151005110345_Triage_Manual
advertisement

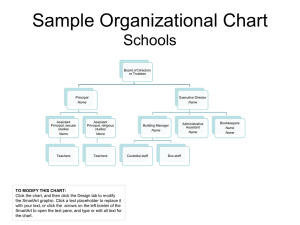
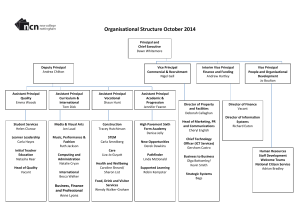
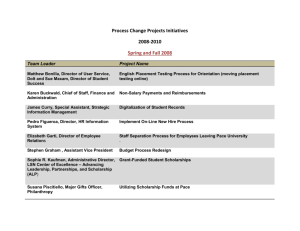
TRIAGE MANUAL 1 Triage Manual Cassandra McAvoy Bryant & Stratton College TRIAGE MANUAL 2 Table of Contents Topic Page No. Anaphylactic Reaction 4 Bleeding, Severe with Open Wound 5 Broken arm, probable 5 Burn, second degree 6 Chest Pain, Severe 7 Confusion, disorientation & slurred speech 8 Facial Paralysis, Partial 8 Fainting 9 Seizures, Myoclonic 9 Unresponsive, No pulse, No respirations 10 TRIAGE MANUAL 3 Table of Severity Severity Topic 1 Unresponsive, No pulse, No respirations 2 Anaphylactic Reaction 3 Severe Chest Pain 4 Severe Bleeding with Open Wound 5 Confusion, disorientation & Slurred speech 6 Partial Facial Paralysis 7 Myoclonic Seizures 8 Second degree burn 9 Fainting 10 Probable broken arm TRIAGE MANUAL 4 Actions Taken to Control an Emergency Some actions that are needed during an emergency are if the patient is conscious try getting information about symptoms to try and identify the problem. Always check for a universal emergency medical identification symbol, which is usually accompanied by an identification card which tells you what life threaten health problems the person has. Observe the patients skin color, size and dilation of the pupils. Also make sure to check pulses and blood pressures. Always make sure (Lindh, Pooler, Tamparo, Dahl, Morris, 2014). Anaphylactic Reaction Immediate Actions of the Medical Assistant If someone is having an anaphylactic reaction the medical assistant’s first action is to ask if he or she is carrying an epi pen to treat the reaction. Have the person lie still on their back and loosen any tight clothing they have on. Cover the person with a blanket and don’t give them anything to drink. Apply CPR if the person is not responsive. Seek further emergency treatment after an episode of anaphylaxis because it’s possible for it to recur (Mayo Clinic Staff 2015). Assess the Equipment, Supplies and Medication Necessary Equipment that is needed during the event of someone having anaphylactic reaction would be a blood pressure cuff and stethoscope. Epinephrine will be needed and also gloves while handling the patient. (Lindh, Pooler, Tamparo, Dahl, Morris, 2014). Post Emergency Patient Education Anaphylaxis is a severe disorder that can be life-threatening without prompt treatment. Symptoms usually get better with the right therapy, so it is important to act right away. A TRIAGE MANUAL 5 medical assistant could inform the patient he or she needs to wear an identification bracelet and to get a good epi pen that is not expired (U.S. National Library of Medicine. 2015). Bleeding, Severe with Open Wound Immediate Actions of the Medical Assistant In the case someone is bleeding severely with an open wound any dirt or debris should be removed from the wound. Never remove larger, deeply embedded objects from someone. Immediately stop the bleeding by applying pressure, once cleaned have person lie down and apply a bandage or tourniquet if necessary. Make sure to immobilize the part of the body that is injured once bleeding has stopped (Mayo Clinic Staff 2015). Assess the Equipment, Supplies and Medication Necessary For a severe bleeding open wound the medical assistant would need to use gauze or a bandage. Also they may need to use a tourniquet. Sterile bandages are going to be needed along with a clean cloth. Also they may need a clean dressing and sterile gloves (Mayo Clinic Staff 2015). Post Emergency Patient Education The medical assistant should instruct the patient to keep sharp objects or knives away or locked up. Also to keep them away from children, and to stay up to date with vaccinations like the tetanus immunization. The patient should be instructed to keep the wound clean with antibiotic creams and to change the sterile dressing daily (U.S. National Library of Medicine. 2015). Broken arm, probable TRIAGE MANUAL 6 Immediate Actions of the Medical Assistant Standard care for someone who has a broken arm is to keep the person still and calm and examine them for any other injuries. If the skin is broken it should be treated right away to prevent infection. Also if needed stabilize the broken limb with a splint or sling, and apply an ice pack to reduce pain and swelling. The medical assistant should also check the blood circulation to reduce damage to tissues from lack of blood (U.S. National Library of Medicine. 