PA Mammals
advertisement

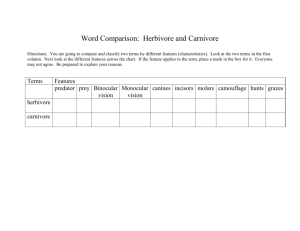
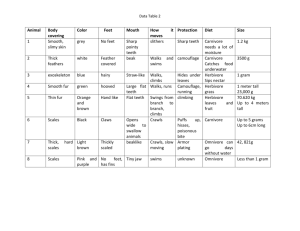
PA Mammals Envirothon 2011 Predator • A predator is an animal that feeds on other animals in order to survive. • Some examples would be bears, coyotes, snakes • Some predators can also be prey as well, like sometimes lions eat other lions • Most of the time predators herbivore Prey • Prey are the animals eaten to keep other animals alive. • More often then not the animals eaten are herbivores. • Some examples of prey are bunnies, mice, and fish. Autotrophs v. Heterotrophs • Autotrophs – Produce food from the sun • Heterotroph – Must eat other things (living or non living) for energy Carnivore • Animals that eat meat, mostly other animals that are smaller than they are or less fierce. • Some examples of carnivores – Bobcats – Coyotes – Owls – Praying mantis Herbivores • Herbivores are animals that eat plants and greens such as leaves and grass. • When herbivores eat it is usually called grazing. • An example of an herbivore would be a rabbit or goat. Omnivore • An omnivore is an animal that eats plants and other animals. • An example of an omnivore would be a bear because a bear eats berries and fish. Food Chain • The food chain is the order in which the animals eat or are eaten. FOOD CHAINS AND FOOD WEBS - illustrate the flow of energy in an ecosystem *Note the direction of the arrows: they indicate where the energy is going when one organism consumes another Each step in a chain or web is called a TROPHIC LEVEL . Identify: Autotroph Primary Consumers Secondary Consumers Tertiary Consumers Find the Omnivore • Autotroph Identify – Two sets of leaves • Primary consumer – Mouse, cricket, rabbit, squirrel • Secondary consumer – Fox, mouse, frog, snake • Tertiary consumer – Fox, owl, snake • Omnivore – mouse Ecological Pyramids Energy Pyramid Biomass Pyramid Pyramid of Numbers Mammal • Mammals (formally Mammalia) are a class of vertebrate, air-breathing animals whose females are characterized by the possession of mammary glands while both males and females are characterized by hair and/or fur, three middle ear bones used in hearing, and a neocortex region in the brain. Some mammals have sweat glands, but most do not. Give birth to live young. Endangered • Pose a threat to go extinct. • Some endangered animals are – Gray wolf, Mexican bobcat, West Indian Manatee, and the jaguar. Extinct • No longer in existence. • Some animals that are extinct are – Barbados Raccoon, Bulldog rat, and Dark flying fox. Why animals go extinct or become endangered. • • • • • • • Loss of habitat Low food source Not enough room to live Poachers Pollution Killed of by other animals Disease Major causes of habitat loss in Pa. • • • • • • • Deforestation Water pollution Mining Logging Trawling- when boats use nets to catch fish. Urban sprawl- when cities get bigger Noise pollution How we can help. • • • • • • • • Reduce Reuse Recycle Refuse Car pool Turn off lights when not in use. Use energy saving light bulbs. Reuse unbleached recycled paper. Adaptations • Usually related to the food they eat – Teeth – Feet – Muscular system – Eyes/eyesight Teeth adaptations 1.Human – omnivore 2.Herbivore 3.Carnivore 4.Carnivore 5.Herbivore