Review for DEC final
advertisement

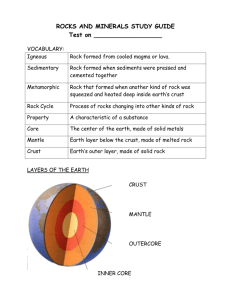
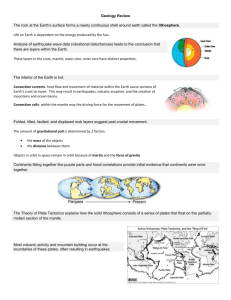
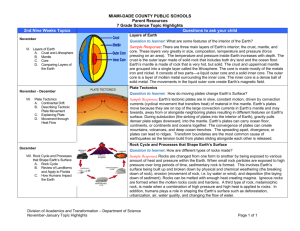
6th Grade Science Semester Exam Review The semester exam will consist of 40 questions (griddable or multiple choice) that reflect information covered in the first semester according to the list of topics below. In addition to knowing specific content, many of the questions require students to apply scientific investigation and reasoning skills to arrive at the answer. Students should be able to: Solar System describe the physical properties, locations, and movements of the Sun, planets, Galilean moons, meteors/meteoroids, asteroids, and comets understand that gravity is the force that governs the motion of our solar system describe the history and future of space exploration, including the types of equipment and transportation needed for space travel; o to describe: the International Space Station the Space Shuttle Endeavor the Hubble Space Telescope the Apollo 11 Rocket o know that the only place visited by man is the Moon Earth Layers of the Atmosphere Layers of Earth’s atmosphere (model) (TEK 6.10A) from the surface of the Earth up Troposphere - weather Stratosphere- jets Mesosphere- weather balloons Thermosphere-really hot Temperature and it filters out harmful radiation Exosphere- contains few atoms; there is no clear boundary between it and space. identify the structural layers of Earth, including the inner core, outer core, mantle, crust, asthenosphere, and lithosphere using a model Crust- outer shell of Earth Lithosphere- uppermost part of the mantle fused with the crust. Broken into about 30 plates Asthenosphere- the part of the mantle that has convection and causes plate movement, it is plastic like. Mantle- largest layer of the Earth Outer core- liquid layer of earth Inner core- solid, made mostly of iron. identify the major tectonic plates, including Eurasian, African, Indo-Australian, Pacific, North American, and South American differentiate between: o Divergent- plates that move____________________ Creates o Rift valleys turn into ocean basins which over time become o Mid ocean ridges o Convergent- plates that move____________________ Creates o Mountains Subduction- when a dense oceanic plate sinks under a continental plate Creates o Mountains o Volcanoes o transform boundaries- plates that move____________________ Creates o Earthquakes o Tsunamis describe how plate tectonics causes major geological events such as: o ocean basins o Earthquakes o volcanic eruptions o mid-ocean ridge o mountain building Rocks and Minerals Review Formation of Sedimentary Rocks and Fossil Fuels (TEK 5.7A) Sedimentary rock form through erosion, deposition, compaction and cementation. When dead layers of plants got compressed a loooong time ago the pressure turned the matter into organic rock like coal or fossil fuel like oil. Rock Cycle (TEK 6.10B) o by the processes of their formation, classify rocks as: metamorphic Igneous sedimentary Two types of igneous o Intrusive- formed when magma cools INSIDE the crust. Ex: Granite. o Extrusive- formed when lava cools on the earth’s surface. Ex: basalt. Three types of sedimentary o Detrital-made of grains of minerals or pieces of other rocks o Organic-form when living matter dies piles up and is compressed into rock like coal o Chemical-when water evaporates ex. stalactites Two types of metamorphic o Foliated- the minerals in the rock have been heated and squeezed into parallel layers. Ex: Slate. o Non-foliated-do not have distinct layers or bands Ex: marble. test the physical properties of minerals: o hardness - (especially be familiar with the Mohs Hardness Scale and testing minerals for hardness) o streak – the color of the mineral in powder form o Luster- the type of shine of the mineral. metallic opalescent dull o color Ecosystems describe air temperature, annual precipitation, number of producers, number of consumers, soil composition, etc. as biotic or abiotic parts of an ecosystem: o biotic- Bio (life) All living organisms abiotic- A(no or without) Bio (life) Plants without life, such as S. A. W. S.: Animals o Soil Bacteria Rocks Protista o Air Fungi o Water o Sunlight Temperature describe the levels of organization within an ecosystem: o o o o Organism– member of a single species in a given area Population- members of the same species in a region Community- different species in a region Ecosystem– all the communities in an area and the abiotic factors that affect them. Organism Population Community Ecosystem Classification understand that all organisms are composed of one or more cells recognize that the presence of a nucleus determines whether a cell is; o prokaryotic or eukaryotic identify the basic characteristics of organisms: o Prokaryotic-before nucleus, simple, not very complex, smaller, examples are eubacteria and archaebacteria o Eukaryotic- true nucleus, complex, larger, membrane bound organelles. Examples are euglena, body cells. o Unicellular – one celled organism, examples are all bacteria and the kingdom Protista o Multicellular- organisms made up of more than one cell. Examples are plants, animals, fungi.