Name

Name: ___________________________________ Date: __________________ Period: _____
Review Chemistry I Unit 11: Kinetic-Molecular Theory and Gases
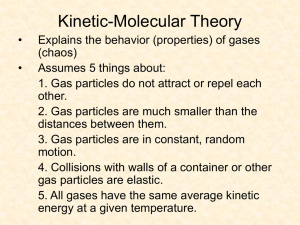
1. Write the 3 main parts of Kinetic-Molecular Theory (KMT) a) __________________________________________________________________ b) __________________________________________________________________ c) __________________________________________________________________
2. List the 3 states of matter in order of decreasing kinetic energy. (highest to lowest)
1) _______________ 2) ________________ 3) _________________
3. What happens to the kinetic energy of a gas as it is heated? ______________________
4. What is temperature? ______________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
5. Which has particles that are moving at 0 o C? (circle all that are correct)
A. solid iron B. liquid iodine C. ammonia vapor
Which has the greatest average kinetic energy?
D. hydrogen gas
A. solid copper at –50 C
B. solid steel at 20 C
C. oxygen gas at 25 C
D. water vapor at 100 C
Choice ____ because __________________________________________________
6. What is the temperature at which there is absolutely NO motion of particles?
It’s called ___________________________ at ______ K or ______ o C.
7. What causes gas pressure? __________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
1
8. Why are gases compressible, but liquids and solids are not? _______________________
_______________________________________________________________________
9. Why does adding more of a gas to a container increase the pressure in the container?
________________________________________________________________________
10. What happens to gas pressure if its volume is decreased? increase or decrease
What happens to the volume of a gas if the pressure is increased? increase or decrease
11. What happens to the volume of a gas if the temperature is increased? increase or decrease
What happens to the temperature of a gas if the volume is increased? increase or decrease
12. List 3 variables and how you could change them to increase the pressure of a gas. a) _________________________________________ b) _________________________________________ c) _________________________________________
Calculations: SHOW WORK for credit & BOX your ANSWER with UNIT
( ALL temperatures MUST be in K , NOT o C )
13. Write the Combined Gas Law equation in the box:
14. What does STP stand for? __________________________________________________
What are the values of STP? ___________ and ___________
2
15. Write the equation to convert Celsius temperature ( o C) to Kelvin (K).
Convert 25.0
o C to K
16. 1 atm = _____ mmHg = ______ kPa
Convert 2.50 atm to mmHg
Convert –86.0
o C to K
Convert 125 kPa to atm
Calculations: SHOW WORK for credit & BOX your ANSWER with UNIT
( ALL temperatures MUST be in K , NOT o C )
17. A gas at 285 K and a volume of 1.28 L is heated to 335 K. What is the new volume is pressure is held constant?
18. 2.00 L of a gas at 2.58 atm is compressed to a volume of 1.20 L. What is the pressure if the temperature is constant?
19. A gas at 25.0
o C and 760 mmHg is cooled to 0.00
o C. What is the pressure if the volume is held constant?
OVER
3
Calculations: SHOW WORK for credit & BOX your ANSWER with UNIT
( ALL temperatures MUST be in K , NOT o C )
20. 35.0L of a gas at 303 K and 1.00 atm . How many moles are present?
21. A gas at 20.0
o C is stored in a 100.mL tank at 546kPa atm. How many moles are present?
22. 5.00 L of a gas at
–15.8
o C and 745 mmHg is stored in a flexible container. What is the volume at STP?
23. A gas is at 855 mmHg in a 10.0 L container at 25.0
o C. When the gas is compressed to
1.00 atm in a 2.00 L container, what is the new temperature in o C ?
4
[ANSWER KEY]
Review Chemistry Unit 13: Kinetic-Molecular Theory and Gases
1. Write the 3 parts of Kinetic-Molecular Theory (KMT) a) gas particles are tiny compared to the distance between them so they take up no space b) gas particles are in constant , random , rapid motion
2. c) all collisions between gas particles are perfectly elastic and do not lose energy
Write the 3 states of water in order of decreasing kinetic energy. (high to low)
1) Gas 2) Liquid 3) Solid
5.
3.
4.
What happens to the kinetic energy of a liquid as it is heated? increases
Define temperature. avg.
KE measure of average
of a substance is proportional
Which has particles that are moving 0 solid iron liquid iodine o kinetic
to the energy of particles of a substance. temperature
C? (circle any that are correct) ammonia vapor hydrogen gas
Choice _D_ because the higher temperature is directly proportional to higher avg KE and a gas has more kinetic energy than a liquid or a solid.
6.
7.
8.
What is the temperature at which there is absolutely NO motion of particles?
It’s called absolute zero at 0 K
What causes gas pressure? collisions of gas particles with walls of the container
Why are gases compressible, but liquids and solids are not? b/c of the great amount of space between the particles (it allows them to be pushed closer together)__________
9. Why does adding more of a gas to a container increase the pressure in the container? more collisions with the walls of the container
10. What happens to gas pressure if its volume is decreased? increase or decrease
What happens to the volume of a gas if the pressure is increased? increase or decrease
5
11. What happens to the volume of a gas if the temperature is increased? increase or decrease
What happens to the temperature of a gas if the volume is increased? increase
12. List 3 variables you could change to cause the pressure of a gas to increase. or decrease a) b) c) increase the number of particles (add more gas) decrease the volume (compress it) increase the temperature
13. Write the Combined Gas Law equation in the box:
P
1
V
1
= P
2
V
2
T
1
T
2
14. S tandard T emperature and P ressure
273 K and 1.00 atm
15. K = o
C + 273
Convert 25.0
o
C to K
298 K
Convert –86.0 o
C to K
187 K
16. 1 atm = 760 mmHg
Convert 2.50 atm to mmHg
1900 mmHg
Convert 125 kPa to atm
1.23 atm
6
Calculations: SHOW WORK for credit & BOX your ANSWER with UNIT
( ALL temperatures MUST be in K , NOT o C )
17. 1.50 L
18. 4.30 atm
19. 696 mmHg (or 0.916 atm)
20.
21.
22. 5.20 L
23.
–220 o
C
P
1
V
1
= P
2
V
2
T
1
T
2
7