Midterm study guide
advertisement
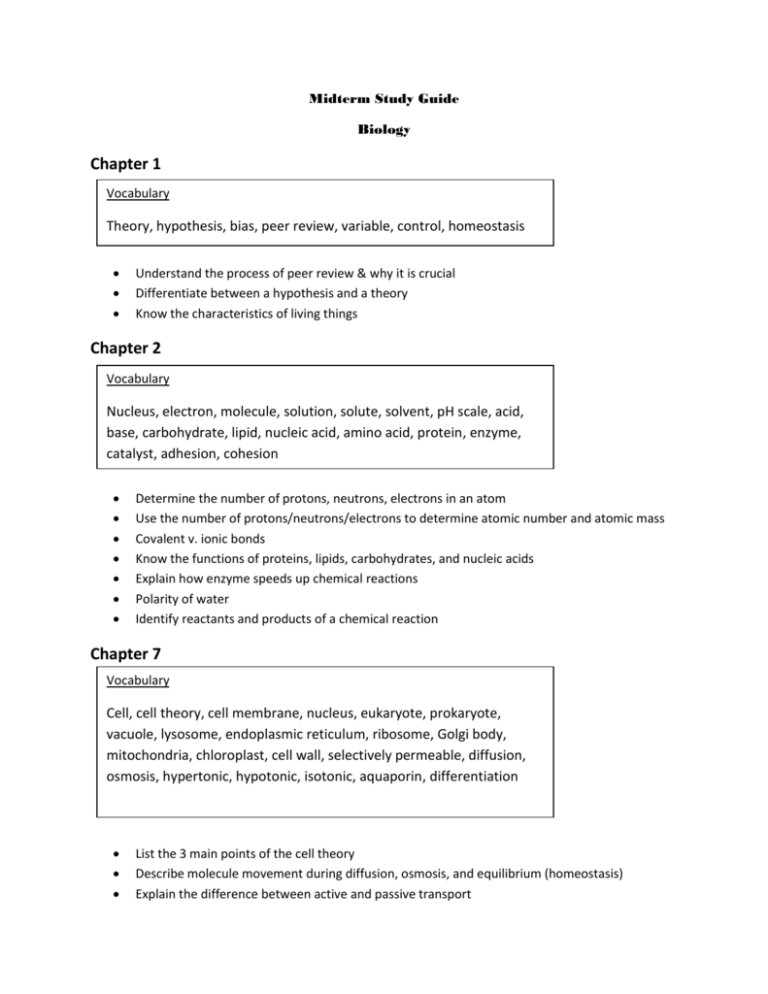
Midterm Study Guide Biology Chapter 1 Vocabulary Theory, hypothesis, bias, peer review, variable, control, homeostasis Understand the process of peer review & why it is crucial Differentiate between a hypothesis and a theory Know the characteristics of living things Chapter 2 Vocabulary Nucleus, electron, molecule, solution, solute, solvent, pH scale, acid, base, carbohydrate, lipid, nucleic acid, amino acid, protein, enzyme, catalyst, adhesion, cohesion Determine the number of protons, neutrons, electrons in an atom Use the number of protons/neutrons/electrons to determine atomic number and atomic mass Covalent v. ionic bonds Know the functions of proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids Explain how enzyme speeds up chemical reactions Polarity of water Identify reactants and products of a chemical reaction Chapter 7 Vocabulary Cell, cell theory, cell membrane, nucleus, eukaryote, prokaryote, vacuole, lysosome, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosome, Golgi body, mitochondria, chloroplast, cell wall, selectively permeable, diffusion, osmosis, hypertonic, hypotonic, isotonic, aquaporin, differentiation List the 3 main points of the cell theory Describe molecule movement during diffusion, osmosis, and equilibrium (homeostasis) Explain the difference between active and passive transport Compare plant/animal cells Compare prokaryotic/eukaryotic cells Predict what will happen to a cell when placed in hyper/hypo/isotonic environments Chapter 10 Vocabulary Chromosomes, cyclin, apoptosis, cancer, tumor, centromere, (sister) chromatid, interphase, mitosis, cytokinesis, metastasis, angiogenesis List the 3 phases of the cell cycle List the stages of mitosis in order & the events of each Explain how cytokinesis differs in plants and animals Identify the stages of the cell cycle in pictures Label the parts of a replicated chromosome Explain why cancer occurs Cancer treatment & tumor types Chapter 11 Vocabulary Fertilization, allele, gamete, homozygous, heterozygous, phenotype, genotype, codominance, incomplete dominance, polygenic, meiosis, crossing-over, homologous chromosomes, karyotype, dihybrid, haploid, diploid Predict the outcomes of a genetic cross using a Punnett square o Complete dominance, incomplete dominance, multiple alleles (blood-type), sex-linked, and dihybrid crosses! List the genotypes and phenotypes of an organism Know the genotypes for each blood type Universal donor and recipient Compare/contrast mitosis and meiosis Explain why crossing over is important and during which phase it occurs