Cell Chemistry: Organic Molecules & Composition
advertisement

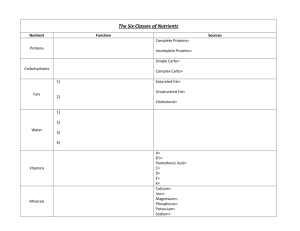
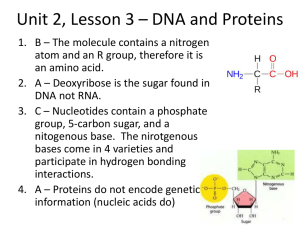
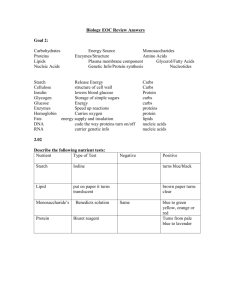
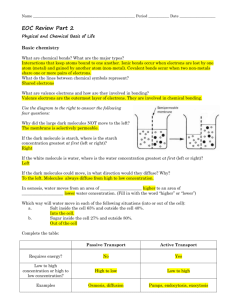
Chapter 2.1 Oxygen 65% Carbon 18.5% Hydrogen 9.5% Nitrogen 3.3% Calcium 1.5% Phosphorus 1% Other 19 elements 1.2% Create a circle graph using this data Carbon Hydrogen Nitrogen Calcium Phosphorus Atoms are the basis of compounds using chemical bonds to create molecules Inside cells, bonds of atoms are broken down to form new molecules releasing energy. Cells use this chemical energy for life activities. Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Provide energy Simple carbohydrates are broken down. Simple carbs link to form complex carbs like starch, cellulose, glycogens. Stored excess plant sugars Cell wall material Fats, oils and waxes Form chains of fatty acids Don’t mix with water Form the cell membrane and organelle membranes Made up of amino acids. Enzymes are proteins that control chemical reactions in the cells. Support the growth and repair of living matter Allow muscles to move Proteins in your blood fight infections Transport materials into and out of cell. Molecules that hold the instructions for the maintenance, growth and reproduction of cell Subunits are nucleotides Two types ◦ DNA – provides the information needed to make proteins ◦ RNA –coded nucleotides in DNA that provides information to cytoplasm to produce proteins. Which large molecule… ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Forms the cell membrane Transports material in and out of the cell Starch and cellulose is a plant produced type Made from amino acids Form chains of fatty acids Provides energy Holds the genetic instruction for the cell Subunit is nucleotides Support the growth of tissue and muscles in particular Water is polar Many substances dissolve in water Lipids in the cell membrane keep water in and out of the cell