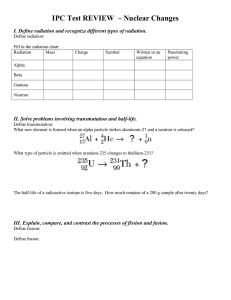
SPECTRA OF SCIENCE Chapter 8/9 Learning Targets
advertisement
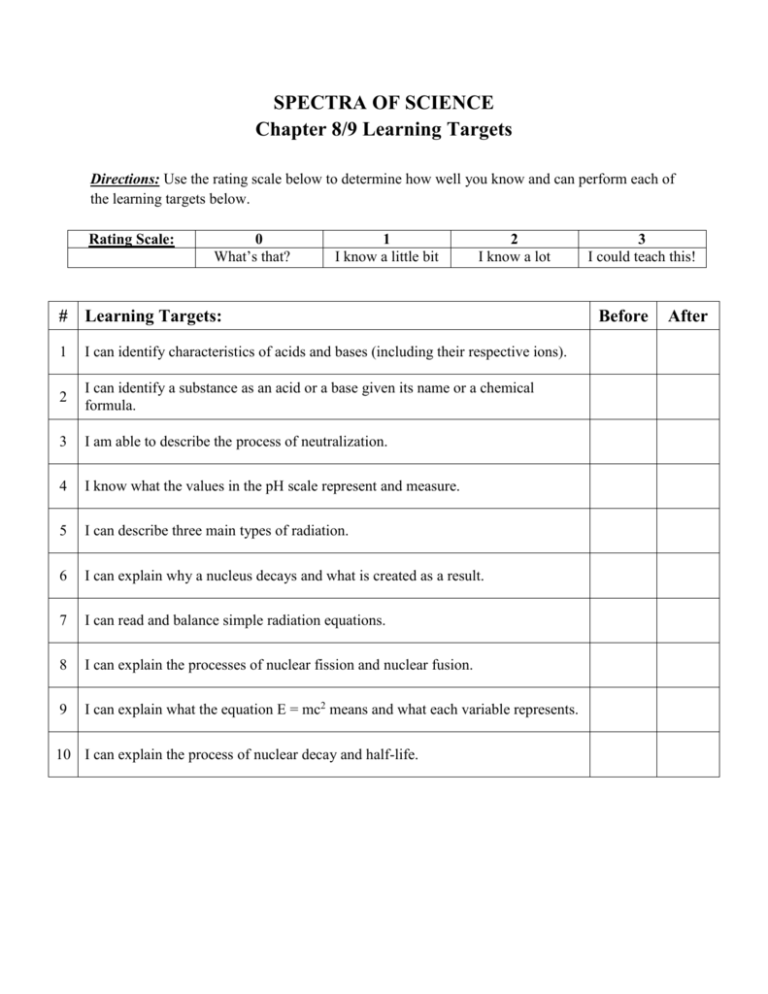
SPECTRA OF SCIENCE Chapter 8/9 Learning Targets Directions: Use the rating scale below to determine how well you know and can perform each of the learning targets below. Rating Scale: 0 What’s that? 1 I know a little bit 2 I know a lot # Learning Targets: 1 I can identify characteristics of acids and bases (including their respective ions). 2 I can identify a substance as an acid or a base given its name or a chemical formula. 3 I am able to describe the process of neutralization. 4 I know what the values in the pH scale represent and measure. 5 I can describe three main types of radiation. 6 I can explain why a nucleus decays and what is created as a result. 7 I can read and balance simple radiation equations. 8 I can explain the processes of nuclear fission and nuclear fusion. 9 I can explain what the equation E = mc2 means and what each variable represents. 10 I can explain the process of nuclear decay and half-life. 3 I could teach this! Before After SPECTRA OF SCIENCE Chapter 8/9 Study Guide **Due on: _______________________** Directions: Complete each of the items below on a separate sheet of notebook paper. Be sure to number each item. 1. List at least 5 characteristics of acids and at least 5 characteristics of bases (including their respective ions). 2. Identify each of the substances below as an acid or a base. a) Orange juice d) Vinegar g) HCl b) Baking soda e) NaOH h) HNO3 c) Detergent f) KOH 3. Describe the process of neutralization. 4. What does pH measure? 5. Which pH values represent acids, bases, and neutrals? 6. List the three types of radiation discussed in class. What occurs with each type? 7. Why does a nucleus decay? What is created as a result? 8. Complete the nuclear radiation equations below by replacing the “X” with the correct element symbol, and the “?’s” with the correct values. a) 212 Bi 4 83 b) 63 Ni 28 c) 217 ? ? X + 0 ? Ac 89 ? He + 2 X e -1 213 Fr + ? 87 X ? 9. Determine the type of decay shown in each of the radiation equations shown in #8. 10. Explain the difference between nuclear fission and nuclear fusion. 11. What does the equation E = mc2 mean? What does each variable represent? 12. Define the following vocabulary terms: a) Strong nuclear force d) Electrolyte b) Chain reaction e) Nuclear Decay c) Half-life