2015). Assess the Equipment, Supplies and Medication Necessary Equipment necessary or that could be used for a broken arm could be a sling or splint. Also an ice pack could be needed and possibly sterile bandages or solution. Gloves will be needed along with a sterile drape. Meds like Tylenol, and Advil may also be needed (U.S. National Library of Medicine. 2015). Post Emergency Patient Education Post patient education in this case would be to inform the patient to wear protective gear when doing or participating in contact sports. If young children are getting hurt protect the home by putting up gate and keeping windows closed. Also instruct the patient to keep the cast elevated to reduce swelling for 24-72 hours. Tell them to never put anything down the cast and to keep water out of the cast to prevent the skin from getting infected. (U.S. National Library of Medicine. 2015). Burn, second degree Immediate Actions of the Medical Assistant TRIAGE MANUAL 7 Immediate action that should be taken for a second degree burn is to cool the burn to help soothe the pain, remove any jewelry from burned area, and never break open the blisters. The medical assistant could apply aloe vera lotion or gel, or a small amount of hydrocortisone cream to the burned area with a sterile dressing (Mayo Clinic Staff 2015). Assess the Equipment, Supplies and Medication Necessary The medical assistant may need to use a sterile towel and nonstick sterile bandages. They may also need Aleve, Advil, or Motrin. (Mayo Clinic Staff 2015). Post Emergency Patient Education The medical assistant should inform the patient be careful around hot surfaces and to keep the pans with handle on them facing inward on the stove to prevent spilling. They should also tell them to check the smoke detectors in the house frequently and to keep lighters and flammables out of reach of children. The patient should be instructed to change the sterile dressing daily and to keep antibiotic creams on the wound (U.S. National Library of Medicine. 2015). Chest Pain, Severe Immediate Actions of the Medical Assistant The MA should ask questions like where the pain is, on a scale how would they describe the pain, and how does it happen or appear. Also find out how long the pain lasts, and make sure to ask the patient if they have taken any angina meds like nitroglycerin or any antacids. Also the MA will need to monitor the vital sings of the patient (U.S. National Library of Medicine. 2015). Assess the Equipment, Supplies and Medication Necessary TRIAGE MANUAL 8 Very limited supplies are needed for someone with chest pain although the medical assistant should use gloves and have a stethoscope and blood pressure cuff handy. Nitro might be needed if they have not taken some already, and chewable aspirins (U.S. National Library of Medicine. 2015). Post Emergency Patient Education Post emergency care should be to check up with his or hers physician, and to take any heart meds they may have or look into getting some. Tell the patient about any symptoms they may experience so they can try to catch it a head of time. Inform the patient they will have to make lifestyle changes like stopping smoking or changing diets (U.S. National Library of Medicine. 2015). Confusion, disorientation & slurred speech Immediate Actions of the Medical Assistant When someone comes in who is having a stroke the MA should react quickly and remembering to use FAST. FAST standing for face; does the face drop on one side while trying to smile, arms; is one arm lower than the other, speech; can a sentenced be repeated without strange or being slurred, and time; because every minute counts. As the MA vital sings should be monitored (Mayo Clinic Staff 2015). Assess the Equipment, Supplies and Medication Necessary Supplies needed would be a blood pressure cuff and stethoscope (Mayo Clinic Staff 2015). Post Emergency Patient Education TRIAGE MANUAL 9 The patient should be told to take post stroke rehabilitation to relearn any skills lost due to the stroke. The patient should also be informed as to what a stroke really is by telling them that a stroke is when the brain can’t get enough blood flow. (U.S. National Library of Medicine. 