Origin of Life Note Packet
advertisement
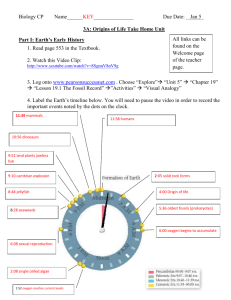
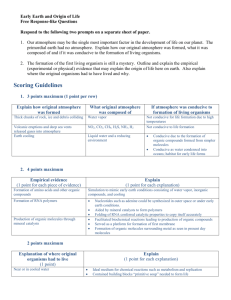
CP Biology 2015-2016 Name ______ ____________ UNIT 3A: Origins of Life How did Life Begin? For thousands of years people believed that living Where did the first life come from? _______________ ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________ organisms originated from nonliving matter. 1) Abiogenesis or Spontaneous Generation: the idea that life can arise from nonliving material. (Ex: haystacks; flies come from rotting meat; bacteria arise from broth) Francisco Redi in the 1600’s and Louis Pasteur in 1862 conducted experiments which disproved the theory of spontaneous generation. 2) Biogenesis: the idea of life arising from other living things. (Ex. Cats make cats; humans make humans, etc.) Origins of the Earth Big Bang Theory (1927): idea which explains what happened at the very beginning of our universe (~13.7 bya) – began as an infinitely small, hot dense “speck” that inflated, expanded and cooled to the size and temperature of our current universe. Earth formed around 4-5-4.6 bya. Franceso Redi’s Experiment:_____________________ ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________ Louis Pasteur’s Experiment:_____________________ ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________ Compounds in the Primitive Atmosphere Compound Elements Present Molecular Formula methane carbon, hydrogen CH4 ammonia nitrogen, hydrogen NH3 hydrogen hydrogen H2 water hydrogen, oxygen H2O carbon dioxide carbon, oxygen CO2 Your personal notes, summary of the lesson, and/or questions that you may have: 1 Formation of the Oceans Label the following in the diagram below: He, Ni, Cu, Fe, H2 1) Tremendous amounts of hydrogen and oxygen were trapped below the crust. These elements combined to form water vapor, which was released to the atmosphere. 2) The water vapor condensed in the atmosphere and rained down to form vast oceans. CaCO3 Cl Sequence of Conditions on Primitive Earth: CH4 1) Heavy particles such as iron, copper and nickel were pulled to the center of the earth. 2) Lighter particles such as helium and hydrogen remained at the surface. 3) Radioactive material and great pressure kept the center of the earth in a molten state. 4) Over a period of years, the outer surface or crust of What major gas, necessary for life, is missing from the atmosphere the earth formed over the molten center (4 BYA). of primitive Earth? _______________ 5) As the outside of the earth cooled, hot gases from the interior escaped to form the primitive atmosphere. Look at the pictures of Primitive Earth and Modern Earth to the right What are the similarities between Primitive Earth and Modern Earth? ____________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ What are the differences between Primitive Earth and Modern Earth? ____________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ Your personal notes, summary of the lesson, and/or questions that you may have: 2 1 Primitive Earth’s Atmosphere Two major differences between primitive Earth and modern earth set the stage for the formation of organic compounds (hydrocarbons) and, eventually, the origin of living things. 1) Oxygen (O2) – a highly reactive compound. Will break bonds that form between simple organic compounds and destroy them. 2) The atmosphere had abundant energy that could be used to join atoms that form hydrocarbons. a) Lacking an ozone (O3) layer, the atmosphere had abundant UV radiation. b) Lightening in the atmosphere. c) Heat from volcanoes above and below ocean level Theory of Chemical Evolution In 1924, Alexander Oparin and J.B. Haldane developed a theory for the origin of organic compounds: Use your own words to describe the conditions of the early Earth and the early atmosphere. (This is #1 from the checklist on the USG of what you should be able to do by the end of this unit) _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ Use the word bank to fill in the blanks below: precursors, inorganic, spontaneously, oxygen, primitive Earth Conditions on primitive Earth gave rise to simple organic compounds, the precursors to life. 1) CO2, H2 and NH3 are types of ________________ molecules found in the atmosphere on ___________________________. 1) Inorganic Matter: like CO2 and NH3, (plus organics like CH4) in the atmosphere combined using the energy sources listed above. 2) Scientific evidence indicates that organic molecules and cells may have formed _________________ on ancient Earth. 