Physical and Chemical Properties and Changes
advertisement

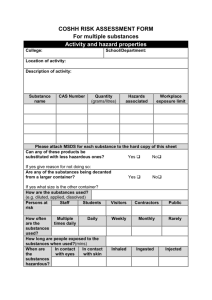
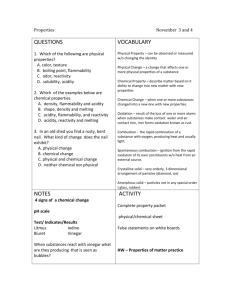
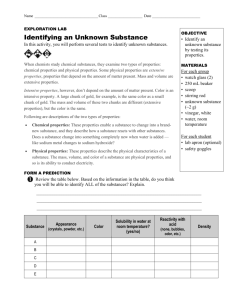
Physical and Chemical Properties and Changes Physical Property Definition: a characteristic of a substance that can be observed without changing it into another substance Examples: color and texture, flexibility, freezing point, state of matter, luster, ability to conduct heat and electricity, attracted to a magnet, etc. Identify some physical properties of silly putty Chemical Property Definition: a characteristic of a substance that describes its ability to change into different substances To observe chemical properties of a substance, you must try to change it to another substance Examples: flammability, ability to react with oxygen (rust vs. gold), ability to react with sulfur (silver tarnishing vs. gold) Identify some chemical properties of a match Physical Change Definition: any change that alters the form or appearance of matter but does not make any substances in the matter into a different substance A substance that undergoes a physical change is still the same substance after the change. Examples: changes of state, dissolving, bending, crushing, breaking, chopping, filtration, distillation Identify the physical change with the lava lamp and dissolving sugar (point out physical properties that are the basis for the changes) Chemical Change Definition: any change in matter that produces one or more new substances Aka: chemical reaction A chemical change produces new substances with properties different from those of the original substances Examples: hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen, rusting, burning methane, combustion, electrolysis, oxidation, tarnishing Define flammability and reactivity Identify the chemical change in the alka seltzer cannon and methane mamba (point out properties of original versus new substances) Conservation of Mass Matter is not created or destroyed in any chemical or physical change Aka: Law of Conservation of Matter Example: Methane + Oxygen Carbon dioxide and water Matter and Thermal Energy Any time there is change, energy is involved Temperature: the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance Thermal energy: the total PE and KE of the particles in a substance Endothermic: energy in, a change in which energy is taken in, ex: melting Exothermic: energy out, a change in which energy is released, ex: combustion