Midterm Study Guide Modified
advertisement

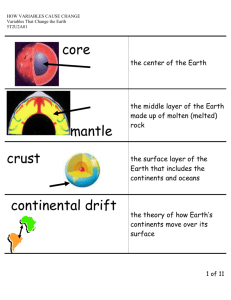
Name _______________________________ Midterm Study Guide-Test __________ Complete and know the following terms: Rocks/Minerals: Mineral Coarse grained- the grains in a rock are large and easy to see. Igneous rock Metamorphic rock Rock cycle Organic rock Fossils: Trace fossil Fossil-trace of an ancient organism that has been preserved in rock Erosion/Deposition: Erosion Deposition Mass movement Beach-wave-washed sediment along a coast; formed from deposition of waves Mudflow- the rapid downhill movement of a mixture of water, rock, and soil. Plate Tectonics: Lithosphere-rigid layer made up of the uppermost part of the mantle and the crust Subduction-oceanic crust sinks beneath a deep-ocean trench and back into the mantle at a convergent plate boundary Plate tectonics- the theory that pieces of Earth’s lithosphere are in constant motion, driven by convection currents in the mantle Crust-the thinnest layer of rock that forms at Earth’s outer surface Transform boundary- a plate boundary where two plates move past each other in opposite directions Sea floor spreading- the process by which molten material adds new oceanic crust to the ocean floor Strike slip fault-rocks on either side move past each other sideways with little up-or-down motion Earthquakes: Richter scale Seismograph Tsunami Weathering: Weathering-chemical and physical processes that break down rock at Earth’s surface Oxidation Chemical weathering Mechanical weathering Soil and Soil Conservation: Humus Decomposers B horizon Soil conservation-the management of soil to prevent its destruction Conservation plowing-soil conservation method in which the dead stalks from the previous year’s crop are left in the ground to hold the soil in place and keep moisture Complete and know the following information: Rocks/Minerals: Hardest mineral Softest mineral How rocks and minerals are related What crust is made of Heat to form metamorphic rock comes from Most useful metamorphic rocks Process to create sedimentary rock Fossils: What part of organism is preserved as fossils What fossil record shows Age of layers of rock (Law of superposition) Plate Tectonics: Order of layers of Earth How scientists study interior of earth How temperature changes as you go from crust to core How density changes as you go from crust to core Process of convection currents Why continental drift theory was rejected Why plates move Landforms found at a convergent boundary Where Earth’s magnetic field comes from Where mid ocean ridges are found Subduction creates which rock Volcanoes: Where volcanoes are found Where magma comes from Formation of Hawaiian Islands Weathering: Examples of mechanical weathering When wind deposits sediment Why/How limestone is easily eroded Soil and Soil Conservation: How soil forms Why soil is valuable How erosion will affect bare land How to slow down erosion of soil on flat land