Periodic Table Elements are organized by: Atomic number
advertisement

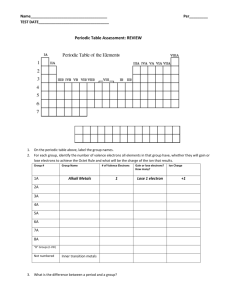
Periodic Table Elements are organized by: Atomic number o Increasing atomic number and mass Similar chemical and physical properties Symbol – unique to each element Atomic Number # of protons and # of electrons Unique to each element – change the proton you change the element Atomic Mass Average # protons and neutrons in a specific amount (6.03 x 1023atoms) Rows = periods, there are 7 total! Elements in the same row DO NOT share similar properties All elements in the same period have the same # of electron orbitals/clouds/energy levels o Row 1 = 1 orbital o Row 5 = 5 orbitals # of rows helps to explain the size and reactivity of an element o More rows = bigger atom = more reactive Columns = groups or families, there are 18 total! Usually represents the number of electrons in the outer most shell – valence electrons o Exception – transition metals # of valence electrons determines an elements physical properties and how it will behave in a chemical rxn. Elements within the same column exhibit very similar properties Elements in the same column form the same charged ion – exception transition metals Important Families! Hydrogen Only 1 member Charge of ion = +1 (usually) Diatomic (never alone in nature) Reactive gas Alkali Metals (group 1) Charge of ion = +1 One valence electron VERY reactive metals (react violently with water) – always combined in nature Soft enough to cut with a knife Alkaline Earth Metals (group 2) Charge of ion = +2 Two valence electrons Reactive metals are always combined with nonmetals in nature Several are important nutrients Transition Metals (group 3-12, etc) Charge of ion varies Less reactive and harder Good conductors of electricity and heat Metals used as “metals” Compounds are often brightly colored Rare Earth Metals Lanthanide and Actinide series Actinides ae mostly man-made Similar to transition metals (often referred to as “inner transition”) Boron Family Charge of ion = +3 Three valence electrons Most are metals (B is a metalloid) Includes Al – most abundant elements in earth’s crust Carbon Family (group 14) Don’t form ions (usually) 4 valence eTends to share e- in bonds Has metals, non-metals, and metalloids 2nd most stable group Nitrogen Family (group 15) Charge = 35 valence eTends to share e- in bonds Has metals, non-metals, and metalloids Chalcogens (group 16) Charge = 26 valence eTends for share e- in bonds O and S (elements responsible for stinky stuff) Halogens (group 17) Charge of ion = 1 7 valence electrons Most reactive non metals – NEVER found free in nature o F can dissolve glass Diatomic and volatile Form “salts” with alkali/earth metals Noble Gases (group 18) Don’t form ions Full outer shell (8) All other atoms want to be them UNREACTIVE, monoatomic gases Staircase indicates metalloids (exception Al)