IT2
advertisement

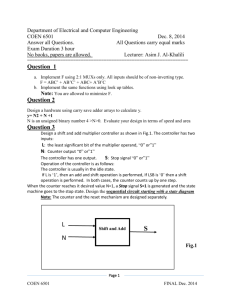
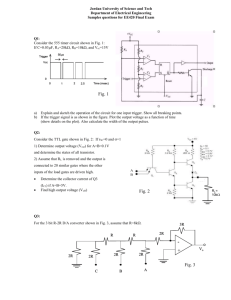
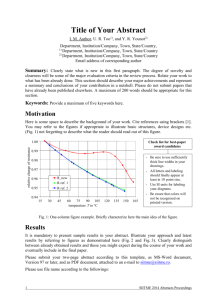
BACHELOR’S DEGREE IN TELECOMMUNICATIONS 3GM1 Digital Circuits and Systems (CSD) F. J. Robert 17 December 2012 Grades will be available on 22 December 2012. Questions about the exam: Lecturer’s office hours. VERY IMPORTANT: Follow general instructions1 to solve the problem Individual Test 2 Our aim is to analyse the asynchronous circuit represented in Fig. 1 found in an application note referring to the 74LS93 chip. Draw it again in a sheet of paper. VCC VCC VCC CHIP1 '1' Q CLK CD '1' T T CLK CD T_FF CD T_FF Q0 Q Q_L CLK CD T_FF Q Q_L CLK CD CD Q Q_L CLK CHIP4 '1' T Q_L CLK CHIP3 '1' T VCC CHIP2 T_FF Q1 Q2 Q3 Q[3..0] b) a) Fig. 1 Example of an application using flip-flops T-type. 1. 2. The T-FF is a simple FSM consisting of 2 states. Its state diagram is in Fig. 1b, invent its internal architecture as a FSM and write its VHDL code. (2p) Analyse the circuit in Fig. 1a and complete the timing diagram in Fig. 2. Because it is not a synchronous system, solve every output independently starting by Q0, then Q1, and so on. We recommend you to copy Fig. 2 in a sheet of paper and add each one of the T-FF’s inverted outputs to the timing diagram. (2p) CLK CD Q0 Q1 Q2 Q3 Fig. 2 Timing diagram for determining the circuit function. 3. Studying the timing diagram, which is the circuit’s function? Which is the circuit’s main problem to discard it for precision applications? (1p) 4. The Fig. 3 represents the state diagram of the FSM of the odometer’s sensor conditioner (the CHIP12) as studied in class notes. Draw its internal architecture as a FSM. (2p) 5. Draw the flow chart for each entity’s process. (1p) 6. Use the processes flow charts to write the VHDL code for the FSM. (2p) Fig. 3 State diagram for the FSM of the odometer’s sensor conditioner circuit. 1 2 http://digsys.upc.es/ed/CSD/terms/1213Q1/cntl.html. A student interview about the submitted work may also be requested. http://digsys.upc.es/ed//CSD/terms/1213Q1/EX/EX3/odometer_sensor_conditioner_design.pdf