The lung as an organ of exchange
advertisement
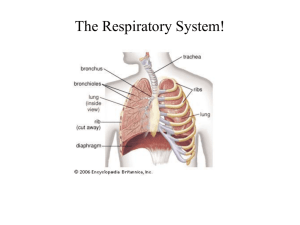
The lung as an organ of exchange Learning intentions • Describe the features of an efficient exchange surface with reference to diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide across an alveolus. • Describe the features of the mammalian lung that adapt it to efficient gas exchange. • Outline the mechanism of breathing. The Lungs How lungs are adapted for exchange Adaptation Importance for gas exchange Breathing Breathing Questions • State three ways in which the structure of the lungs allows efficient gas exchange • Explain why the barrier to diffusion must be as thin as possible • Describe how a steep diffusion gradient is achieved in the lungs. Lesson 2: Tissues in the lungs Learning Intentions • Describe the distribution of cartilage, ciliated epithelium, goblet cells and smooth muscle and the elastic fibres in the trachea, bronchi and bronchioles and alveoli • Describe the functions of cartilage, cilia, goblet cells, smooth muscle and elastic fibres in the mammalian gaseous exchange system. Starter • In order for air to enter the lungs through the trachea, bronchi and bronchioles, what features do you think they must have? • Students will be able to look at various slides of these structures Tissues in the lungs Goblet cells CILIATED EPITHELIUM Ciliated epithelium Ciliated epithelium Role of each tissue TISSUE Cartilage Smooth Muscle Elastic Fibres Goblet cells and glandular tissue Ciliated epithelium ROLE WHERE IS IT FOUND Questions • Explain the importance of the cartilage found in the trachea and bronchi. • Describe the action of the cilia and mucus in helping to reduce the risk of infection • The action of smooth muscle and elastic fibres in the bronchioles can be described as antagonistic. Explain the meaning of this term using this example to illustrate your answer.