Energy in Ecosystems Web Activity
advertisement

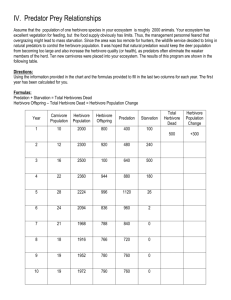
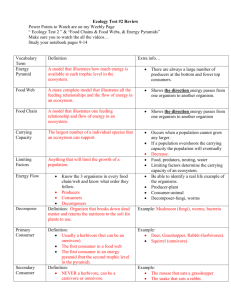
Date ______ Energy in Ecosystems Name ____________________ Go to http://www.learner.org/courses/envsci/interactives/ecology/producers.php and open simulator. Part 1: The Producers Competition Imagine the ecosystem is newly forming—the previous ecosystem has been destroyed by fire or flood—and the first colonizers of the successive ecosystem are, of course, producers. Given the two species of plants in the simulator (Plant A & Plant B), predict what will happen in this young system. Then run the simulator to 100 time steps and record the population numbers for both plants. 1. Describe what happened to the populations of Plant A and Plant B by the end of the simulation. _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 2. Explain why one species of plant may be more successful than another species of plants. _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ Part 2: Primary Consumers Reset the simulator. Now you'll introduce an herbivore into the environment. In theory, an herbivore native to the ecosystem should feed primarily on the dominant species. In this system, the herbivore may consume enough of the dominant species to give the non-dominant species a chance for proliferation and survival. Click on herbivore A (the rabbit) and choose "eats plant A." Predict and record what will happen to the population numbers in the ecosystem. Then, run the simulator and record your results. 3. Record your results in the space below. Date ______ Energy in Ecosystems Name ____________________ 4. Looking at the graph above, what happens to the plant populations when the rabbit population is at _____________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ its highest point? 5. Why must the rabbit population always be less than the population of plants A and B? _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 6. Explain why adding an herbivore is necessary for Plant B to survive. _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ Part 3: Food Chains Choose only one organism from each trophic level and make sure that the food chain goes in a straight line from one trophic level to the next, i.e., Herbivore A eats Plant A, Omnivore A eats Herbivore A, and the Top Predator eats Omnivore A. Run the simulator to see how the population changes after 100 time units. 7. Record your results in the space below. 8. What trend did you see when looking at the population size and the trophic level of each organism? _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 9. Remove the top predator from this food chain and re-run the simulation. Did the top predator have a large effect on other populations? Explain. _____________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ Energy in Ecosystems Date ______ Name ____________________ 10. What would happen to this imaginary ecosystem if the producers were to die out? _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ Part 4: Food Webs Now try a more "real-life" scenario and experiment with what might happen in an ecosystem that is more like a food web. This time click the "all on" button. The model shows who eats who and the paths by which energy is transferred. Run the simulation once and record the results in your Data Table. (HINT: move your cursor over the lines on the graph to show the exact population size) 11. Complete the data table. Species Ending Population 12. Why do you think that the ominvores were unable to survive? Plant A Plant B Plant C 13. Why do you think that Plant C was unable to survive? Herbivore A Herbivore B Herbivore C Omnivore A 14. Explain why the top predator was able to survive even after both omnivores died out? Omnivore B Top Predator Part 5: Creating a food web Use the simulator to create a food web where every organism survives. Use lines to show the feeding relationships in the diagram.