory reserve volume C) Inspiratory reserve volume D) Enhanced tidal volume E) Inspiratory capacity 25) When the diaphragm and external intercostal muscles contract, A) the volume of the thorax increases. B) the volume of the thorax decreases. C) the volume of the lungs decreases. D) the lungs shrink. E) expiration occurs. 26) Which of the following is an accessory organ of digestion? A) appendix B) pancreas C) spleen D) colon E) esophagus 27) Digestion refers to the A) progressive dehydration of indigestible residue. B) mechanical breakdown of food. C) chemical breakdown of food. D) mechanical and chemical breakdown of food. E) All of the answers are correct. 28) Which of the following is not a function of the digestive system? A) mechanical processing B) absorption C) secretion D) ingestion E) filtration 29) Which of the following descriptions best matches the term submucosal plexus? A) component of mucosa B) sensory neural network C) secretes a watery fluid D) coordinates activity of muscularis externa E) loose connective tissue layer containing blood vessels 4 30) Waves of muscular contractions that propel the contents of the digestive tract are called A) segmentation. B) pendular movements. C) peristalsis. D) churning movements. E) mastication. 31) The activities of the digestive system are regulated by A) hormones. B) parasympathetic and sympathetic neurons. C) the contents of the digestive tract. D) intrinsic nerve plexuses. E) All of the answers are correct. 32) The digestive tract is also referred to as the A) alimentary canal. B) esophagus. C) GI tract. D) alimentary canal and the GI tract. E) All of the answers are correct. 33) The lamina propria and mucous epithelium are components of the A) serosa. B) adventitia. C) muscularis mucosa. D) mucosa. E) submucosa. 34) The enzyme amylase digests A) peptides. B) polysaccharides. C) disaccharides. D) triglycerides. E) nucleotides. 35) An enzyme that digests proteins into peptides is A) lipase. B) amylase. C) nuclease. D) maltase. E) trypsin. 36) Carbohydrate digestion begins in the A) mouth. B) esophagus. C) stomach. D) duodenum. E) ileum. 5 37) If digestion of a carbohydrate results in equal amounts of glucose and galactose, this carbohydrate is probably A) sucrose. B) maltose. C) lactose. D) cellulose. E) glycogen. 38) Which of the following is false concerning the process known as cotransport? A) Only neutral compounds such as sugars are transported. B) More than one molecule or ion is moved through the cell membrane at one time. C) ATP is not required by the transport protein. D) Molecules can be moved against a concentration gradient. 39) Products of fat digestion are transported initially by A) capillaries. B) veins. C) lymphatic vessels. D) the interstitial fluid. E) the arterioles. 40) The absorption of some sugars in the small intestine involves A) osmosis. B) diffusion. C) cotransport. D) phagocytosis. E) pinocytosis. 41) Absorption of glucose from the gut lumen depends on A) the sodium-potassium pump in the basolateral membrane of the epithelial cell. B) cotransporter proteins in the apical membrane of the epithelial cell. C) higher sodium ion concentration in the lumen than in the epithelial cell. D) sodium-linked cotransport. E) All of the answers are correct. 42) Products of fat digestion are transported initially by A) capillaries. B) veins. C) lymphatic vessels. D) the interstitial fluid. E) the arterioles. 43) The absorption of some sugars in the small intestine involves A) osmosis. B) diffusion. C) cotransport. D) phagocytosis. E) pinocytosis. 6 Match a. duodenal glands b. gastric glands c. intestinal crypts d. liver e. pancreas f. salivary glands A 44. produce(s) mucus; found in the submucosa of the small intestine 45. produce(s) a product containing amylase that begins starch breakdown in the mouth 46. produce(s) many enzymes and an alkaline fluid that is secreted into the duodenum 47. produce(s) bile that it secretes into the duodenum via the bile duct 48. produce(s) HCl and pepsinoges 49. found in the mucosa of the small intestine; produce(s) intestinal juice Match A. mesentery B. rugae C. esophagus D. Peyer’s patches E. villi F. circular folds G. lesser omentum H. pharynx I. tongue J. oral cavity 7 50. structure that suspends the small intestine from the posterior body wall 51. fingerlike extensions of the intestinal mucosa that increase the surface area for absorption 52. large collections of lymphoid tissue found in the submucosa of the small intestine 53. deep folds of the mucosa and submucosa that extend completely or partially around the circumference of the small intestine 54. region that breaks down foodstuffs mechanically 55. mobile organ that manipulates food in the mouth and initiates swallowing 56. conduit for both air and food 57. structure continuous with and representing modifications of the peritoneum (there are three answers above – just choose one) 58. the “gullet”; no digestive/ absorptive function 59. folds of the gastric mucosa Xtra Credit (1 point each) 1) ________ is the most common lethal inherited disease affecting individuals of Northern European descent. A) MRSA B) Congestive heart failure C) Cystic fibrosis D) Myasthenia gravis E) Parkinson's disease 2) A patient with a connective tissue disease experiences increased pulmonary vascular resistance. Over a period of time, you would expect to observe A) increased cardiac output from the right ventricle. B) increased cardiac output from the left ventricle. C) increased thickness of the right ventricular wall. D) distension of the pulmonary veins from the right lung. E) no appreciable changes in heart structure or function. 3) During a choking episode, most foreign objects are lodged in the ________ bronchus due to its larger diameter and steeper angle. A) right primary B) left primary C) right secondary D) left secondary E) medial 4) Blockage of pulmonary blood flow by a clot or similar obstruction is A) emphysema. B) COPD. C) anoxia. D) pulmonary embolism. E) pneumothorax. 8 5) Which of the following is true regarding lactose intolerance? A) The stomach produces inadequate amounts of lactase. B) Lactose-intolerant infants cannot digest dairy fat and are at risk of starvation. C) The person cannot digest any type of monosaccharide. D) The intestinal crypts are not producing the enzyme lactase. E) The enzyme maltase begins to digest lactose. 9