I have… Speed Who has… Speed of an object with direction. I have
advertisement
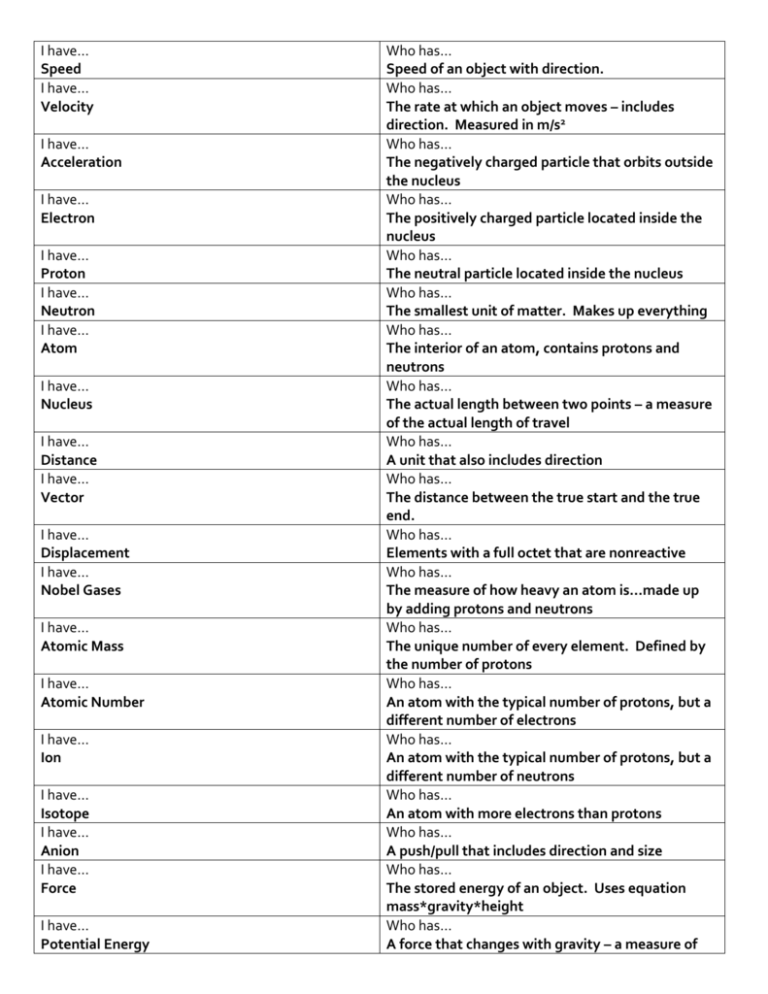
I have… Speed I have… Velocity I have… Acceleration I have… Electron I have… Proton I have… Neutron I have… Atom I have… Nucleus I have… Distance I have… Vector I have… Displacement I have… Nobel Gases I have… Atomic Mass I have… Atomic Number I have… Ion I have… Isotope I have… Anion I have… Force I have… Potential Energy Who has… Speed of an object with direction. Who has… The rate at which an object moves – includes direction. Measured in m/s2 Who has… The negatively charged particle that orbits outside the nucleus Who has… The positively charged particle located inside the nucleus Who has… The neutral particle located inside the nucleus Who has… The smallest unit of matter. Makes up everything Who has… The interior of an atom, contains protons and neutrons Who has… The actual length between two points – a measure of the actual length of travel Who has… A unit that also includes direction Who has… The distance between the true start and the true end. Who has… Elements with a full octet that are nonreactive Who has… The measure of how heavy an atom is…made up by adding protons and neutrons Who has… The unique number of every element. Defined by the number of protons Who has… An atom with the typical number of protons, but a different number of electrons Who has… An atom with the typical number of protons, but a different number of neutrons Who has… An atom with more electrons than protons Who has… A push/pull that includes direction and size Who has… The stored energy of an object. Uses equation mass*gravity*height Who has… A force that changes with gravity – a measure of I have… Weight I have… Friction I have… Newton I have… Newton’s first law of motion I have… Inertia I have… Newton’s second law of motion I have… Kinetic Energy I have… Mass I have… Intensive Properties I have… Newton’s third law of motion I have… Luster I have… Malleability I have… Conductivity I have… Melting Point I have… Freezing Point I have… Density I have… Extensive property amount of mass Who has… A force that opposes the motion between two objects Who has… The man who came up the laws of motion and gravity Who has… An object in motion stays in motion… Who has… The tendency of an object to resist motion Who has… It takes more force to move heavier objects, less to move lighter Who has… The energy associated with movement. Defined with the formula ½ mass*velocity Who has… The measure of amount of matter in an object. Remains constant, no matter the amount of gravity. Who has… Physical properties that do not depend on the amount of material in a sample (example: density, color) Who has… Every action has an equal and opposite reaction Who has… The measure of how reflective the surface of an object is (shiny) Who has… The ability of an object to be pounded into sheets Who has… The measure of how easily an object transfer heat or energy…happens most easily in metal solids due to touching particles Who has… The temperature at which a solid turns to a liquid Who has… The temperature at which a liquid turns into a solid Who has… How heavy an object is when considering mass divided by volume Who has… Physical property that depends on the amount of substance available (size, shape, weight, mass..) Who has… The machine associated with watch gears and cars. Made of a large wheel and fixed, rotating axel I have… Wheel and axel I have… Pulley I have… Incline Plane I have… Energy I have… Valence Electrons I have… Oxidation Numbers I have… Alloy I have… Work I have… The law of conservation of energy I have… Joules I have… Watt I have… Convection I have… Radiation I have… Acid I have… Power Equation I have… Base I have… Screw I have… Work Equation I have… Salt Who has… Can be fixed or moving…designed to change the direction through the use of a grooved wheel Who has… Increases mechanical advantage, decreases force needed, but also increases distance Who has… The ability to do work Who has… The outermost electrons – defined by the family number, can have 8 max for a full octet Who has… The charge of atoms, how easily they will gain or lose electrons. (+1, +2, +3, -3, -2, -1) Who has… Two metals that are bonded together (Steel) Who has… Increasing energy…if the motion and force are in the same direction. Who has… Energy cannot be created nor destroyed, only transferred or transformed Who has… The unit of measure for work and energy Who has… The unit of measure for power Who has… The movement of heat through air and liquids. This makes currents when hot rises and cold falls Who has… The movement of heat in a straight line – can even occur in a vacuum Who has… Tastes sour and donates H+ ions to a solution Who has… Work/Time Who has… Slippery and donates OH- ions to a solution Who has… A incline plane that is wrapped around to make a device that will hold things together Who has… Force * Distance Who has… The product of an acid + a base. Ionic compound Who has… Object with a field of positives and negatives which create two poles (north/south) I have… Magnet I have… Lever I have… Wedge I have… Ionic Bond I have… Covalent Bond I have… Evidences of chemical changes Who has… A machine with a fulcrum, load, and effort Who has… Two inclined planes put together, inclines on outside, that will either separate or hold something together Who has… A bond between a metal and a nonmetal – crystalline structure and low melting point Who has… Bond between two nonmetals, also includes hydrogen as well as polar and nonpolar Who has… Color change, precipitate formed, odor, or heat/light release Who has… The measure of how fast or slow something gets between two points. Does not include direction and measured with m/s











