Matter Test Review
advertisement

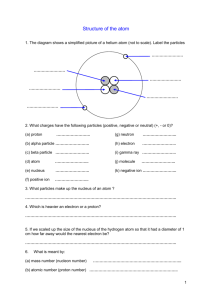
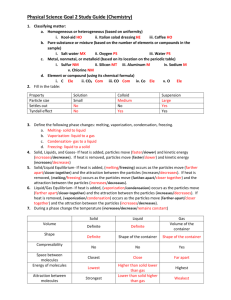
Matter Test Review Name _________KEY_______________________ 1. Fill out the following table comparing elements, compounds, and mixtures. Elements Compounds Define A substance that cannot be Two or more elements broken down into a simpler combined CHEMICALLY substance Represented Chemical symbol by 3 examples Hydrogen- H Oxygen- O Carbon- C Chlorine- Cl Sodium- Na Iron- Fe Mixtures Substances simply physically mixed together Chemical formula No symbol or formula Water- H2O Sodium Chloride- NaCl Iron Oxide- FeO Baking Soda- NaHCO3 Sugar- C12H22O11 Salad Saltwater Pizza Mountain dew cereal 2. Draw the basic structure of an atom and label the proton, neutron, nucleus, electron cloud, and electron. Be sure to include the charge of each particle. 3. Describe the relative mass of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons are both large (1 amu) and make up nearly 100% of the mass of an atom. Electrons are extremely small and have VERY little mass. 4. Draw a Na+2 ion. 11P 12N 5. What makes an ion have a charge? + charge= atom has lost electrons - Charge= atom has gained electrons 11 protons (+), 9 electrons (-)= +2 charge 6. What does it mean if an atom is neutral? It has the same number of protons (+) and electrons (-) and the charges cancel each other out. 7. DRAW and compare Hydrogen-1, Hydrogen-2, and Hydrogen-3 isotopes. H-1 H-2 H-3 1 proton 0 neutrons 1 electron 1 proton 1 neutron 1 electron 1 proton 2 neutrons 1 electron (total mass= 1 amu) (total mass= 2 amu) (total mass= 3 amu) 8. What makes an atom an isotope of an element? It has a different number of neutrons as listed on the periodic table (different mass) 9. List the 5 states of matter in order from greatest to least energy and give 2 properties of each. a. Greatest energy= plasma, so much energy that photons (light) is emitted. b. Gas- no fixed shape or volume/ particles bounce off each other and walls of the container/ particles move independently. c. Liquid- fixed volume, but take the shape of the container. Particles have enough energy to overcome some of the attraction between them and they flow past each other. d. Solid- fixed shape and volume. Particles vibrate in place and have a great attraction for each otherkeeps them locked in place. e. Least energy= Bose-Einstein- particles have so little energy that they coalesce and appear as one. Only occurs in laboratories at temperatures VERY close to absolute zero. 10. What does the Kinetic Molecular Theory say? All particles move! The more kinetic energy the particles have, the higher their temperature. 11. For gases… a. When the pressure of a gas increases, its temperature ___increases_____. b. When the temperature of a gas increases, its volume __increases__. c. When the volume of a gas increases, its pressure ___decreases____. 12. Describe what happens when energy is removed from a substance. When energy is removed from a substance, its particles slow down. When particles of a gas slow down, the gas can condensate into a liquid. When particles of a liquid slow down (lose thermal energy), they freeze into a solid. 13. Describe what happens when energy is added to a substance. When energy is added to a substance, its particles speed up. When particles of a solid speed up, they melt into a liquid. When you keep adding energy, the liquid can vaporize into a gas.