Heading Zone - Wansdyke Community School
advertisement

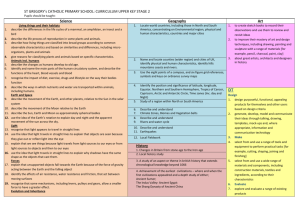
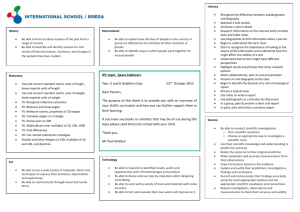
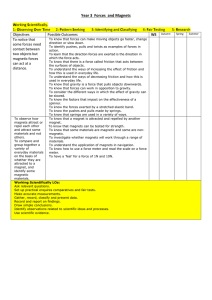
WANSDYKE SCHOOL’S CURRICULUM SUBJECT CONTRIBUTIONS YEAR 3 Year 3 is the first Year of learning in Key Stage 2. We are moving in to learning towards Milestone 2 as well as building on learning from Milestone 1 and the end of Key Stage 1 expectations. The children are becoming increasingly independent learners and are starting to make choices about their learning and how they learn and also evaluating their work and their feelings about their learning. KEY LEARNING Learn to use text books independently To underline the date and ‘Can I?’ To take responsibility for resources To change reading books independently Begin to use increased independent techniques for learning To complete ‘steps to success’ and explain learnings dots in response to work completed. WOW MOMENTS ENGLISH Resources • Somerset Literacy Network resources • Sue Palmer • Ros Wilson • Skeletons for Teaching English Grammar • Big Write • Clicker MATHEMATICS Resources • Abacus • Mathletics • Numicon • Dienes • Wansdyke Counting Progression HISTORY Context Changes in Britain from the Stone Age to the Iron age including: Avebury and Stonehenge (visit) British history: Britain’s settlement by AngloSaxons and Scots Ancient Egyptians (visit) Evidence (e.g. documents, printed sources, databases, pictures, photographs, music, artefacts, historic buildings, visits to sites) Place events, artefacts and historical figures on a time line using dates. Knowledge Dates and vocabulary relating to the passing of time, (inc. ancient, modern, BC, AD, century, decade) Characteristic features and significant events of periods and societies studied (e.g. ideas, beliefs, attitudes, experiences of men, women and children in the past) • Describe changes that have happened in the locality of the school throughout history. • Give a broad overview of life in Britain from ancient until medieval times. Resources • History KS folder on Staff Share GEOGRAPHY Context Underground, Over ground topic (Volcanoes, Earthquakes, Tsunami’s and Mining) World Weather (?) Compare and contrast two regions of the United Kingdom River Nile (Egyptians) Fairtrade and The Gambia Geographical Skills and Fieldwork Fieldwork: inc. surveys, field sketches, photographs, plans, graphs, and digital technologies. Measurements (e.g. rain gauge) Use atlases, globes, maps and plans at a range of scales (e.g. contents, keys, grids); Draw plans and maps at a range of scales (e.g. sketch map) Use secondary sources, inc. aerial photographs Use an eight point compass (use N, NE, E, SE, S, SW, W, NW) Place Knowledge Location (e.g. by region/country, whether near rivers or hills, what the nearest towns or cities are…) Name and locate key countries and capital cities in Europe Understand similarities and differences between regions of the United Kingdom Interdependence (e.g. food) Locational Knowledge Recognise how places fit within a wider geographical context Locate the world’s continents and countries. Know, and locate on a world map: Africa, Asia, Europe, North America, Oceania, South America, Antarctica, The Sahara and the principal oceans: Arctic, Atlantic, Indian, Pacific Identify the position and significance of latitude, longitude, Equator, Northern Hemisphere, Southern Hemisphere the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, Arctic and Antarctic Circle. Resources Text Skills • Place events, people, changes into correct periods, on a time-line How to find out about events, people and changes from a range of sources Use dates Use evidence to ask questions and find answers to questions about the past. Suggest suitable sources of evidence for historical enquiries. Use more than one source of evidence for historical enquiry in order to gain a more accurate understanding of history. Use appropriate historical vocabulary to communicate, including: dates, time period, era, change, chronology SCIENCE Concepts Reasons for, and results of, historical events, situations, and changes in the periods studied Social, cultural, religious and ethnic diversity Links between main events, situations, changes, within and across periods and societies The past is represented and interpreted in different ways and why this is so Skills Scientific inquiry skills: See unit plans Knowledge Programmes of Study: Plants [Green Plants: What would we do without them?] Identify and describe the functions of different parts of flowering plants, roots, stem/trunk, leaves and flowers Explore the requirements of plants for life and growth [: air, light, water, nutrients, from soil, and room to grow.] and how they vary from plant to plant. Investigate the way in which water is transported within plants Explore the part that flowers play in the life cycle of flowering plants: including pollination, seed formation and seed dispersal. Light [Light] Recognise that they need light to see things and that dark is the absence of light Notice light is reflected from surfaces Recognise that light from the sun can be dangerous and that there are ways to protect their eyes Recognise that shadows are formed when the light from a light source is blocked by a solid object Find patterns in the way that the size of shadows change Forces and Magnets [Contact Forces and Forces that work at a Distance] Compare how things move on different surfaces Notice that some forces need contact between two objects, but magnetic forces can act at a distance