Human Reproductive System: Male & Female Anatomy, Pregnancy
advertisement

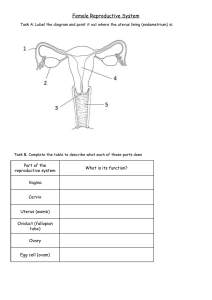
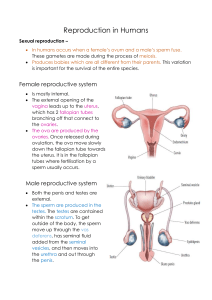
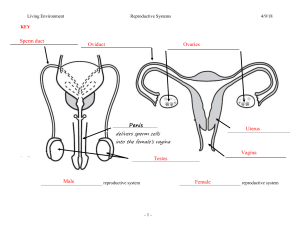
Human Reproductive System Male Reproductive System Sperm Formation • • • • • MEIOSIS Form in testes Temperature important! Scrotum Leave testes via epididymus to the vas deferens Semen • Fluids help to transport, feed, and protect sperm • Seminal vesicles • Prostate gland • Bulbourethral glands Secondary Sexual Characteristics - Male • Produced by testosterone – Deeper voice – Axillary and pubic hair – Chest and facial hair – Lengthen bones – Increased size of testes for sperm production Female Reproductive System Ovum Formation • MEIOSIS • Ova are formed before birth • 1 ovum per month is matured and released from ovaries Secondary Sexual Characteristics - Female • Induced by increased LH, FSH, estrogen, and progesterone hormone levels – Axillary and pubic hair – Widen pelvis – Enlarge mammary tissue – Begin menstrual cycles Fertilization • Occurs in upper 1/3 of Fallopian tube • Once one sperm enters, egg membrane changes • Fertilized egg = zygote Implantation • Implanted into thick walls of uterus • Chorion membranes dig into uterus to form placenta • Embryo supported via umbilical cord • Once pregnant, progesterone levels stay high in mom st 1 Trimester • Heart develops first • Neural tube develops • All body systems appear by Week 8 – Now a Fetus nd 2 Trimester • Mostly growth • Looks more like a baby • Some preemies survive at this stage rd 3 • • • • • Trimester More growth Kicking, rolling, stretching Eyes open – Week 32 Lungs mature Rotates to head-down position Birth • Labor – Uterine contractions begin – Cervix dilates to 10 cm. • Birth – Uterus pushes baby through vaginal canal • Placenta delivered after Most of this not fun?