Short/Long Answer
advertisement

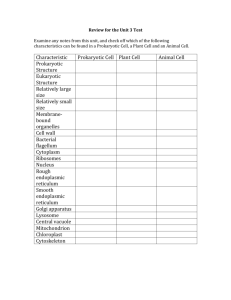
Study Guide for Test: Cells, Osmosis, Diffusion, Cell membrane, Plant transport Essential Knowledge Topic Chapter in Campbell (7th Ed.) 2B1 Cell Membranes are selectively permeable 7.1, 7.2 2A3 Exchange of matter osmosis, diffusion, root hairs 6.2, 36 2B2 Homeostasis by movement of molecules across a membrane, 7.3-7.5 4A2 Structure and Function of organelles 6.2-6.5 4B2 Cooperative interactions within organisms 6.4 4A4 Complex properties due to their environment (plants) 36 Short/Long Answer Explain the rate of transpiration in plants, what affects it, and how plants have adapted to prevent water loss in various environments. Identify how water and molecules will move across a membrane. Use the comparative terms isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic. Predict what will happen to plant and animal cells in each environment. Predict which tissues and cells would contain certain organelles. Describe the function of organelles. Describe the phospholipid membrane structure. Explain how molecules can cross the cell membrane. List the types of transport. Connect biochemistry and membrane transport to how plants obtain, transport and release water back to the environment. Solve water potential problems. Predict the effect of salts on a system (relate to water potential). Know what the water potential formula means and how variation of concentration, pressure, temperature affect water potential Multiple Choice Questions 1. The organelle that is the major producer of ATP and is found in both heterotrophs and autotrophs is the (90:07) A. chloroplast B. nucleus C. ribosome D. Golgi apparatus E. mitochondrion 2. Simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion are related in that both A. require protein carriers B. depend on a concentration gradient C. occur via contractions of cytoskeletal elements attached to membrane proteins D. are endergonic processes and thus require the hydrolysis of ATP E. occur in eukaryotic cells but not in prokaryotic cells 3. Which of the following is correct concerning a spherical cell? (02:53) A. As the diameter decreases, the surface area remains the same. B. As the diameter decreases, the surface area increases. C. As the diameter decreases, the surface-to-volume ratio increases. D. As the diameter increases, the volume decreases. E. The surface-to-volume ratio is independent of the diameter. 4. The nucleolus functions in the production of (94:12) A. Golgi apparatus B. microtubules C. mitochondria D. ribosomes E. endoplasmic reticulum 5. If plant cells are immersed in distilled water, the resulting movement of water into the cells is called (90:34) A. conduction B. active transport C. transpiration D. osmosis E. facilitated diffusion 6. Which of the following is the primary role of the lysosome? (90:46) A. ATP synthesis B. intracellular digestion C. lipid transport D. carbohydrate storage E. protein synthesis 7. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells generally have which of the following features in common? (99:23) A. a membrane-bound nucleus B. a cell wall made of cellulose C. ribosomes D. flagella or cilia that contain microtubules E. linear chromosomes made of DNA and protein 8. Hydrophilic portion of lipid molecule (90:85) 9. Cell-recognition component (90:86) 10. Carriers or permeases involved in cell transport (90:87) 11. Site of glucose synthesis (02:82) 12. Site of conversion of chemical energy of glucose to ATP (02:83) 13. Site of modification and packaging of proteins and lipids prior to export from the cell (02:84) 14. Site of transport of materials into and out of the cell (02:85) 15. Evolved from a photosynthetic prokaryote (02:86) More to come for plant transport.