Observe how magnets attract or repel each other and attract some materials and no others Compare and group together a variety of everyday materials on the basis of whether they are attracted to a magnet, and identify some magnetic materials Describe magnets as having two poles Predict whether two magnets will attract or repel each other, depending on which poles are facing Rocks [Rocks, Fossils and Soil] Compare and group together different kinds of rocks on the basis of their simple physical properties. Describe in simple terms how fossils are formed when things that have lived are trapped within sedimentary rock Recognise that soils are made from rocks and organic matter. Animals, including Humans [What goes in must come out] Identify that animals, including humans, need the right types and amount of nutrition, and that they cannot make their own food: they get nutrition from what they eat Identify that humans and some animals have skeletons and muscles for support, protection and movement. Resources • ART & DESIGN Use experiences, other subjects across the curriculum and ideas as inspiration for artwork. Develop and share ideas in a sketchbook and in finished products. Improve mastery of techniques. Learn about the great artists, architects and designers in history. To Develop Ideas Develop ideas from starting points throughout the curriculum. Collect information, sketches and resources. Adapt and refine ideas as they progress. Explore ideas in a variety of ways. Comment on artworks using visual language. To Master Techniques of Drawing Use bold lines to draw a simple shape. Develop a drawing from something observed into something abstract but obviously related Combine drawing and collage elements to make a simple, effective picture. Use different hardnesses of pencils to show line, tone and texture. Annotate sketches to explain and elaborate ideas. To Master Techniques of Sculpture To be able to build a base structure to cover, using wir masking tape, card and junk. To develop layering skills in construction when layers ar placed uniformly and evenly to create a solid structure i.e. papier-mache. To use design ideas from artefacts they have researched Timbre: identify to a range of non-percussion create a 3D object closely related to the design. instruments by name; distinguish different ways of Use clay and other mouldable materials. playing percussion instruments Add materials to provide interesting detail. Structure: develop understanding of a range of repetition and contrast structures, including use of To Master Techniques of Painting ostinati Develop skills in mixing skin tones through paint mixing and Context using ready mix paints. As above using water colour paints. Identify how combinations of elements are To wash out paintbrushes and water pots in correct way used a in a variety of musical styles, and to To match colour to mood or temperature. communicate musical effects To play with paint in creative way but still showing control Identify different families of instruments and of materials. their qualities Use a number of brush techniques using thick andthinUse brushes and explore to notations which are linked to produce shapes, textures, patterns and lines. understanding of elements to communicate Mix colours effectively. own musical ideas, including relative pitch Identify composers' intent in music heard and To Master Techniques of Printing performed To be able to make a poly print. To be able to make a block print using card and usingIdentify press. how music is produced in different ways including the use of ICT To add detail to a print using another medium. Make printing blocks (e.g. from coiled string glued Introduction to playing a tuned instrument: weekly recorder tuition, developing to a block). understanding and use of staff and other To Master Techniques of Mixed Media notation. To be able to use two mediums and comment on effect. Skillsinto To be able to use two created artworks and combine piece) Extend accuracy of vocal range (use low A-C' one (e.g. a pastel work cut out and stuck onto a collage a guide) To Master Techniques of Collage Continue to develop expressive effect and To be able to weave a regular design with paper quality of sound when singing through To work in a collaborative way on a weaving. increased control of diction, dynamics and To make simple stitches on binca. tempi To Master Techniques of Textiles Sing rounds and partner songs, maintaining Shape and stitch materials. Demonstrate accuracy and control of Use basic cross stitch and back stitch. technique on full range of untuned percussion To Master Techniques of Digital Media and begin use classroom keyboards and own Create images, video and sound recordings and explain instruments why they were created. Practise use of two beaters on tuned To take inspiration from the greats percussion (classic and modern) Maintain steady beat, and copy and match Replicate some of the techniques used by rhythm patterns in 2, 3 and 4 metre notable artists, artisans and designers. Use and follow hand and eye signals to and Skills lead Record from first-hand observation, and Improve their own work experience and imagination Rehearse and perform individually, in pairs, Use a sketchbook to collect visual and other groups and as a class with increasing information (e.g. images, materials) awareness of balance Represent observations, ideas and feelings Creating Explore and investigate ideas, materials, tools, Explore the way sounds can be combined and techniques, processes; Develop control of