Study Guide for Test
advertisement

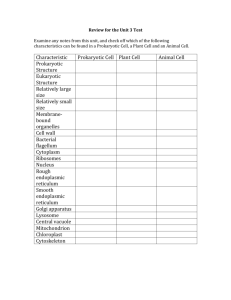
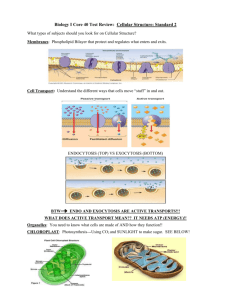
Study Guide for Test Cell Evolution, Structure and Function, Membrane Structure and Transport, Animal Form and Function, Osmoregulation and Excretion Identify how water and molecules will move across a membrane. Use the comparative terms isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic. Predict what will happen to plant and animal cells in each environment. Predict which tissues and cells would contain certain organelles. Describe the function of organelles. Describe the phospholipid membrane structure. Explain how molecules can cross the cell membrane. List and describe different types of transport. Connect biochemistry and membrane transport to how plants obtain, transport and release water back to the environment. Solve diffusion, osmosis, and water potential problems. Predict the effect of salts on a system (relate to water potential). Know what the water potential formula means and how variation of concentration, pressure, temperature affect water potential. Apply concepts of negative and positive feedback, animal form and function, and kidney function. Suggest why a disease but damages connective tissue is likely to threaten most of the bodies organs. Describe the main difference between positive and negative feedback systems. Do question 10 on page 843………In fact, try and self-score -- all Self-Quizzes for Ch 6, 7, 40, 44 The movement of salt from the surrounding water to the blood of a freshwater fish requires the expenditure of energy in the form of ATP. Why? Dragonfly larvae which are aquatic excrete ammonia, whereas adult dragonflies which are terrestrial excrete uric acid. Explain. Review surface area to volume ratios and different types of cells found in plant and animal tissues. Practice Multiple Choice Questions 1. The organelle that is the major producer of ATP and is found in both heterotrophs and autotrophs is the (90:07) A. chloroplast B. nucleus C. ribosome D. Golgi apparatus E. mitochondrion 2. Simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion are related in that both A. require protein carriers B. depend on a concentration gradient C. occur via contractions of cytoskeletal elements attached to membrane proteins D. are endergonic processes and thus require the hydrolysis of ATP E. occur in eukaryotic cells but not in prokaryotic cells 3. Which of the following is correct concerning a spherical cell? (02:53) A. As the diameter decreases, the surface area remains the same. B. As the diameter decreases, the surface area increases. C. As the diameter decreases, the surface-to-volume ratio increases. D. As the diameter increases, the volume decreases. E. The surface-to-volume ratio is independent of the diameter. 4. The nucleolus functions in the production of (94:12) A. Golgi apparatus B. microtubules C. mitochondria D. ribosomes E. endoplasmic reticulum 5. If plant cells are immersed in distilled water, the resulting movement of water into the cells is called (90:34) A. conduction B. active transport C. transpiration D. osmosis E. facilitated diffusion 6. Which of the following is the primary role of the lysosome? (90:46) A. ATP synthesis B. intracellular digestion C. lipid transport D. carbohydrate storage E. protein synthesis 7. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells generally have which of the following features in common? (99:23) A. a membrane-bound nucleus B. a cell wall made of cellulose C. ribosomes D. flagella or cilia that contain microtubules E. linear chromosomes made of DNA and protein Matching 8. Hydrophilic portion of lipid molecule (90:85) 9. Cell-recognition component (90:86) 10. Carriers or permeases involved in cell transport (90:87) 11. Site of glucose synthesis (02:82) 12. Site of conversion of chemical energy of glucose to ATP (02:83) 13. Site of modification and packaging of proteins and lipids prior to export from the cell (02:84) 14. Site of transport of materials into and out of the cell (02:85) 15. Evolved from a photosynthetic prokaryote (02:86) 16. The observation that chloroplasts and mitochondria each contain their own DNA and synthesize some of the proteins that function in these organelles suggests what? (A) (B) (C) (D) These organelles are produced from genetic code located in the nucleus. These organelles are part of the endomembrane system and simply arose from a pinching off of these membranes. These organelles contain two or more membranes. These organelles must divide each time the cell containing them divides. 17. Which of the following is true of ammonia? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) It is soluble in water. It can be stored as a precipitate. It has low toxicity relative to urea. Only A and C are true. A, B, and C are true. 18. All of the following are functions of the mammalian kidney except (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) water reabsorption. filtration of blood. excretion of nitrogenous waste. regulation of salt balance in the blood. production of urea as a waste product of protein catabolism. 19. Which aspects of cell structure best reveals the unity of all life? (A) (B) (C) (D) All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane All cells have at least 1 nucleus All cells carry out cellular respiration in the mitochondria The surface to volume ratio of all cells is the same. 20. Kangaroo rats are better able to concentrate urine than humans are. It would be expected that compared to the nephrons of human kidneys, the nephrons of kangaroo rat kidneys would have (A) (B) (C) (D) Thicker walls which are impermeable to water Shorter loops of Henle Longer loops of Henle Shorter collecting ducts Compare and Contrast: • Y and Ys, Yp • Nucleolus and nucleus • Integral protein and fluid mosaic model • Plasmolyze and wilting • Amphipathic molecule and aquaporin • Receptor-mediated endocytosis and facilitated diffusion Explain these images An artificial cell consisting of an aqueous solution enclosed in a selectively permeable membrane has just been immersed in a beaker containing a different solution. The membrane is permeable to water and to the simple sugars glucose and fructose but completely impermeable to the disaccharide sucrose. 1. Which solute(s) will exhibit a net diffusion into the cell? 2. Which solute(s) will exhibit a net diffusion out of the cell? 3. Which solution is hypertonic to the other? 4. In which direction will there be a net osmotic movement of water? Identify and describe each structure. Explain a logical conclusion that can be drawn from this graph. • Justify your conclusion. • What factors impact ? • If a plant cell immersed in distilled water has a s of -0.7 MPa and a of 0 MPa, what is the cell’s p? If you put the same cell in an open beaker of solution that has a of -0.4 MPa, what would be the cells p at equilibrium? Explain what you understand about this image.