PHYSICS UNIT 1 OUTLINE
advertisement

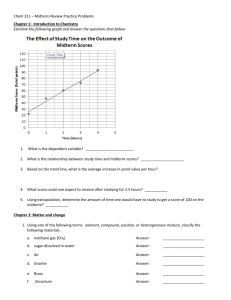
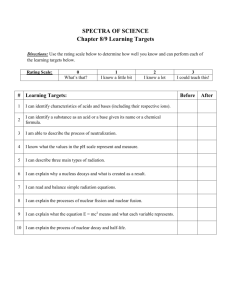
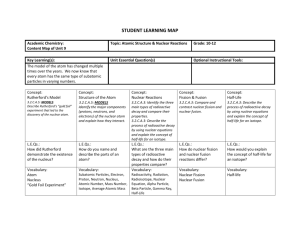
PHYSICS UNIT 30 and 31 STUDY GUIDE Describe isotopes as evidence for neutrons. Explain the terms Nuclide, isotope and nucleon. Define mass and atomic number. Describe the interactions in the nucleus. Describe evidence for the existence of nuclear energy levels Describe the phenomenon of natural radioactive decay. Describe alpha, beta (+ and -), and gamma radiation and their properties, and write reactions describing them. Explain why the neutrino and antineutrino were postulated. Describe the ionizing properties of radiation and the equipment used to detect radiation. Explain why some nuclei are stable and others are not. Determine the atomic and mass numbers of products of nuclear decay. State the random nature of radioactive decay and exponential nature of that decay. Define the term half-life and derive the relationship between the decay constant and half-life Sketch the graph of decay or determine the half-life of material from a decay curve. Solve problems involving decay for a given elapsed time interval. Outline methods for measuring the half-life of an isotope (long and short half-lives) Recognize the independence of half-life on the amount of material present or external conditions. Describe and give examples of artificial transmutation. Interpret the symbols used for nuclear reactions. Construct and complete nuclear reaction equations. State the conservation of charge and mass number. Determine the mass number and charge of a nucleus after it has undergone a specified decay process. Define the unified atomic mass unit. Explain the concepts of mass defect and binding energy. Solve problems involving binding energy. Compare the strong force to the electromagnetic force. Describe a typical neutron-induced fission reaction and why a chain reaction is possible. Describe the process of nuclear fusion. Draw and annotate a graph of binding energy per nucleon against atomic number and predict nuclear energy changes for both fusion and fission processes. State that nuclear fusion is the main source of the sun’s energy. Solve problems involving fission and fusion reactions.