5.1-5.3 Review KEY
advertisement

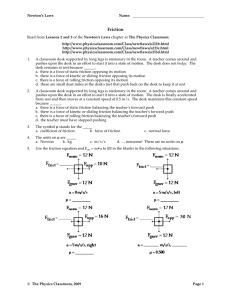
NAME KEY ANSWERS ARE IN RED CLASS ______ DATE ____________________________ FORCES: 5.1-5.3 REVIEW DIRECTIONS: ANSWER THE QUESTIONS OR FILL IN THE NECESSARY BLANKS. 1. You push on a desk with a force of 120 N to the right. Your friend pushes on the same desk with a force of 90 N to the left. What is the net force on the desk? CALCULATE The net force is 30 N to the right 2. Your friend increases her force on the desk by 30 N. She doesn’t change the direction of her push. What happens to the net force on the desk? Will the desk accelerate? PREDICT The forces on the desk would be equal on each side. The net force is zero and there is no acceleration. 3. The net force determines how and if an object will Accelerate 4. When two forces act in opposite directions, the object will accelerate in the same direction as the larger force. 5. A force is described by its strength and by the direction in which it acts. 6. What is work? Work is when you exert a force on an object and that object moves a certain distance in the same direction of the force. 7. Do simple machines reduce work? Explain. No. Simple machines do not lessen the amount of work done, they just change how the work is being done. 8. You’re holding your dog’s leash and trying to stand still as he pulls on the leash at an angle. You move forward. (All of/Some of/None of) his force does work on you. Circle one. 9. CALCULATE How much work do you do when you push a shopping cart with a force of 50 N for a distance of 5 m? 50N x 5m = 250 Joules EXPLAIN 10. Work divided by time equals Power 11. The unit of work is the Joule 12. The unit of power is the Watt 13. Force multiplied by distance equals Work 14. A force of 100 N is applied to a simple machine in order to lift a box that weighs 300 N. The input force is applied over a distance of 4 meters, causing the box to rise 1 meter. a. What is the input force? What is the input distance? The input force is 100 N. The input distance is 4m. b. What is the output force? What is the output distance? The output force 300 N. The output distance is 1m. c. Calculate the input work. 100N x 4m = 400 J d. Calculate the output work. 300N x 1m = 300 J e. Determine the mechanical advantage for the machine. 300N/100N = 3 15. PREDICT What happens to the efficiency of a bicycle as it gets rusty? It decreases. What must you do to maintain the same amount of output work? Use grease or oil to prevent rusting and to keep the chain smooth. 16. Describe the three ways a machine can help you do work and tell why machines are not 100 percent efficient. Increasing Force: The output force is greater than the input force. This machine makes it feel easier for us to complete the job. (Ex: faucet handle) Mechanical advantage is greater than one. Increasing Distance: The machine increases the distance desired. The input force is higher than the output force. (Ex: chop sticks) Mechanical advantage is less than one. Changing Direction: The machine changes the direction of the motion. The input and output work are the same, and the input and output distances are the same. (Ex: Pulley) Mechanical advantage is one. Machines are not 100% efficient because friction must always be considered. DIRECTIONS: If the statement is true, write true. If the statement is false, change the underlined word or words to make the statement true. 17. False A machine’s mechanical advantage is the output force Divided by the input force. 18. True If the output force is greater than the input force, the mechanical advantage of the machine is greater than one. 19. False If the machine increases distance, the output force is greater than the input force. 20. False If a machine changes the direction, but not the amount of the input force, the mechanical advantage is equal to 1. 21. True An ideal machine has no friction.