A theory that about the behavior
advertisement

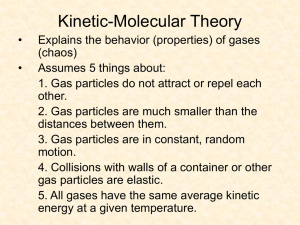
Key HOMEWORK for Chapter 11: Gases 11.1 Properties of Gases (Read pgs. 327 - 330 in the chemistry textbook) 11.2 Gas Pressure (Read pgs. 330 - 332 in the chemistry textbook) 1. What is the Kinetic Molecular Theory (KMT) of Gases? A theory that about the behavior of gas particles: 5 tenets (principles) 2. I. Small, random movement, high velocity II. VERY small IMFs (often considered nonexistent) III. Average EK is proportional to Kelvin temperature IV. Volume occupied by the individual gas particles is VERY small (considered negligible) V. Constant motion, straight-line paths What are the 4 gas properties and their units? PROPERTIES UNITS I. Pressure (P) atmospheres (atm) Torricelli (torr) millimeters of mercury (mmHg) Pascals (Pa) kilopascals (kPa) II. Volume (V) Liters (L), milliliters (mL) III. Temperature (T) Kelvin (K) IV. Amount in moles(n) moles (n) 1 3. Explain each of the 4 gas properties. PROPERTIES Explanation Gas Pressure the force of the collisions of gas molecules with the walls of the container Atmospheric pressure the force of the collisions of the gas molecules making up the atmosphere with whatever they touch more collisions = more pressure less collisions = less pressure Volume the space occupied by the gas – if the gas is in a container the volume of the gas is equal to the volume of the container Temperature determines the average EK and therefore the number of collisions of the particles Amount the quantity of gas present in the container 2 4. Use the KMT to explain why a gas completely fills a container of any size and shape. Gas particles are constantly moving at high speeds in random, but straight-line directions. They would travel indefinitely if nothing stopped them. Eventually they encounter the walls of the container – at which point the volume being occupied by all the gas particles is equal to the volume of the container 5. Identify the property of a gas that is described by each of the following: Temperature a) increases the EK of gas particles Pressure b) the force of the gas particles hitting the walls of the container Volume c) the space that is occupied by a gas 6. Use the KMT to explain each of the following: (a) Gases move faster at higher temperatures. the average EK of a gas is proportional to the Kelvin temperature – as T↑ so does the average EK of the gas particles (b) Gases can be compressed more easily than liquids or solids. individual gas particles are considered to occupy NO space, and to be very far apart (c) Gases have low densities. the IMFs between individual gas particles is considered negligible – so the particles are free to move away from one another – less mass per unit of space = lower density (d) A container of nonstick cooking spray explodes when thrown into a fire. at higher temperatures the gas particles collide more often with the walls of the container – eventually the number of collisions creates a pressure greater than can be borne by the walls of the container – so it “explodes” 3 6. Continued: (e) The air in a hot-air balloon is heated to make the balloon rise. the higher temperature inside the balloon makes the gas particles move away from each other so that the gas inside the balloon is less dense than the gas of the surrounding atmosphere (f) You can smell the odor of cooking onions from far away. gas molecules move at very high velocities in