Unit 9: Atomic Structure & Nuclear Chemistry
advertisement
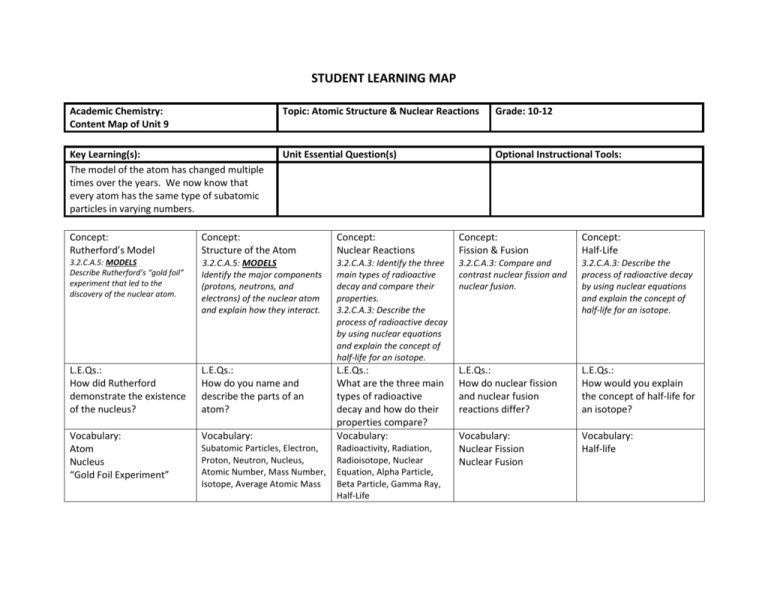
STUDENT LEARNING MAP Academic Chemistry: Content Map of Unit 9 Topic: Atomic Structure & Nuclear Reactions Grade: 10-12 Key Learning(s): The model of the atom has changed multiple times over the years. We now know that every atom has the same type of subatomic particles in varying numbers. Unit Essential Question(s) Optional Instructional Tools: Concept: Rutherford’s Model Concept: Structure of the Atom Concept: Nuclear Reactions Concept: Fission & Fusion Concept: Half-Life 3.2.C.A.5: MODELS Describe Rutherford’s “gold foil” experiment that led to the discovery of the nuclear atom. 3.2.C.A.5: MODELS Identify the major components (protons, neutrons, and electrons) of the nuclear atom and explain how they interact. 3.2.C.A.3: Identify the three main types of radioactive decay and compare their properties. 3.2.C.A.3: Describe the process of radioactive decay by using nuclear equations and explain the concept of half-life for an isotope. 3.2.C.A.3: Compare and contrast nuclear fission and nuclear fusion. 3.2.C.A.3: Describe the process of radioactive decay by using nuclear equations and explain the concept of half-life for an isotope. L.E.Qs.: How did Rutherford demonstrate the existence of the nucleus? L.E.Qs.: How do you name and describe the parts of an atom? L.E.Qs.: How do nuclear fission and nuclear fusion reactions differ? L.E.Qs.: How would you explain the concept of half-life for an isotope? Vocabulary: Atom Nucleus “Gold Foil Experiment” Vocabulary: L.E.Qs.: What are the three main types of radioactive decay and how do their properties compare? Vocabulary: Vocabulary: Nuclear Fission Nuclear Fusion Vocabulary: Half-life Subatomic Particles, Electron, Proton, Neutron, Nucleus, Atomic Number, Mass Number, Isotope, Average Atomic Mass Radioactivity, Radiation, Radioisotope, Nuclear Equation, Alpha Particle, Beta Particle, Gamma Ray, Half-Life











