2011-2012Pacing Guide (Block)
advertisement
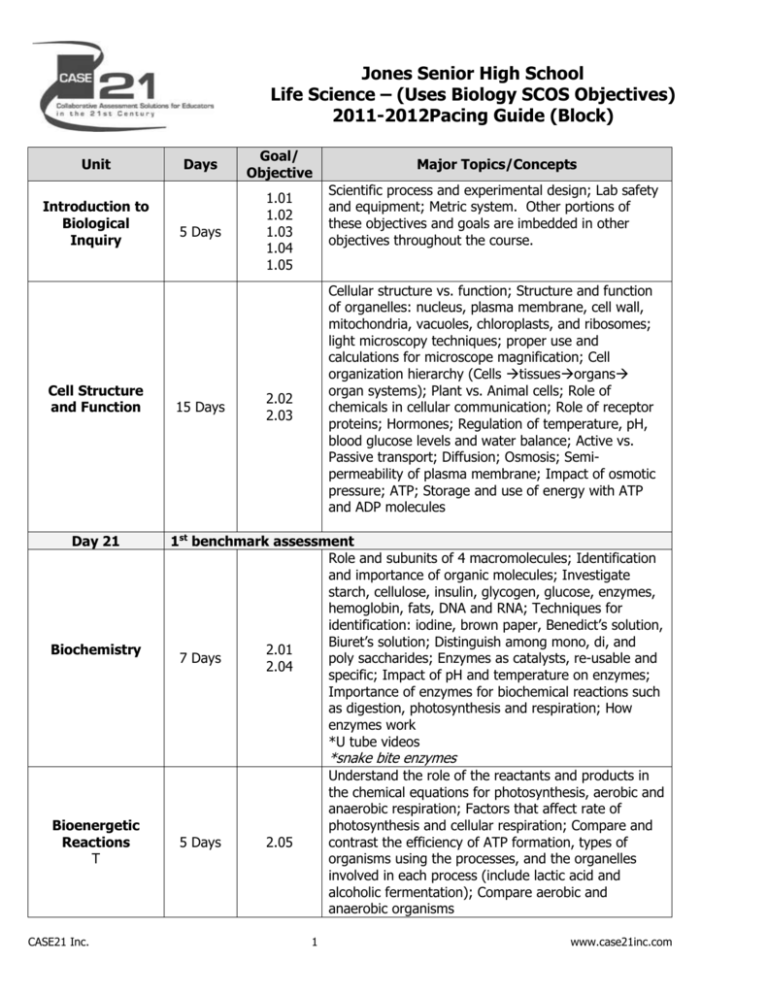
Jones Senior High School Life Science – (Uses Biology SCOS Objectives) 2011-2012Pacing Guide (Block) Unit Introduction to Biological Inquiry Cell Structure and Function Day 21 Biochemistry Days Goal/ Objective 5 Days 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 15 Days Major Topics/Concepts Scientific process and experimental design; Lab safety and equipment; Metric system. Other portions of these objectives and goals are imbedded in other objectives throughout the course. Cellular structure vs. function; Structure and function of organelles: nucleus, plasma membrane, cell wall, mitochondria, vacuoles, chloroplasts, and ribosomes; light microscopy techniques; proper use and calculations for microscope magnification; Cell organization hierarchy (Cells tissuesorgans organ systems); Plant vs. Animal cells; Role of chemicals in cellular communication; Role of receptor proteins; Hormones; Regulation of temperature, pH, blood glucose levels and water balance; Active vs. Passive transport; Diffusion; Osmosis; Semipermeability of plasma membrane; Impact of osmotic pressure; ATP; Storage and use of energy with ATP and ADP molecules 2.02 2.03 1st benchmark assessment Role and subunits of 4 macromolecules; Identification and importance of organic molecules; Investigate starch, cellulose, insulin, glycogen, glucose, enzymes, hemoglobin, fats, DNA and RNA; Techniques for identification: iodine, brown paper, Benedict’s solution, Biuret’s solution; Distinguish among mono, di, and 2.01 7 Days poly saccharides; Enzymes as catalysts, re-usable and 2.04 specific; Impact of pH and temperature on enzymes; Importance of enzymes for biochemical reactions such as digestion, photosynthesis and respiration; How enzymes work *U tube videos *snake bite enzymes Bioenergetic Reactions T CASE21 Inc. 5 Days Understand the role of the reactants and products in the chemical equations for photosynthesis, aerobic and anaerobic respiration; Factors that affect rate of photosynthesis and cellular respiration; Compare and contrast the efficiency of ATP formation, types of organisms using the processes, and the organelles involved in each process (include lactic acid and alcoholic fermentation); Compare aerobic and anaerobic organisms 2.05 1 www.case21inc.com Unit Review of cell parts and biochemistry Plant Comparative Anatomy and Physiology Days Goal/ Objective Prokaryotes vs eukaryotes, photosynthesis and cellular respiration locations and which cell parts are made of which biomolecules. Compare and contrast how plants accomplish the essential life functions focusing on physiology rather than on the names of parts. Transport—howplants get what they need to cells Excretion—balancefluids (pH, salt concentration, water). Regulation—hormones Respiration—howplants exchange gases. Nutrition—howplants absorb nutrients. Synthesis—howorganisms build necessary molecules. Reproduction—sexual vs. asexual, seeds, spores Growth and development—growthfrom seed or spore. Structural adaptations of non-vascular, vascular, gymnosperms and angiosperms- form to function; Co-evolution: Emphasize the relationship between angiosperms and their pollinators 2nd benchmark assessment Changing nature of classification based on new knowledge generated by research on evolutionary relationships; History of classification system including the development of the seven level classification system (KPCOFGS) and binomial nomenclature; Basis of classification system: evolutionary phylogeny, DNA and biochemical analysis, embryology, morphology; Review basic differences and similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic; Use dichotomous keys to identify organisms; For the eukaryotic kingdoms compare: Cellular structures, Unicellular vs. Multicellular, Methods of making/getting food and breaking down food to get energy, and Reproduction; Focus on structural adaptations; Essential life functions of unicellular protists; Structure of viruses, mutation of viruses and other microorganisms, and a variety of disease causing agents (viruses, bacteria) including: HIV Influenza Smallpox Streptococcus 1 day 10 Days 4.02 4.03 10 Days 4.01 4.02 (Protists) 4.03 15 Days 4.02 4.03 Day 60 Classification, Taxonomy and Microorganisms Animal Comparative CASE21 Inc. Major Topics/Concepts Compare and contrast how animals (annelids, insects, amphibians & mammals) accomplish the essential life 2 www.case21inc.com