Environmental and Nuclear Chem Study Guide
advertisement

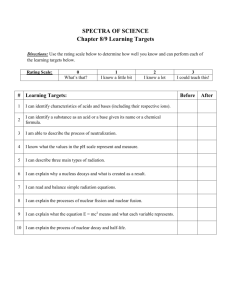
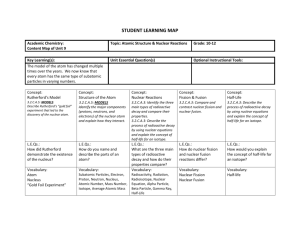
Study Guide Nuclear and Environmental Chemistry Start by printing and reading the summary on page 1. As you read through the text you will need to take good notes, “answer” the unit objectives, and define all of the key concept terms. Nuclear Chemistry: Radioactivity, Radiochemistry, and Nuclear Decay Read the summary on page 4 then read the first section. Radioactive Decay All forms of decay create new substances. Remember that alpha decay produces alpha particles. An alpha particle is really a slow moving Helium atom without electrons. Beta decay produces beta particles that are really single electrons moving at very high speeds. Gamma decay produces very high energy light waves. Half-life - the length of time for half of the parent atoms to change into daughter atoms. Half-life is specific to the parent atom. Each element has a unique half-life. Radiocarbon Dating - a process using the half-life of carbon-14 to determine the age of an artifact. Complete the Practice Activity and re-read the summary on Page 4. At this point you should be able to complete the unit objectives through “describe the use of carbon-14 in radiocarbon dating” as well as define the terms through “carbon-14” Nuclear Fusion and Fission Read the summary on page 5 then read the second section. Fusion vs. Fission Fusion - joining of 2 or more small nuclei to make a new larger atom. This process releases large amounts of energy and a new larger atom. This process occurs naturally in the core of the sun and other stars. Fission - the breaking down of larger nuclei to make a new atom. This process generally releases large amounts of energy and more stable “daughter” atoms. Occurs naturally when radioactive atoms decay. Also, fission is induced by “splitting” the nucleus of large atoms by bombarding with free neutrons. This process is used in nuclear power plants. First discovered by Dr. Lise Meitner, a Jewish female physicist in Germany from 1907 to the late 1930’s. Her research partner, of more than 20 years, took all of the credit and the Nobel Prize. Complete the Practice activity on page 4; and re-read the summary. At this point you should be able to complete the unit objectives through “identify the key disadvantages of nuclear waste disposal” as well as define the concepts through “meltdown.” Complete: The virtual lab: Half-Life Half- life homework HW#1 for this unit The Science of the Environment Read the summary on page 5 first, then read section three, also known as Environmental Chemistry In order to study Environmental Chemistry, you need to have a good understanding of several different scientific disciplines ranging from biology to geology and earth science. You need to know the biochemical cycles – the pathways that chemicals travel in the different parts of the biosphere. They include the water cycle, carbon cycle, and nitrogen cycle. Diagrams of each are found in this section. You will also need to know the different parts of the biosphere- all parts of the earth where life occurs. Hydrosphere= water; Lithosphere=land; Atmosphere=air (the parts to this one are commonly known) troposphere, ionosphere, stratosphere; Geosphere = underground. Environmental Chemistry - study of chemical and biological phenomena in our environment. This topic includes, but is not limited to the following: hydrology, which includes the water cycle and water contamination; meteorology; geology; civil and environmental engineering; and of course biochemistry. Complete the Practice Activity on page 5 and re-read the summary. At this point you should be able to complete the study guide unit objectives through “list and describe the three biogeochemical cycles” and define the concepts through “snow melt”. Water Quality and Wastewater Treatment Read the summary on page 5 then read section four. Water quality There are several indicators as to the quality of water. The 2 main chemical tests are actually measurements of dissolved oxygen and biochemical oxygen demand. Water that is safe to drink is said to be potable. When there is not enough oxygen present to support a health amount of life hypoxia can occur. This usually happens when the oxygen saturation level falls below 30% saturated. Wastewater treatment The mechanical, chemical and biological method of cleaning water used by human populations before it is returned to the environment. This is usually a 3 stage approach. Re-read the summary on page 5. At this point you should be able to: Answer the Practice Activity on page 5. Complete the Nuclear and Environmental Chemistry HW#2 Virtual lab: Water Cycle Gizmo Virtual lab: Water Pollution Gizmo Study your outlines and summaries. You have completed this section. It is now time to take the Unit 7: Nuclear and Environmental Chemistry Unit Test