2015). Facial Paralysis, Partial Immediate Actions of the Medical Assistant The medical assistant should ask if both sides of the face have been affected and if he or she has recently been sick or injured. Also they should ask if they have had any symptoms like drooling or excessive tears from the eyes. The medical assistant should also monitor vital sings. (U.S. National Library of Medicine. 2015). Assess the Equipment, Supplies and Medication Necessary Gloves should be worn by the medical assistant while accessing the patient. A blood pressure cuff is needed along with a stethoscope (U.S. National Library of Medicine. 2015). Post Emergency Patient Education Post care should be to take any medications instructed by the doctor. Patient should also be informed of warning signs of a stroke which are sudden numbness in the face, arms, or legs. Also sudden confusion or blurred vision are signs of a stroke (U.S. National Library of Medicine. 2015). Fainting Immediate Actions of the Medical Assistant TRIAGE MANUAL 10 The medical assistant should take the blood pressure of the patient and keep them calm and relaxed. Also they should check the patient for heart arrhythmias (U.S. National Library of Medicine. 2015). Assess the Equipment, Supplies and Medication Necessary A blood pressure cuff will be needed along with a stethoscope and gloves. Smelling salt will also be needed (U.S. National Library of Medicine. 2015). Post Emergency Patient Education Instruct the patient to avoid doing things they know will trigger them to faint, also to get up slowly from a sitting or laying position to prevent from fainting (U.S. National Library of Medicine. 2015). Seizures, Myoclonic Immediate Actions of the Medical Assistant The medical assistant should immediately protect them from injury, and don’t restrict them. Also in a warm quiet room making sure the patient is at ease. Also the medical assistant should never put anything in the patient mouth (Mayo Clinic Staff 2015). Assess the Equipment, Supplies and Medication Necessary Gloves may be needed along with some seizure medications or injections to relive any symptoms (Mayo Clinic Staff 2015). Post Emergency Patient Education TRIAGE MANUAL 11 Post emergency patient education should be to use therapies like injections, and to further be checked out by a referred doctor. The patient should be taught on what a seizure is by telling them that a seizure is an uncontrolled activity of the brain (Mayo Clinic Staff 2015). Unresponsive, No pulse, No respirations Immediate Actions of the Medical Assistant Immediately look for responsiveness, if there is no responses perform CPR after laying the person on their back. Open the airway and check the chest for movement (U.S. National Library of Medicine. 2015). Assess the Equipment, Supplies and Medication Necessary An AED will be needed along with the regular PPE’s. Also needed will be a blood pressure cuff and stethoscope. Post Emergency Patient Education Patient post emergency education should be to avoid activities that can cause or lead to cardiac arrest. Exercise should be cooperated into the patient’s daily routine and should be referred to see a doctor regularly. Also to avoid using any illegal drugs. A heart attack is similar and happens when the vessels in the heart become blocked (U.S. National Library of Medicine. 2015). Scope of Practice of the MA in the Emergency As a medical assistant my scope of practice allows me to give vital signs, perform ECG’s, taking laboratory specimens and blood work. In my scope of practice as a Medical Assistant I can make TRIAGE MANUAL 12 sure the patient is comfortable and relaxed and apply any bandages to wounds that may need it. Making sure to keep the patient calm until the doctor or physician has arrived (American Association of Medical Assistants. 2015). TRIAGE MANUAL 13 References American Association of Medical Assistants. (2015). State Scope of Practice Laws. Retrieved from: http://www.aama-ntl.org/employers/state-scope-of-practice-laws Lindh, W.Q. Pooler, M.S. Tamparo, C.D. Dahl, B.M. Morris, J.A.(2014). Delmar’s Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administration and Clinical Competencies(5th). Clifton Park, NY: Cengage Learning. Mayo Clinic Staff (2015). First aid. Retrieved from: http://www.mayoclinic.org/first-aid/firstaid-severe-bleeding/basics/art-20056661 U.S. National Library of Medicine. (2015). First aid. Retrieved from: http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/000045.htm