Unit Days Anatomy and Physiology and Adaptive Behaviors Origin of Life and Evolution Ecology CASE21 Inc. Goal/ Objective 4.04 10 Days 3.05 a, b and c 15 Days 5.01 5.02 5.03 3 Major Topics/Concepts functions focusing on physiology rather than on the names of parts. Transport—howanimals get what they need to cells and move wastes to organs of excretion Excretion—howthey get rid of wastes; balance fluids (pH, salt concentration, water). Regulation—hormones, nervous system Respiration—getoxygen from environment and release carbon dioxide Nutrition—howthey break down and absorb foods Synthesis—howthey build necessary molecules. Reproduction—sexual vs. asexual, eggs, placental, types of fertilization Growth and development—metamorphosis, development in egg or in uterus Structural adaptations for feeding and mating—formto function; Behaviors: Innate behavior—Taxesand instincts, including: scratching behavior of dog (instinct), insects moving away from or toward light (taxis), migration, estivation, hibernation Learned behavior—Imprinting, conditioning, and trial and error. Social behavior—Communication, territorial defense, and courtship, including: communication within social structure using pheromones (ex: bees and ants), courtship dances, and territorial defense (ex: Fighting Fish) Development of the theory of evolution by natural selection; Biogenesis vs. Abiogenesis and supporting experiments; Origin and history of life including atmosphere hypotheses and experiments; Early conditions impact on development of organisms (anaerobic and prokaryotic); Evolution of eukaryotic and aerobic organisms; Fossil evidence (relative and absolute dating methods); Patterns in the fossil record and resulting inferences. Symbiotic relationships; Predator/prey relationships and patterns; Field ecology techniques; Abiotic vs. Biotic factors; Limiting factors influence on carrying capacity; Interpret population growth graphs; Relationship of carbon cycle to photosynthesis and respiration; Analyze direction and efficiency of energy transfer within food chains, food webs and energy pyramids; Factors influencing birth and death rates; Environmental impacts from human population size, density, and resource use to include acid rain, habitat www.case21inc.com Unit Days Goal/ Objective Major Topics/Concepts destruction, and non-native species; Climatic changes due to greenhouse effect and natural processes such as volcanoes; Direct and indirect human impact on natural resources (deforestation, pesticide use and bioaccumulation research); Examples of sustainable practices and stewardship Emphasis on Populations 2nd assessment DNA vs. RNA structure; Complementary base pairing; DNA nucleotide sequence codes for proteins; DNA replication’s role in ensuring exact copy of parental DNA; Semi-conservative nature of replication; Mutation as a change in DNA; Replication in the cell cycle; Importance of weak hydrogen bonds; Role of transcription in protein synthesis; Role of mRNA, tRNA and rRNA; Role of translation; Amino acids, peptide bonding and polypeptides; Use codon chart to determine amino acid coded by sequence of bases; Cells within an organism have same DNA but vary due to expression of genes; Cell differentiation in multicellular organisms; Cells respond to environment by producing different types and amounts of protein; Advantages and disadvantages of overproduction or underproduction of proteins; Relevance of human genome project including gene therapy; Gel electrophoresis; DNA fingerprinting; Applications of transgenic organisms in agriculture and industry including pharmaceutical; Implications and ethics of genomics and biotechnology including stem cell research andgenetically modified organisms Day 60 Molecular Genetics and Biotechnology Immune System Function 8 Days 2 days 3.01 3.04 Internal and external factors in health and disease: role of genetics and the environment in determining a specific response to disease, including sickle cell and malaria, PKU and diet, lung/mouth cancer and tobacco use, diabetes; Immune response including a basic understanding of: function and relationship of T-cells, B-cells, antibodies/antigens, passive and active immunity and vaccines; Emphasize aspects of nutrition that contribute to optimal health and poor nutrition; Focus on the life cycle, vector, symptoms, and treatments for the Malarial parasite (Plasmodium); Environmental toxins such as Tobacco and UV radiation 4.05 Final exam CASE21 Inc. 4 www.case21inc.com