File
advertisement
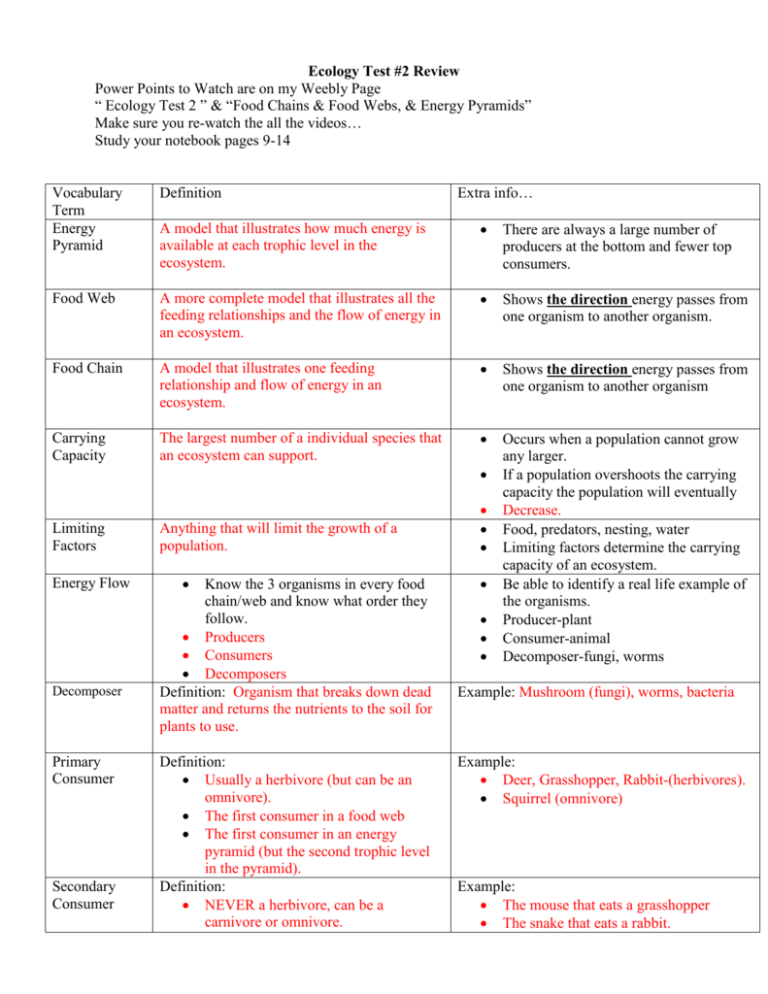
Ecology Test #2 Review Power Points to Watch are on my Weebly Page “ Ecology Test 2 ” & “Food Chains & Food Webs, & Energy Pyramids” Make sure you re-watch the all the videos… Study your notebook pages 9-14 Extra info… Vocabulary Term Energy Pyramid Definition A model that illustrates how much energy is available at each trophic level in the ecosystem. There are always a large number of producers at the bottom and fewer top consumers. Food Web A more complete model that illustrates all the feeding relationships and the flow of energy in an ecosystem. Shows the direction energy passes from one organism to another organism. Food Chain A model that illustrates one feeding relationship and flow of energy in an ecosystem. Shows the direction energy passes from one organism to another organism Carrying Capacity The largest number of a individual species that an ecosystem can support. Occurs when a population cannot grow any larger. If a population overshoots the carrying capacity the population will eventually Decrease. Food, predators, nesting, water Limiting factors determine the carrying capacity of an ecosystem. Be able to identify a real life example of the organisms. Producer-plant Consumer-animal Decomposer-fungi, worms Limiting Factors Energy Flow Decomposer Primary Consumer Secondary Consumer Anything that will limit the growth of a population. Know the 3 organisms in every food chain/web and know what order they follow. Producers Consumers Decomposers Definition: Organism that breaks down dead matter and returns the nutrients to the soil for plants to use. Definition: Usually a herbivore (but can be an omnivore). The first consumer in a food web The first consumer in an energy pyramid (but the second trophic level in the pyramid). Definition: NEVER a herbivore, can be a carnivore or omnivore. Example: Mushroom (fungi), worms, bacteria Example: Deer, Grasshopper, Rabbit-(herbivores). Squirrel (omnivore) Example: The mouse that eats a grasshopper The snake that eats a rabbit. The second consumer in a food web. The second consumer in an energy pyramid (but the third trophic level in the pyramid) Tertiary Consumer Definition: NEVER a herbivore, can be a carnivore or omnivore. The third consumer in a food web. The third consumer in an energy pyramid (but the fourth trophic level in the pyramid) Apex Predator Definition: Top predator, no one eats this organism. Energy Pyramid Example: The snake that eats the mouse that eats a grasshopper The Hawk that eats the snake that eats a rabbit. Where do the organisms in the first trophic level get their energy from? Sun How much energy from the sun is passed on in each trophic level? 10% Which trophic level is most important? Producer Which is the largest level and why? Producer because they make all the energy for the ecosystem. Exponential Growth Shows… HOW MUCH energy is available. Definition: Populations that grow fast at a constant rate. Occurs when there are (few limiting factors) If the producer level has 9000 kcal… How much does level 2 have? 900 How much does level 3 have? 90 How much does level 4 have? 9 Energy Pyramid Energy Pyramid Why is there usually only one apex predator in an ecosystem? Because there is not enough energy for more than one. Label the organisms in each level A. tertiary consumer B. secondary consumer Be able to identify examples of each type of organisms. A. hawk B. snake C. primary consumer D. producer Biotic Potential Definition: An organism’s ability to reproduce under ideal conditions. C. grasshopper D. plants Occurs when there are (few limiting factors)