Pressure and Phase Changes
advertisement

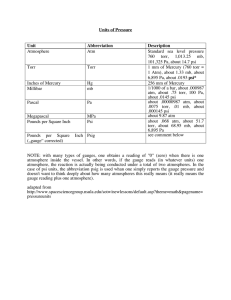
Pressure and Phase Relationships Ch. 13 States of Matter Fahrenheit, Celsius and Kelvin • Fahrenheit based on reference temperatures of brine solution at 0 and in mouth at 96 or wife’s armit • Celsius based on freezing pt and boiling point of water] F = 1.8C + 32 • Kelvin based upon absolute zero and no negative values K = C + 273 Pressure • Pressure: Defined as force per unit area caused by gas molecules colliding with surface • P = F/A • 1 Pa = 1 N/m2 Temperature: defined as a measure of the AVERAGE kinetic energy of a substance (this means that some molecules are moving faster than average and some slower than average) Liquid-Vapor Equilibrium The temperature and pressure at which equal amounts of high energy liquid molecules A are escaping to become vapor and vapor molecules B are being slowed down and trapped at surface to return to liquid Barometer (or manometer) measures pressure • SI unit is the pascal (1 Pa = 1 N/m2) or kilopascal kPa • Meteorologists (weather) like mmHg, the height the atmospheres pressure pushes a liquid column upward (more dense liquids don’t get pushed as high and Hg is very dense) • mmHg are also called Torrs, so 1mmHg = 1Torr Gas molecules in the atmosphere • A standard atmosphere (atm) of pressure is defined as typical air pressure at earth mean sea level Pressure conversions 1 atmosphere is a measure of the normal pressure at sea level 1 atm = 101.3kPa = 101,300 Pa = 760 mmHg = 760 Torr = 14.7 psi • This means 760mmHg = 14.7psi and 101.3kPa = 760 Torr as well A typical atmospheric pressure in Fort Collins CO might be 690 mmHg. Convert this to atmospheres of pressure. 690mmHg x 1 atm = 0.91 atm 760mmHg Convert the same pressure above into both psi and Torr 13.3 psi and 690 Torr Phase Diagram of Water