random, straightline directions – eventually they will fill the entire house (or even the entire outside area surrounding a bakery) 7. Identify the property of a gas that is measured in each of the following. Temperature a) 350 K Volume b) the space occupied by a gas Amount c) 2.00 mole of O2 Pressure d) the force of gas particles colliding with the walls of the container Temperature a) 425 K Pressure b) 1.0 atm Volume c) 10.0 L Amount d) 0.50 mol of He 4 8. What is the definition of pressure? the force acting on a certain area Pressure (P) = 𝑭𝒐𝒓𝒄𝒆 𝑨𝒓𝒆𝒂 9. What is a barometer? a device used for measuring atmospheric pressure 10. How does a barometer work? The pressure of the earth’s atmosphere pushing down on the surface of the mercury in the open dish will “push” the mercury a certain height up the evacuated tube. The greater the pressure of the atmosphere the higher up the tube the mercury will be pushed – and vice versa. The units used to measure the height of the column can vary with the type of liquid in the barometer and the measurement system being used. At STP the earth’s atmosphere will push a column of mercury up 760 millimeters – o r – 760 mmHg 5 11. What is STP? Standard Temperature and Pressure at sea level Standard Temperature = 0oC, or 273 Kelvin Standard Pressure = 1 atm this means that at sea level, when the temperature is 0oC the pressure of the earth’s atmosphere is defined as 1 atmosphere 12. Why isn’t standard pressure 760 mmHg? IT IS!!!! Standard pressure is measured in many different units, but it is customary (and simpler) to use “atmospheres” because it equals 1 13. What are some other “units” of standard pressure? Units Abbreviation 1 atmosphere 1 atm 760 millimeters of mercury 760 mmHg 29.9 inches of mercury 29.9 in. Hg 760 torricelli 760 torr 101,325 Pascal 101,325 Pa* 101.325 kilopascal 101.325 kPa 14.70 pounds per square inch 14.70 lb/ in2 * The official SI unit of pressure 6 14. Is atmospheric pressure the same at all location on Earth? Explain. NO The pressure is greatest at the lowest spots on Earth and least at the highest spots. Example: top of Mt. Everest ≈ 20,500 ft above sea level ≈ 33 kPa bottom of Death Valley = 282 ft below sea level ≈ 105 kPa 15. Why does the height of a column of mercury in a barometer change from day to day? b/c the atmospheric pressure changes day to day on days with higher atmospheric pressure the column is higher, and vice-versa 16. Water is cheaper and safer to use than mercury, and, it will rise and fall with daily changes in atmospheric pressure. Why aren't barometers commonly made out of water? HINT: Mercury is approximately 13.5 times more dense than water. 29.9 inches × 13.5 = 403.65 inches ÷ 𝟏 𝐟𝐭 𝟏𝟐 𝐢𝐧𝐜𝐡𝐞𝐬 = 33.6 ft a water barometer would have to be over 30 foot tall!! 7 17. An oxygen tank contains oxygen (O2) at a presure of 2.00 atm. What is the pressure in the tank in terms of the following units? (a) torr 2.00 atm ( 𝟕𝟔𝟎 𝐭𝐨𝐫𝐫 𝟏 𝐚𝐭𝐦 ) = 1520 torr (b) kPa 2.00 atm ( 𝟏𝟎𝟏.𝟑𝟐𝟓 𝐤𝐏𝐚 𝟏 𝐚𝐭𝐦 ) = 203 kPa (c) mmHg 2.00 atm ( 𝟕𝟔𝟎 𝐦𝐦𝐇𝐠 𝟏 𝐚𝐭𝐦 ) = 1520 mmHg (d) lb/in2 𝐥𝐛 2.00 atm ( 𝟏𝟒.𝟕𝟎 𝟐 𝐢𝐧 𝟏 𝐚𝐭𝐦 𝒍𝒃 ) = 29.4 𝒊𝒏𝟐 17. On a climb up Mt. Whtney, the atmospheric pressure drops to 467 mmHg. What is the pressure in terms of the following units? (a) atm 𝟏 𝐚𝐭𝐦 467 mmHg ( 𝟕𝟔𝟎 𝐦𝐦𝐇𝐠 ) = 0.614 atm (b) torr 𝟕𝟔𝟎 𝐭𝐨𝐫𝐫 467 mmHg ( 𝟕𝟔𝟎 𝐦𝐦𝐇𝐠 ) = 467 torr (c) Pa 𝟏𝟎𝟏,𝟑𝟐𝟓 𝐏𝐚 467 mmHg ( 𝟕𝟔𝟎 𝐦𝐦𝐇𝐠 ) = 62, 300 Pa (d) in. Hg 𝟐𝟗.𝟗 𝐢𝐧.𝐇𝐠 𝒍𝒃 467 mmHg ( 𝟕𝟔𝟎 𝐦𝐦𝐇𝐠 ) = 18.4 𝒊𝒏𝟐 8