atmosphere
advertisement

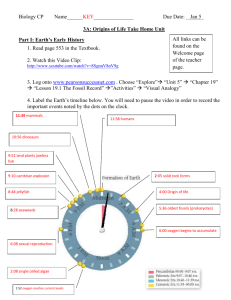
CP Biology 2015-2016 Name ______ ____________ UNIT 3A: Origins of Life How did Life Begin? For thousands of years people believed that living Where did the first life come from? _there are many theories but nobody knows for sure ____________________________________________ organisms originated from nonliving matter. 1) Abiogenesis or Spontaneous Generation: the idea that life can arise from nonliving material. (Ex: haystacks; flies come from rotting meat; bacteria arise from broth) Francisco Redi in the 1600’s and Louis Pasteur in 1862 conducted experiments which disproved the theory of spontaneous generation. 2) Biogenesis: the idea of life arising from other living things. (Ex. Cats make cats; humans make humans, etc.) Origins of the Earth Big Bang Theory (1927): idea which explains what happened at the very beginning of our universe (~13.7 bya) – began as an infinitely small, hot dense “speck” that inflated, expanded and cooled to the size and temperature of our current universe. Earth formed around 4-5-4.6 bya. Franceso Redi’s Experiment:_Two jars of meat, one jar covered in cheese cloth and the other left open to the air. Maggots formed on the meat in the jar left open and did not form in the covered jar. This disproved the theory of spontaneous generation. Louis Pasteur’s Experiment: He had the goose neck flask of boiled broth that allowed air to enter but not living organisms (bacteria). As a result the broth remained clear without any bacteria appearing. Compounds in the Primitive Atmosphere Compound Elements Present Molecular Formula methane carbon, hydrogen CH4 ammonia nitrogen, hydrogen NH3 hydrogen hydrogen H2 water hydrogen, oxygen H2O carbon dioxide carbon, oxygen CO2 Your personal notes, summary of the lesson, and/or questions that you may have: 1 Formation of the Oceans Label the following in the diagram below: He, Ni, Cu, Fe, H2 1) Tremendous amounts of hydrogen and oxygen were trapped below the crust. These elements combined to form water vapor, which was released to the atmosphere atmosphere. 2) The water vapor condensed in the atmosphere and NH3 rained down to form vast oceans for 40 million yrs. H2 Sequence of Conditions on Primitive Earth: He CH4 CaCO3 crust core Cl Fe Cu Ni H2 1) Heavy particles such as iron, copper and nickel were pulled to the center of the earth. He 2) Lighter particles such as helium and hydrogen remained at the surface. 3) Radioactive material and great pressure kept the center of the earth in a molten state. 4) Over a period of years, the outer surface or crust of What major gas, necessary for life, is missing from the atmosphere the earth formed over the molten center (4 BYA). of primitive Earth? _oxygen gas (O2)_______ 5) As the outside of the earth cooled, hot gases from the interior escaped to form the primitive atmosphere. Look at the pictures of Primitive Earth and Modern Earth to the right What are the similarities between Primitive Earth and Modern Earth? _Oceans were present along with the_____ __sun; Water vapor is present___________________ ___________________________________________________ What are the differences between Primitive Earth and Modern Earth? _the gases in the atmosphere are _ _different (P: H2, CH4, NH3 and M: O2, N2, CO2); ozone layer on modern earth; life on land; P: volatile (lots of lightning and UV radiation) Your personal notes, summary of the lesson, and/or questions that you may have: 2 1 Primitive Earth’s Atmosphere Two major differences between primitive Earth and modern earth set the stage for the formation of organic compounds (hydrocarbons) and, eventually, the origin of living things. 1) Oxygen (O2) – a highly reactive compound. Will break bonds that form between simple organic compounds and destroy them. NOT PRESENT! 2) The atmosphere had abundant energy that could be used to join atoms that form hydrocarbons. a) Lacking an ozone (O3) layer, the atmosphere had abundant UV radiation. b) Lightning in the atmosphere. c) Heat from volcanoes above and below ocean level Theory of Chemical Evolution In 1924, Alexander Oparin and J.B. Haldane developed a theory for the origin of organic compounds: Use your own words to describe the conditions of the early Earth and the early atmosphere. (This is #1 from the checklist on the USG of what you should be able to do by the end of this unit) _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ Use the word bank to fill in the blanks below: precursors, inorganic, spontaneously, oxygen, primitive Earth Conditions on primitive Earth gave rise to simple organic compounds, the precursors to life. 1) CO2, H2 and NH3 are types of __inorganic___ molecules found in the atmosphere on __primitive Earth__________. 1) Inorganic Matter: like CO2 and NH3, (plus organics like CH4) in the atmosphere combined using the energy sources listed above. 2) Scientific evidence indicates that organic molecules and cells may have formed __spontaneously__ on ancient Earth. 2) Simple Organic Molecules: like HCN (hydrogen cyanide) and formaldehyde formed primitive clumps of organic matter. – not life (living)…may have eventually led to life!!! 3) The lack of free atmospheric _oxygen______ and the abundance of energy on early Earth facilitated the formation of organic compounds from inorganic _precursors (to life)_____. Your personal notes, summary of the lesson, and/or questions that you may have: 3 1