2) Simple Organic Molecules: like HCN (hydrogen 3) The lack of free atmospheric _____________ and the abundance of energy on early Earth facilitated the formation of organic compounds from inorganic __________________________. cyanide) and formaldehyde formed primitive clumps of organic matter. Your personal notes, summary of the lesson, and/or questions that you may have: 3 1 Miller and Urey Support the Theory of Chemical Evolution Label Miller and Urey’s apparatus using the word bank below: C __________ In 1953, Stanley Miller and Harold Urey developed a model to test the Oparin/Haldane Hypothesis. F __________ Gases in the apparatus are CH4, NH3, H2O, & H2 Sources of energy: electricity (to represent lightening) __________B Analysis of substances (organic soup) collected in the trap: HCN (hydrogen cyanide), lactic acid, acetic acid, simple amino acids, formaldehyde. D __________ What would happen if you add O2 to the above mixture?: __________________________________________ __________________________________________ Other scientists used UV light in this model and formed simple organic molecules like HCN which can be used to form adenine, a nitrogen base. E _______________ ____________ A organic soup, lightning (electricity), oceans, rainfall, heat source, primitive atmosphere Your personal notes, summary of the lesson, and/or questions that you may have: 4 1 The Heterotroph Hypothesis Once simple, organic compounds were formed, polymers of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids could give rise to protocells. Protocells: simple precursors to cells then evolved into primitive cells with RNA as the genetic material. simple organic compounds polymers protocells primitive cells Were the first primitive cells autotrophs or heterotrophs? 1) Heterotroph: an organism which requires an external supply of energy in the form of food as it cannot make (synthesize) its own. 2) Autotroph: an organism that produces complex organic compounds from simple inorganic molecules using energy from light (by photosynthesis) or inorganic chemical reactions. Forms of Cellular Respiration 1) Aerobic Respiration: form of cellular respiration that requires oxygen Which form of life – autotrophic or heterotrophic – is a simpler design? Explain. _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ Which form of cellular respiration was used by the first organisms? Why? _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ 2) Anaerobic Respiration: form of cellular respiration _______________________________________________ that does not require oxygen Your personal notes, summary of the lesson, and/or questions that you may have: 5 1 Anaerobic heterotrophs consumed organic matter (organic “soup”) and underwent anaerobic respiration. The first autotrophs: 2.5 bya – primitive cyanobacteria – blue green algae Photosynthesis provide two important things: 1) a source of food for heterotrophs AND 2) free oxygen for the environment and aerobic respiration The evolution of O2-producing autotrophs transformed Earth's atmosphere to one suitable for the evolution of aerobic metabolism and complex life Weigh the significance of the evolution of autotrophs in changing the conditions on early earth. (This is #7 from the checklist on the USG of what you should be able to do by the end of this unit) _____________________________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ The effects of photosynthesis on the development of the ozone layer: 1) some of the O2 formed by producers is used to form the ozone layer O2 + UV light O3 2) ozone blocks most ultraviolet (UV) radiation from reaching the Earth 3) One source of energy for formation of organic compounds is reduced, BUT Organisms exposed to the atmosphere are not harmed by the UV radiation 4) O2 becomes available for aerobic cellular respiration Your personal notes, summary of the lesson, and/or questions that you may have: 6 1 Evidence About the Past Based on the following information and the geological “clock”, label the outside of the clock with the occurrence of each type of organism listed. By studying fossil records, we can determine the occurrence of different types of organisms. Time from the Present 4.5 BYA *3.8 – 3.5 BYA *2.5 – 3 BYA 1.5 BYA 650 million years ago 400 million years ago 300 million years ago 200 million years ago 150 million years ago 100 million years ago *100,000 years ago Geological Clock First Records of: origin of the Earth prokaryotic heterotrophs prokaryotic autotrophs, first Evidence of photosynthesis unicellular eukaryotes multicellular eukaryotes plants invade the land animals invade the land first mammals first dinosaurs last dinosaurs human development Your personal notes, summary of the lesson, and/or questions that you may have: 7 1 Diversity of Life 3 Domain and Kingdom System of Classification 1) Label the kingdoms as eukaryotic or prokaryotic. 2) Label the kingdoms as unicellular, multicellular, or both. 3) Label the kingdoms as heterotrophic, autotrophic, or both. 4) Did the Fungi evolve from Plants? ________ 5) Are Protists the ancestors of Animals? ________ 6) Are Archaebacteria the ancestors of Eubacteria? ___ 7) Did plants evolve from Protists? _______ Archaebacteria Eubacteria Protista Animalia Fungi Plantae Eukaryotic Prokaryotic Unicellular Multicellular Both Uni&Multi Heterotrophic Autotrophic Both Hetero&Auto 8 1