The Male - Mr. Lesiuk
advertisement

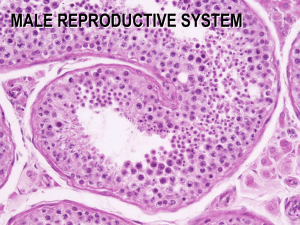
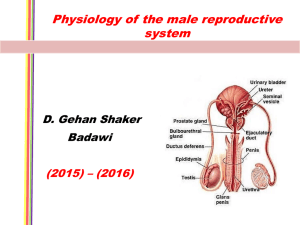
Chapter 21: Reproductive System Male Reproductive System Genital Tract In males the testes, held outside the body in the scrotum (optimum temp of about 350C), produce sperm. Sperm mature in coiled tubes atop each testis, called the epididymis (plural, epididymides). At ejaculation, sperm leave the testes through the vas deferens (plural, vasa deferentia), and pass through the ejaculatory ducts to the urethra. Along the way, secretions (seminal fluid) are added from three glands: two seminal vesicles, the donut-shaped prostate gland at the base of the urinary bladder, and paired bulbourethral glands. These glands add fructose (SV) for energy so sperm can swim, and prostaglandins (SV) that cause uterine contractions; the secretions are slightly basic (prostate) Sperm with secretions from these glands is called semen. The male reproductive system 21-4 Orgasm in Males The penis, the organ of sexual, intercourse, becomes erect from sexual arousal that stimulates cGMP in smooth muscle cells to allow erectile tissue to fill with blood; arterioles dilate and veins are compressed. Orgasm involves ejaculation and muscular tension followed by muscular contractions and relaxation. Over 400 million sperm may be in each ejaculate. Penis anatomy 21-6 Male Gonads, the Testes The testes, which produce sperm and male sex hormones, contain Seminiferous tubules (Spermatogenesis) surrounded by Interstitial cells (Testosterone) Testes originate in the abdominal cavity but descend into the scrotum where it is cool enough for sperm development. 21-7 Testes Interstitial cells that lie between the seminiferous tubules within testes produce testosterone. 21-8 Seminiferous Tubules Seminiferous tubules inside the testes produce haploid sperm through spermatogenesis. Sustentacular cells (Sertoli cells) support, nourish, and regulate the cells during spermatogenesis. Sperm have a head, middle piece, and tail. The head of the sperm is covered by a cap called the acrosome which stores enzymes needed to penetrate the egg. Sperm do not live more than 48 hours in the female genital tract. 21-10 Hormonal Regulation in Males In both males and females, gonadotropin-releasing hormone, or GnRH, secreted by the hypothalamus stimulates the anterior pituitary to release two Gonadotropin Hormones from the Anterior Pituitary Gland. - FollicleStimulating Hormone (FSH) - Spermatogenesis and Luteinizing hormone (LH) Testosterone. FSH stimulates the seminiferous tubules to produce sperm and the hormone Inhibin. LH stimulates interstitial cells to produce testosterone. Testosterone brings about and maintains the male secondary sex characteristics. Testosterone exerts feedback control over the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary resulting in a constant amount of hormones and sperm production over time. Lutenizing Hormone = Testosterone Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) = Spermatogenesis