Animal Physiology - Chapters 48, 43, 11 Animals employ a number
advertisement
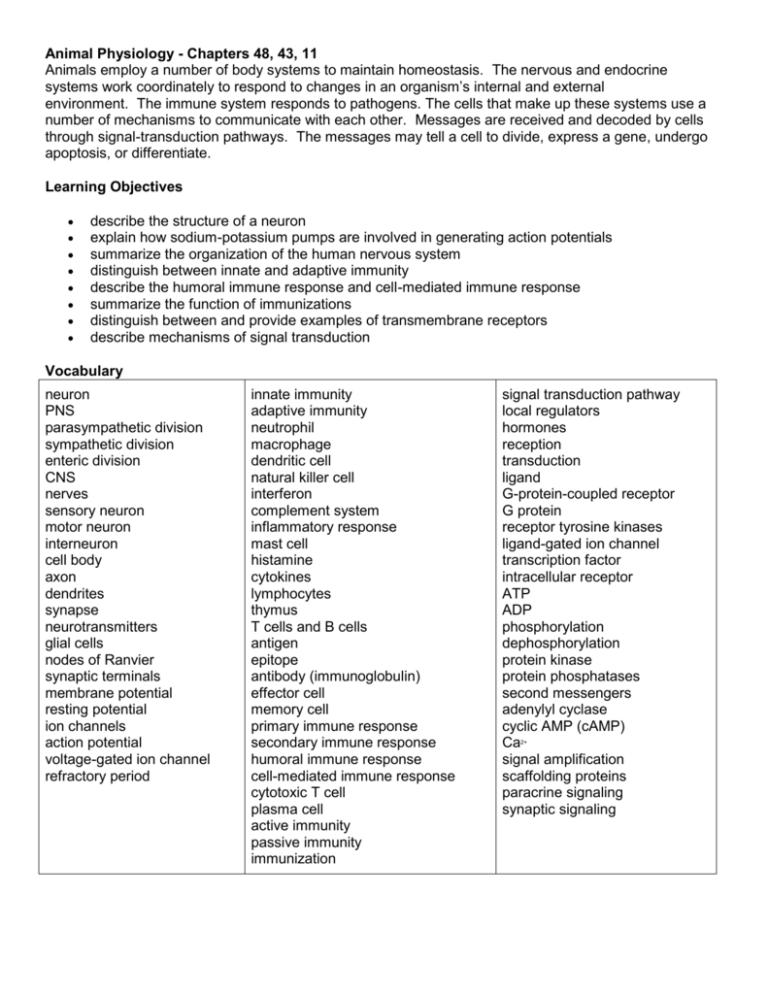
Animal Physiology - Chapters 48, 43, 11 Animals employ a number of body systems to maintain homeostasis. The nervous and endocrine systems work coordinately to respond to changes in an organism’s internal and external environment. The immune system responds to pathogens. The cells that make up these systems use a number of mechanisms to communicate with each other. Messages are received and decoded by cells through signal-transduction pathways. The messages may tell a cell to divide, express a gene, undergo apoptosis, or differentiate. Learning Objectives describe the structure of a neuron explain how sodium-potassium pumps are involved in generating action potentials summarize the organization of the human nervous system distinguish between innate and adaptive immunity describe the humoral immune response and cell-mediated immune response summarize the function of immunizations distinguish between and provide examples of transmembrane receptors describe mechanisms of signal transduction Vocabulary neuron PNS parasympathetic division sympathetic division enteric division CNS nerves sensory neuron motor neuron interneuron cell body axon dendrites synapse neurotransmitters glial cells nodes of Ranvier synaptic terminals membrane potential resting potential ion channels action potential voltage-gated ion channel refractory period innate immunity adaptive immunity neutrophil macrophage dendritic cell natural killer cell interferon complement system inflammatory response mast cell histamine cytokines lymphocytes thymus T cells and B cells antigen epitope antibody (immunoglobulin) effector cell memory cell primary immune response secondary immune response humoral immune response cell-mediated immune response cytotoxic T cell plasma cell active immunity passive immunity immunization signal transduction pathway local regulators hormones reception transduction ligand G-protein-coupled receptor G protein receptor tyrosine kinases ligand-gated ion channel transcription factor intracellular receptor ATP ADP phosphorylation dephosphorylation protein kinase protein phosphatases second messengers adenylyl cyclase cyclic AMP (cAMP) Ca signal amplification scaffolding proteins paracrine signaling synaptic signaling 2+ Analysis Questions 1. Describe the basic pathway of information flow through neurons that causes you to turn your head when someone calls your name. 2. Suppose a cell’s membrane potential shifts from -70mV to -50mV. What changes in the cell’s permeability to K+ and Na+ could cause such a shift? 3. Ouabain, a plant substance used in some cultures to poison hunting arrows, disables the sodium-potassium pump. What changes in the resting potential would you expect to see if you treated a neuron with Ouabain? Explain. 4. Why is the adaptive immune response to an initial infection slower than the innate response? 5. Describe two advantages of having memory B cells when a pathogen is encountered for the first time. 6. Suppose that a snake handler bitten by a particular venomous snake species was treated with antivenin. Why might the same treatment for a second such bite have different results? 7. How do your lymphocytes distinguish between what is your cells (self) and what is not (non-self)? 8. The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infects helper T cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells. Explain how lower numbers of these leukocytes are likely to affect the performance of immune system. In your explanation, discuss whether the HIV has a greater effect on the humoral immune response or cell-mediated response. 9. What determines whether a cell responds to a hormone such as epinephrine? What determines how a cell responds to such a hormone? 10. How are the structures of a GPCR and a RTK similar? In what key way does triggering of signal transduction pathways differ for these two types of receptors? 11. What is the difference between a protein kinase and a second messenger? Can both types of molecules operate in the same signal transduction pathway? 12. What mechanisms in the cell terminate its response to a signal and maintain its ability to respond to new signals?