tools used expressively and techniques; Select for use in own work Improvise short repeated rhythmic patterns, Design and make images and artefacts building a repertoire of patterns and Review and compare what they and others sequences have done (e.g. ‘Gallery’) and say what they Begin to combine layers of sound with think and feel about different ideas, methods awareness of the combined effect and approaches Experiment with capturing, repeating and re Identify what they might change or add in ordering patterns and sections music their current work, or develop in their future Devise non-standard symbols to indicate when work to play and rest. Concepts Colour, pattern, texture, line and tone, shape, form & space Knowledge Differences and similarities in the work of artists, craftspeople, designers in different times, cultures Materials and processes used in art and design; How these are matched to ideas and intentions Roles and purposes of artists, craftspeople and designers working in different times and cultures Topics: Look at Me Favourite Lines Amulete and Armour Natural Environment Shine and Drip Texture & printing (TBC) MUSIC Pupils should be taught: Pitch: distinguish between steps, leaps and repeats in melodies; major and pentatonic scales Duration: consolidate understanding of how rhythmic patterns fit to the steady beat; begin to understand 2, 3 and 4 metre Dynamics: understand and identify getting louder and quieter Tempo: understand and identify getting faster and slower Texture: recognise the density of different textures Responding and reviewing Compare and contrast music heard and performed with an awareness of the music's context and purpose Use a variety of art forms to respond to character, mood and other elements of music Build an appropriate musical vocabulary and use when talking about music and developing ability to express an aesthetic response Improve their own and others' work with an awareness of music's context and purpose Focus Composers and Genres GENRES: Medieval/ Renaissance (a comparison between the two eras), Egyptian music COMPOSERS: J Dunstable/ Claude de Jeune (comparitively), Zakariya Ahmad Begin to develop and an understanding of the history of music and great composers. Resources • Application of learning to sharing assemblies and other performances, including Christmas production D&T See Chris Quigley for Mastery of Practical Skills Concepts Design and make process: develop ideas→ plan→ make product→ evaluate Product ‘fit-for-purpose’ (user, purpose, appearance) Context Investigating and evaluating a range of familiar products Focused practical tasks that develop a range of techniques, skills, processes and knowledge Design and make assignments using a range of materials, including food, items that can be put together to make products, and textiles ‘Structures’, ‘Food’, ‘Mechanisms’ Select and arrange materials for a striking effect. Skills Generate, develop, plan and communicate ideas, inc. use of models Select tools, techniques, materials to make product Explore the qualities of materials Measure, mark out, cut, shape a range of materials accurately Assemble, join and combine materials and components accurately Use simple finishing techniques to strengthen and improve appearance, using a range of equipment Follow safe procedures for food safety and hygiene Reflect on the progress of work; Identify ways to improve it, carrying out appropriate tests before making improvements Evaluate by saying what they like and dislike, what they could have done differently or how they could improve in the future Knowledge The working characteristics of materials inc. how they can be combined to make more useful properties (e.g. reinforcing card triangles on a wooden structure) How mechanisms can be used in different ways, inc. ICT control How electrical circuits, inc. those with simple switches, can be used to achieve results that work. Resources • Text COMPUTING Concepts & Context Pupils should be taught to: design, write and debug programs that accomplish specific goals, including controlling or simulating physical systems; solve problems by decomposing them into smaller parts use sequence, selection, and repetition in programs; work with variables and various forms of input and output use logical reasoning to explain how some simple algorithms work and to detect and correct errors in algorithms and programs understand computer networks including the internet; how they can provide multiple services, such as the world wide web; and the opportunities they offer for communication and collaboration use search technologies effectively, appreciate how results are selected and ranked, and be discerning in evaluating digital content select, use and combine a variety of software (including internet services) on a range of digital devices to design and create a range of programs, systems and content that accomplish given goals, including collecting, analysing, evaluating and presenting data and information use technology safely, respectfully and responsibly; recognise acceptable/unacceptable behaviour; identify a range of ways to report concerns about content and contact Knowledge Not all internet information is accurate or factual Know about different ways to communicate online (e.g. email, blogs, instant messaging) e-Safety: How to make a safe decision if receiving an unwanted communication Skills Save, retrieve, print documents independently Use online communication safely (e.g. email, blog, learning platform) Use ‘Save as’ to keep draft copies Edit text: use