Exam Review Sheets
advertisement

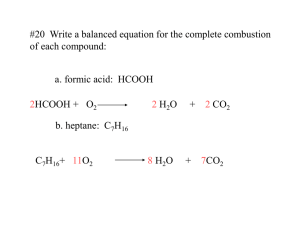
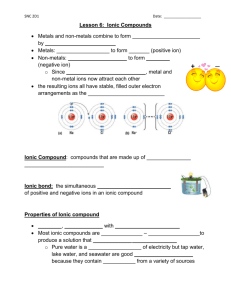
SNC 2D Exam Review June 2014 Chemistry Chapters 5, 6 and 7 identify/distinguish between a binary ionic compound, a polyatomic ionic compound and a molecular compound (see flow chart in notes) make the formula for a binary ionic compound, a polyatomic ionic compound and a molecular compound when given the name (see worksheets) name a binary ionic compound, a polyatomic ionic compound and a molecular compound when given the formula (see worksheets) write a word equation when given a sentence or explanation of a chemical reaction (see worksheets) write the skeleton/chemical equation when given the word equation (see worksheets) balance a skeleton/chemical equation (see worksheets) articulate/explain the reasons for the various formulas for compounds and how equations are balanced identify the following types of reactions synthesis, decomposition, single displacement, double displacement, complete combustion, incomplete combustion, corrosion, rusting, neutralization write examples of the following types of reactions synthesis, decomposition, single displacement, double displacement, complete combustion, incomplete combustion, corrosion, rusting, neutralization explain the law of conservation of mass. distinguish between an acid and base by what colour litmus paper / phenolphthalein changes. state the properties of an acid and those of a base. state similarities and differences between an acid and a base. identify an acid or a base by its chemical formula. name and write formula for binary acids, oxyacids and common bases use the pH scale to identify an acid, a base and neutral substance. use the pH scale to identify a weak or strong acid or base. use indicators to identity an acid, a base or neutral substance. neutralize an acid or a base spill safely. identify at least 3 practical uses of neutralization, combustion and corrosion reactions identify both hazards and safety precautions for neutralization, combustion and corrosion reactions Chapter reviews in text, unit review in text, class quiz and 3 class tests SNC 2D Exam Review June 2014 Biology Chapters 2, 3 and 4 state the basic unit of life and describe the general structure of a cell state the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells label a plant and animal cell state the function of the organelles label the parts of a microscope find and focus a specimen under low, medium and high power draw a good biological drawing of a specimen calculate the size of a specimen calculate the magnification of a biological drawing distinguish these types of cells – paramecium, onion skin cell, cheek cell, spirogyra cell describe the cell cycle state the purpose of mitosis describe the phases of mitosis apply the concept of mitosis to explain the theory of aging and cancer describe the hierarchy of structure in animal from atom to multicellular organism such as ourselves outline the event from fertilized egg to specialized cells describe the role of stem cells, both embryonic and adult label the human anatomy of the: skeleton, joint, bone, basic muscles, respiratory system, digestive system and circulatory system state the function of the: skeleton, joint, bone, basic muscles, respiratory system parts, digestive system and circulatory system parts describe the physiology of gas exchange and the systemic and pulmonary circuit of blood flow describe how the various systems interact to meet the needs of the whole organism state the 4 organs and 4 tissues of a plant; can you compare them to animals state the function of the organs and tissues of a plant label the basic anatomy of a plant – root, stem, leaves, flower Chapter reviews in text, unit review in text, microscope assignment, class test * NO test or quiz on cells, microscope, cell cycle, mitosis or plants SNC 2D Exam Review June 2014 Weather and Climate Change Chapters 8, 9 and 10 match the weather instrument to what is measures write a weather report to include as many weather measures as possible state what drives the weather state what causes weather distinguish between weather and climate label the layers of the atmosphere and state the significant characteristic of the layer describe how each of the following affect the climate: the atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere and living things distinguish the positive and negative role of ozone describe how latitude, elevation, proximity of large bodies of water can affect climate distinguish between weather of a low pressure system and high pressure system describe how convection currents are set up in both air and water make a climate graph and interpret the results describe the proxy records used to tell climate conditions of the past clearly and concisely state what the greenhouse effect is name three main greenhouse gases state how is CO2 and methane produced anthropogenically and naturally describe how carbon is cycled in the environment state the evidence that climate change is happening state possible impacts of climate change in the world state the concerns of climate change in the Canadian Arctic what can governments, industry and individuals do to lessen climate change what does Going Green refer to; give examples in travel, water, food and energy Chapter reviews in text, unit review in text, weather/climate test * NO test on Climate Change