Name: Date: The Structure of the Atmosphere Atmospheric Layer
advertisement
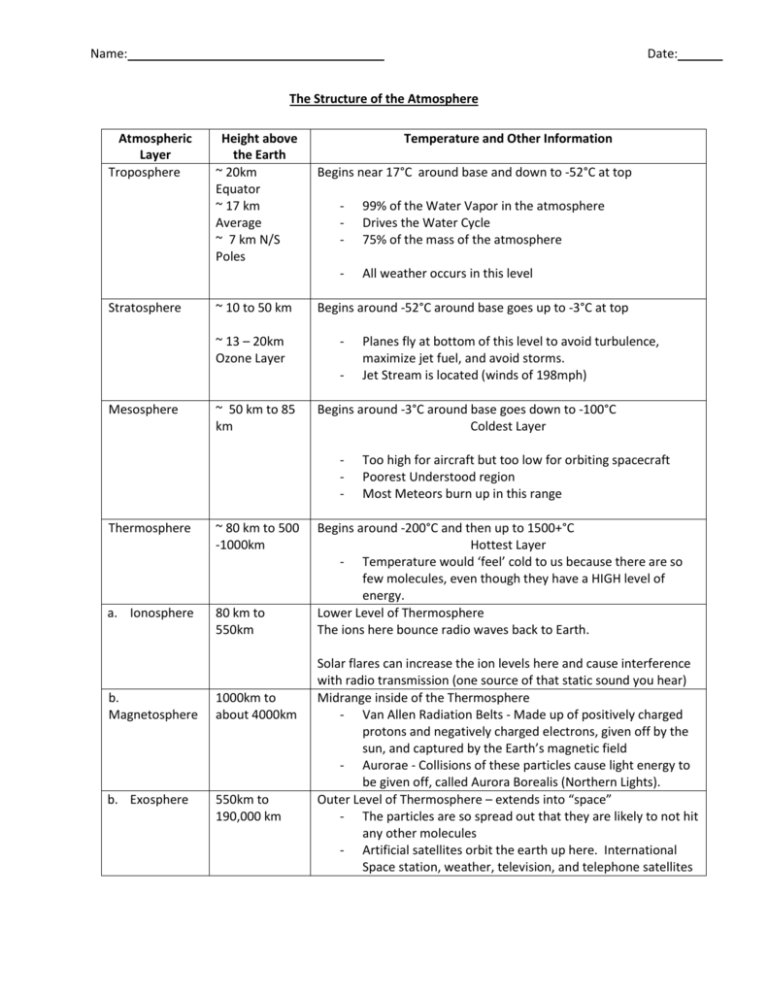
Name: Date: The Structure of the Atmosphere Atmospheric Layer Troposphere Stratosphere Height above the Earth ~ 20km Equator ~ 17 km Average ~ 7 km N/S Poles ~ 10 to 50 km ~ 13 – 20km Ozone Layer Temperature and Other Information Begins near 17°C around base and down to -52°C at top - 99% of the Water Vapor in the atmosphere Drives the Water Cycle 75% of the mass of the atmosphere - All weather occurs in this level Begins around -52°C around base goes up to -3°C at top - Mesosphere ~ 50 km to 85 km Begins around -3°C around base goes down to -100°C Coldest Layer - Thermosphere ~ 80 km to 500 -1000km a. Ionosphere 80 km to 550km b. Magnetosphere 1000km to about 4000km b. Exosphere 550km to 190,000 km Planes fly at bottom of this level to avoid turbulence, maximize jet fuel, and avoid storms. Jet Stream is located (winds of 198mph) Too high for aircraft but too low for orbiting spacecraft Poorest Understood region Most Meteors burn up in this range Begins around -200°C and then up to 1500+°C Hottest Layer - Temperature would ‘feel’ cold to us because there are so few molecules, even though they have a HIGH level of energy. Lower Level of Thermosphere The ions here bounce radio waves back to Earth. Solar flares can increase the ion levels here and cause interference with radio transmission (one source of that static sound you hear) Midrange inside of the Thermosphere - Van Allen Radiation Belts - Made up of positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons, given off by the sun, and captured by the Earth’s magnetic field - Aurorae - Collisions of these particles cause light energy to be given off, called Aurora Borealis (Northern Lights). Outer Level of Thermosphere – extends into “space” - The particles are so spread out that they are likely to not hit any other molecules - Artificial satellites orbit the earth up here. International Space station, weather, television, and telephone satellites Instructions: In the graph on the right, make a color-coded cross section of the 5 main layers of the atmosphere. Be sure to include the starting (lower) and ending temperatures of each level, AND one thing that is actively happening in 900 km that layer of the atmosphere. Composition of Atmosphere 0Nitrogen – 78% Oxygen – 20.9% Ar, CO2, Ne, He, CH4, Kr, = 1.1% H2, N20, Xe, O3, NO2, I, CO Greek Roots Sphere – Ball Hemi – Half Atmo – Air Litho – Stone Bio – Life Meso – Middle Exo – Outer Thermo – Heat Strat - Stratify Trop - Turning Ion – Ion 800 700 600 500 km 400 300 200 100 km 20 0