cut, copy, paste; add border Control: use pen up, pen down Modelling: predict, explain consequences of choosing different options, be systematic Contribute to blogs that are moderated by teachers. Give examples of the risks posed by online communications. See Chris Quigley for Coding skills Use some of the advanced features of applications and devices in order to communicate ideas, work or messages professionally. Devise and construct databases using applications designed for this purpose in areas across the curriculum. Resources • • • • Year 3 Skills Wall iPads Website Blog E-safety Week RE Context Christianity and Hinduism Local religious communities: visiting places of worship, listening and responding to visitors A range of religious stories and sacred writings Times of quiet reflection Skills Use a range of religious words Reflect on and consider religious/spiritual feelings, experiences, concepts (e.g. worship, wonder, praise, thanks, concern, joy, sadness) Ask and respond imaginatively to puzzling questions Identify what matters to them and others Reflect on how values relate to their own behaviour Develop the attitudes of: self-awareness, respect for all, open mindedness, curiosity, empathy and appreciation. Recognise diversity of the religions studied, comparing similarities and differences between religions and beliefs. Knowledge Beliefs, celebrations, worship and rituals of the religions studies Topics: • ‘Discovery RE’: ‘Divali’, ‘Christmas’, ‘Jesus’ Miracles’, ‘Easter – Forgiveness’, ‘Hindu Beliefs’, ‘Pilgrimage to the River Ganges’ PE Real PE- One unit equivalent to one lesson per week for one term. Sports taught in Year 3: Swimming, Netball, Dance, Rugby, Gym, Tennis, Athletics Context Individual, pair, small-group and small-team activities Games (play and make up small-sided and modified competitive net, striking/fielding and invasion games) Gymnastics (create and perform fluent sequences on the floor and using apparatus, inc. variations in level, speed, direction) Dance (create and perform using range of movement patterns, inc. from different times, places, cultures) Swimming (25m) ‘Athletics’ (take part in and design challenges and competitions that call for precision, speed, power, stamina; use running, jumping, throwing skills; pace themselves) ‘Outdoor and adventurous activities’ (inc. following trails, in familiar, unfamiliar and changing environments; use orienteering and problem solving skills; work with others) Skills Perform actions and skills with more consistent control and quality Plan, use and adapt strategies, tactics and compositional ideas Develop and use knowledge of principles behind strategies, tactics and ideas to improve effectiveness Apply rules and conventions for different activities Evaluate and improve performance Knowledge Rules, conventions and tactics for different activities How exercise affects the body in the short term; Why physical activity is good for health and well-being How to warm up and prepare appropriately Why wearing appropriate clothing and being hygienic is good for their health and safety Resources • • • Real PE ‘Devizes Schools’ Sports Network’ Application of athletic and games skills to intraschool and inter-school tournaments and competitions and dance skills to sharing assemblies and other performances, including Christmas production PSHE Context Discussions, day-to-day school experience Skills Maintain personal hygiene Concepts Likes and dislikes, fair and unfair, right and wrong Feelings, opinions, rules, choices (good and bad) Communities, contributing Knowledge Growing up, body parts, medicines, road safety Resources • SEAL • Real PE • Anti-bullying Week • Living and Growing • Kindness Cup • House Points • School Council • 5 Rs Learnability Wheel • Wiltshire Learning for Life • Jigsaw LANGUAGES Locating France within Europe Greetings, What is your name? Numbers 1-20 .Classroom commands and objects .Responding to register in French. Christmas traditions. Francophone world and nationalities. Days of the week. Alphabet. Weather. Where do you live? How old are you? Easter traditions. Family members .Days, months, date. When is your birthday? Colours. Numbers 20-31.I like/do not like? Story ‘Jacques le Gourmande’ ‘Les Trois Cabris’ Songs eg.’Mon Beau Sapin’ ‘Les jours de la Semaine’’Mon Pique nique’ Continue link with school Understand the main points from spoken passages. Ask others to repeat words or phrases if necessary. Ask and answer simple questions and talk about interests. Take part in discussions and tasks. Demonstrate a growing vocabulary. Describe with some interesting details some aspects of countries or communities where the language is spoken. Make comparisons between life in countries or communities where the language is spoken and this country. Resources • • • Southend SoW:Year 3 Units 1,2,3. ‘Bonjour, je parle français’, ‘Je me présente’, ‘En Famille’ ‘J’aime Chanter’ ‘Storymaking in French’ ILRC OUTDOOR LEARNING Science units: Plants: What would we do without them? Rocks, Fossils and soils Geography: Fieldwork: including surveys, field sketches, photographs, plans, graphs, and digital technologies. Measurements e.g rain gauge, temperature and wind speed/direction History: Visits e.g. Roman Baths/Devizes Museum (Romans). Highclere Castle, (Egyptians), Big Pit, South Wales (Mining). Avebury/Stonehenge (Stone Age) Art: Using a range of mediums in outdoor locations e.g. Sketching/painting objects in our environment Focus Artists: Georgia O’Keefe, Andy Goldsworthy Drama/Music/Performance: Staging